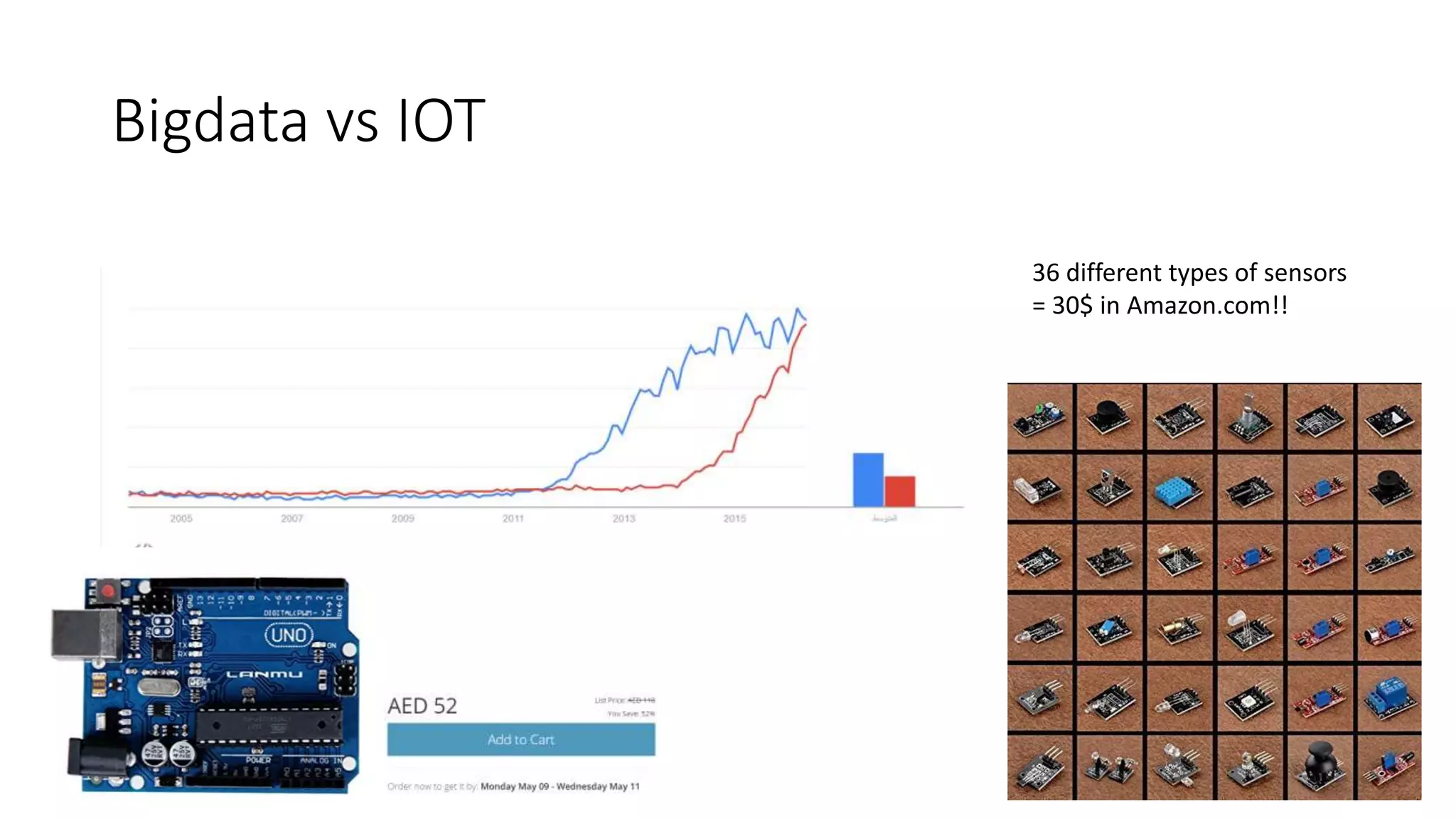
