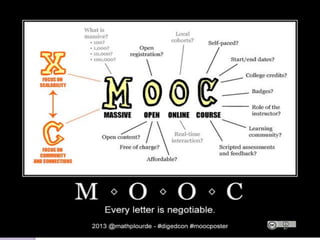
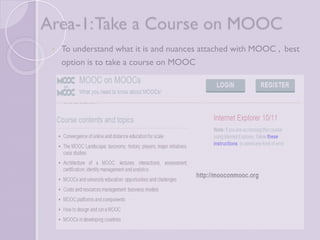
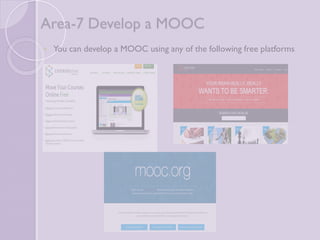
The document discusses MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) as a transformative force in higher education, highlighting their ability to provide free access to courses from prestigious universities. It explores the implications for libraries and librarians, emphasizing the need for collaboration, support for MOOC learners, and the development of course-specific guides. The conclusion suggests that embracing MOOCs can enhance librarianship and the quality of library and information science education.