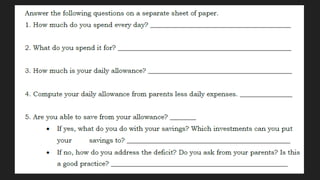
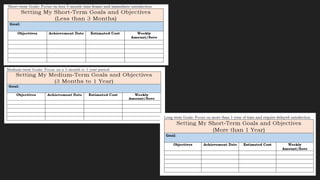
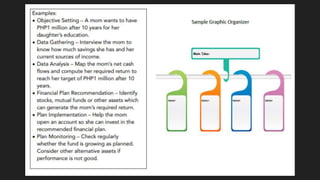
The document discusses the key areas of personal finance: income, spending, saving, investing, and protection. It explains the money management cycle which includes earning income, spending on goods and services, saving excess funds, and investing savings. The optimal financial planning process involves setting objectives, gathering personal data, analyzing the data, developing a customized plan, implementing the plan, and monitoring it over time.