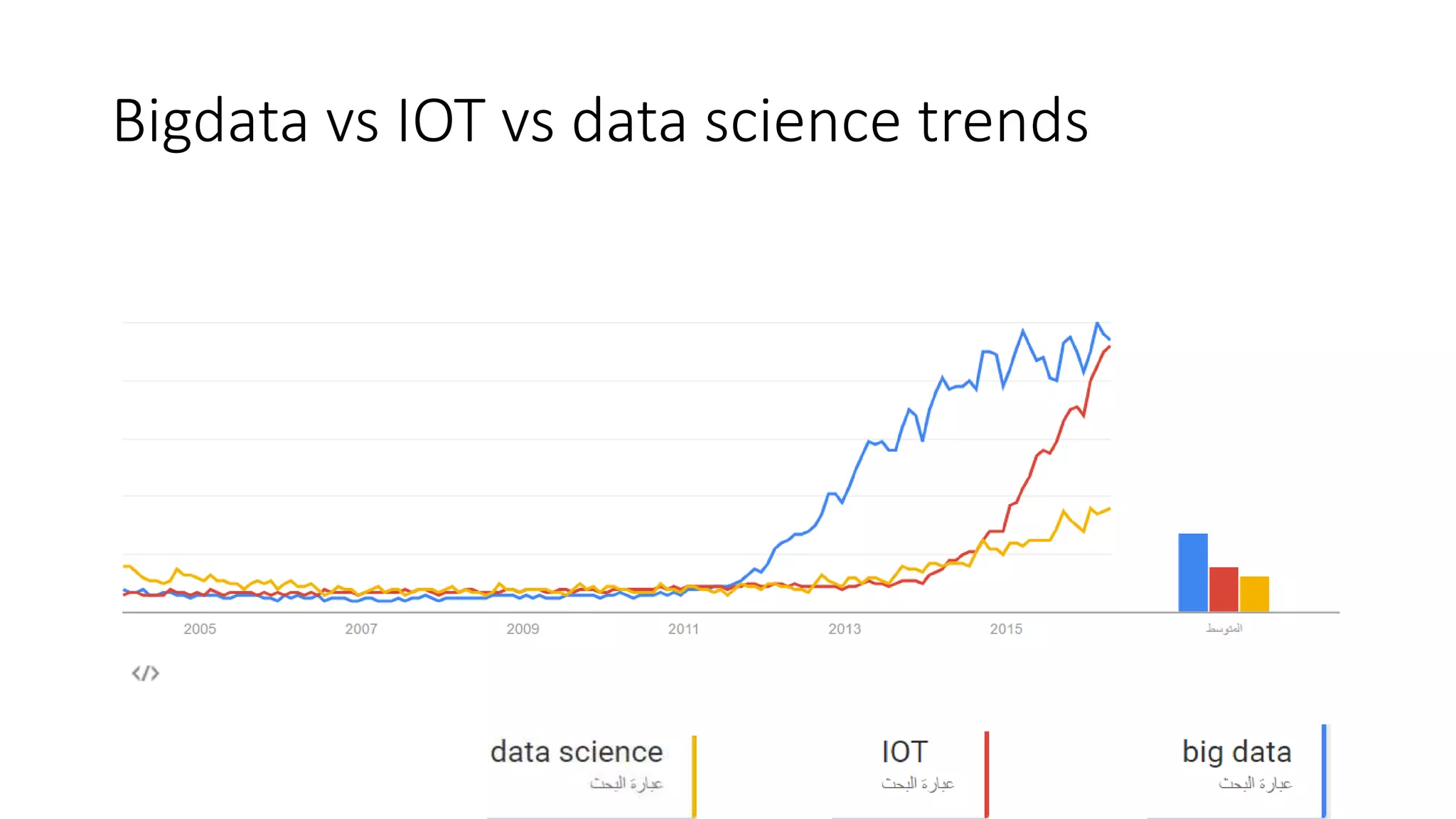
