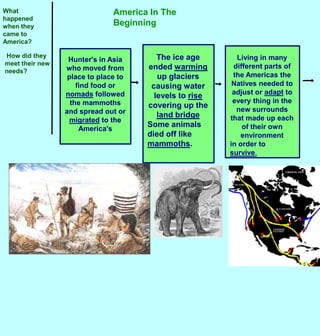
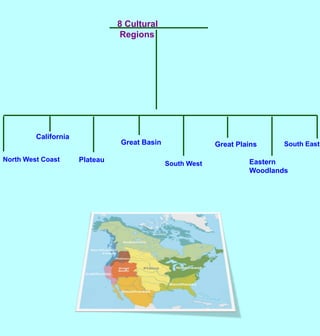
Hunter-gatherers from Asia migrated to North America over a land bridge that connected Siberia to Alaska during an ice age approximately 30,000 years ago. As the climate warmed, ice sheets melted and sea levels rose, submerging the land bridge. Native Americans adapted to various environments across North America by developing distinct cultural practices and livelihoods based on local natural resources and conditions. Though cultural practices varied regionally, most Native American societies shared beliefs about respecting nature, not owning land, and only utilizing necessary resources.