This document provides an overview of MongoDB, including:
- MongoDB is a non-SQL, document-oriented database that provides high performance, high availability, and easy scalability.
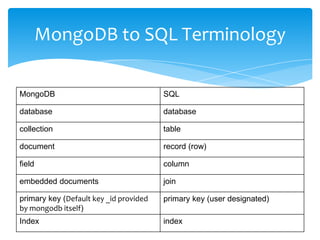
- In MongoDB, databases contain collections of documents rather than tables of rows. Documents can contain different fields and are equivalent to rows in a SQL database.
- Some key advantages of MongoDB over SQL databases include its schemaless nature, ease of horizontal scaling, and rich query capabilities.