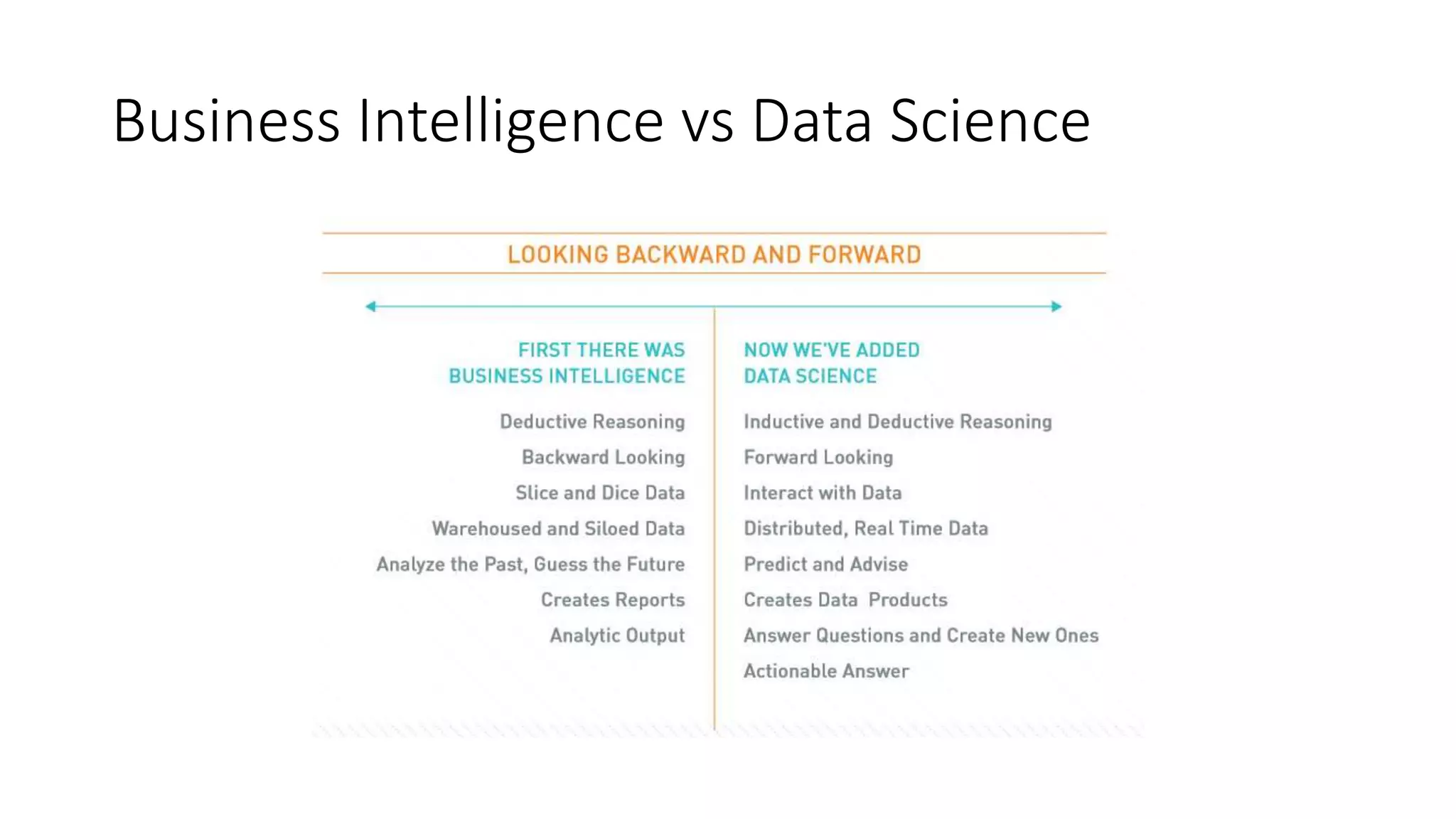
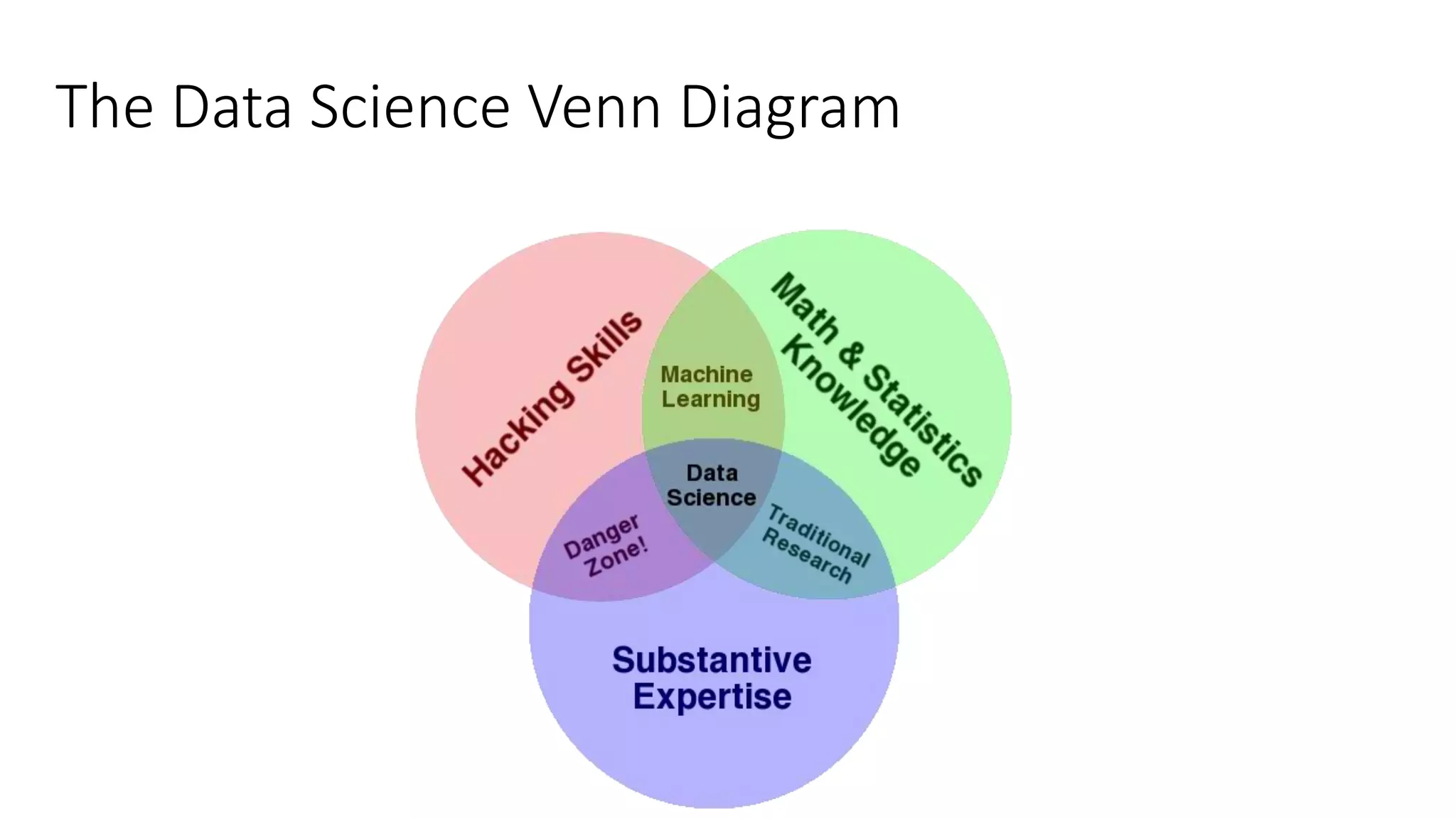
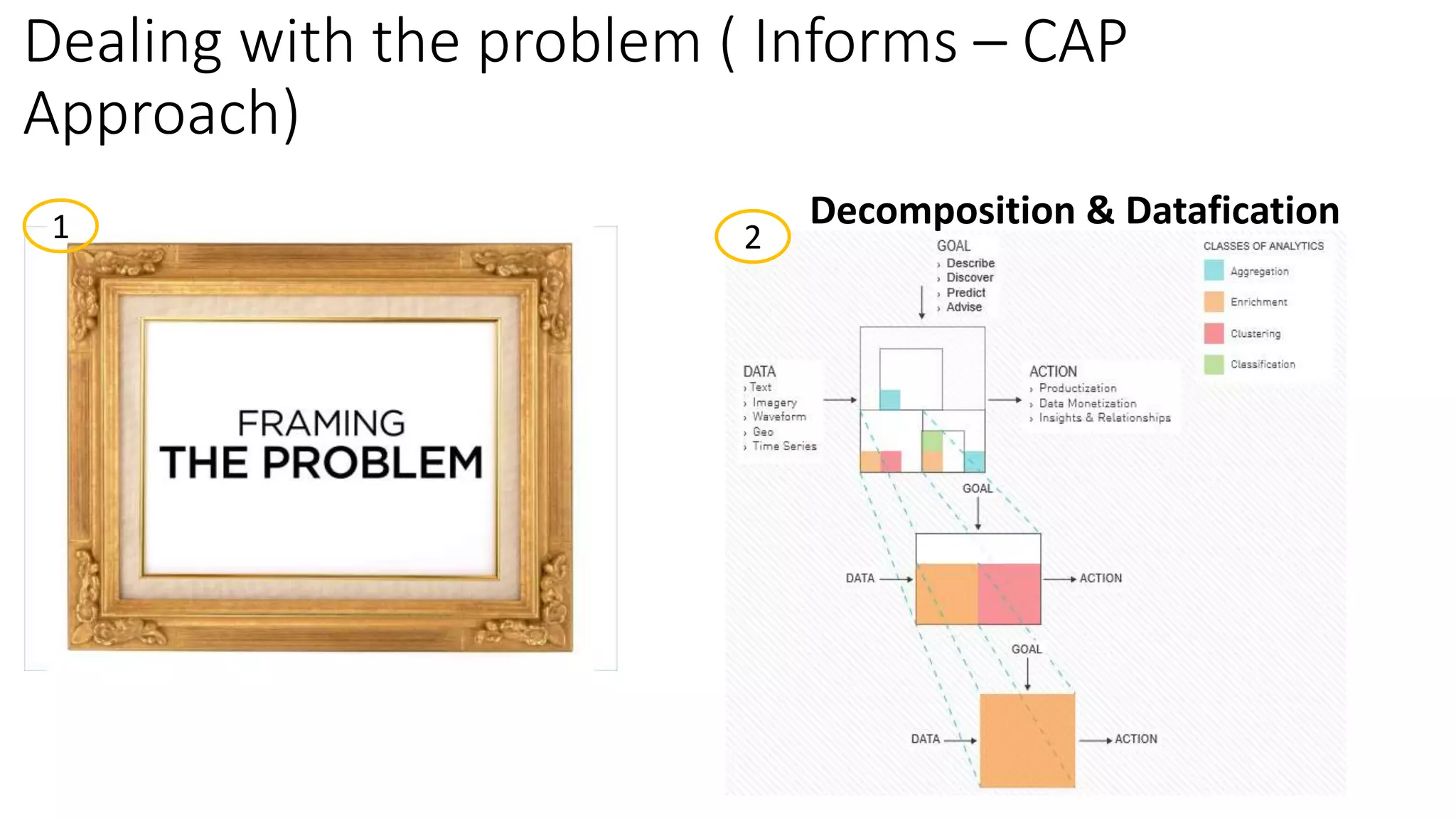
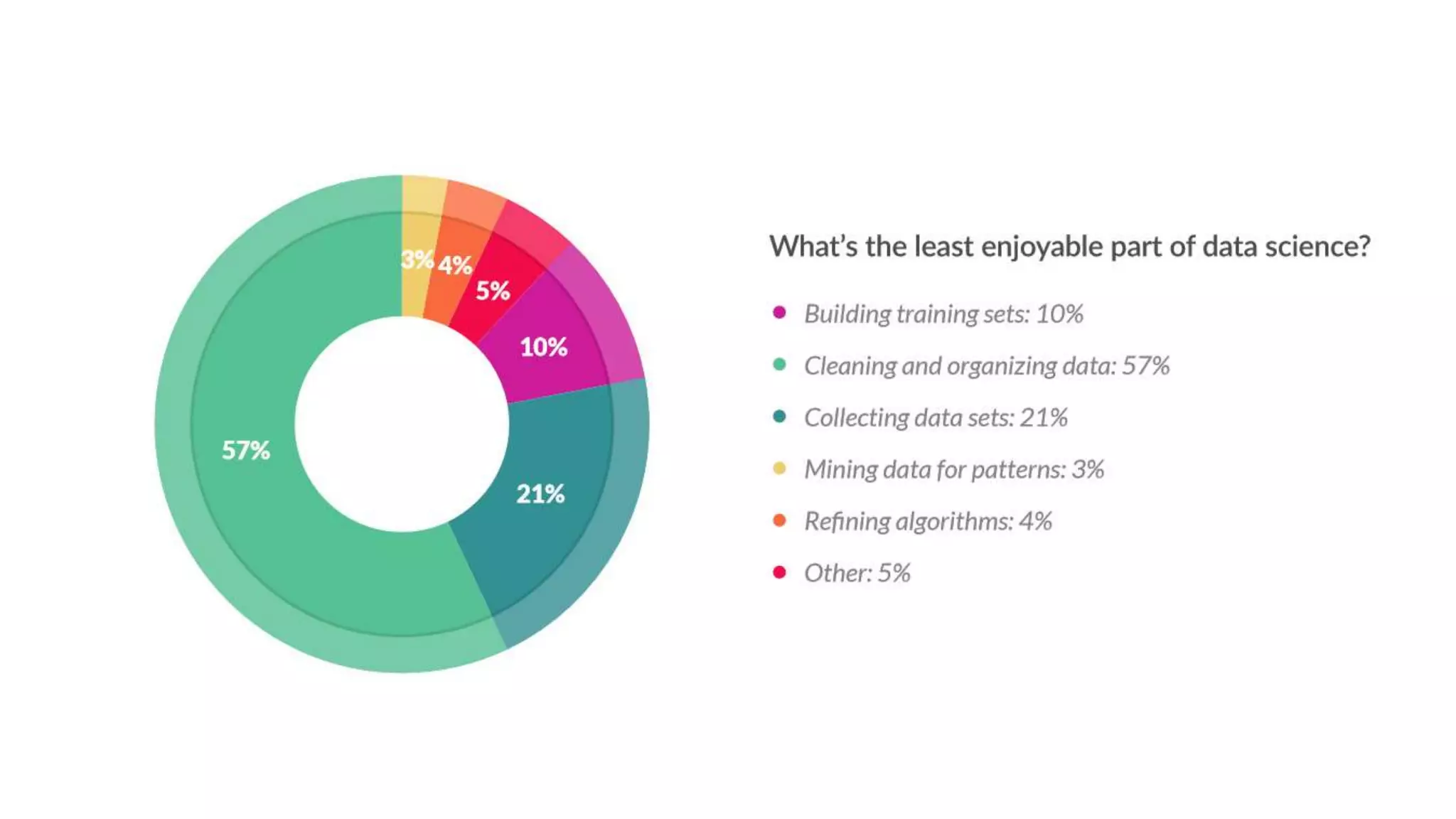
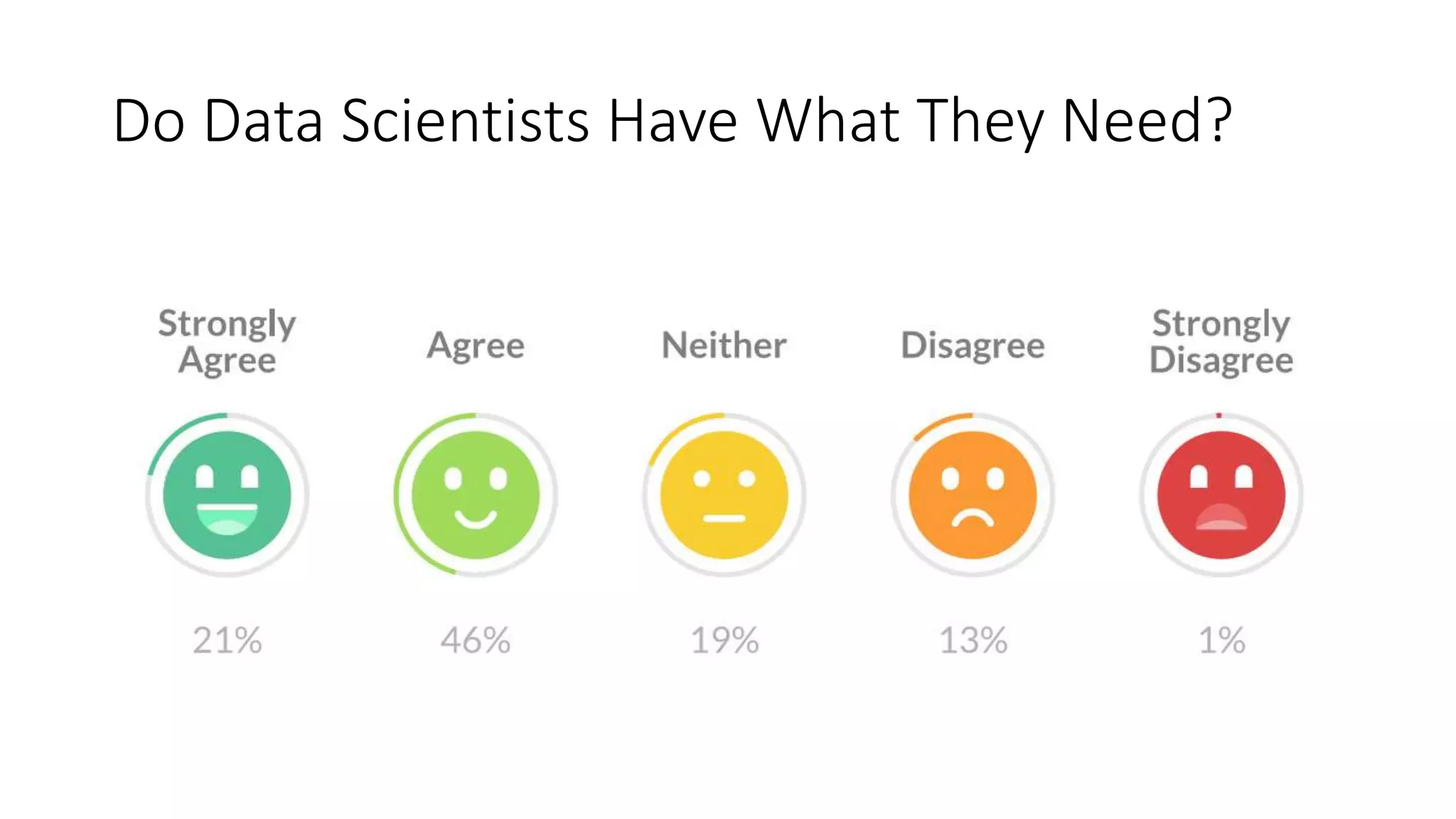
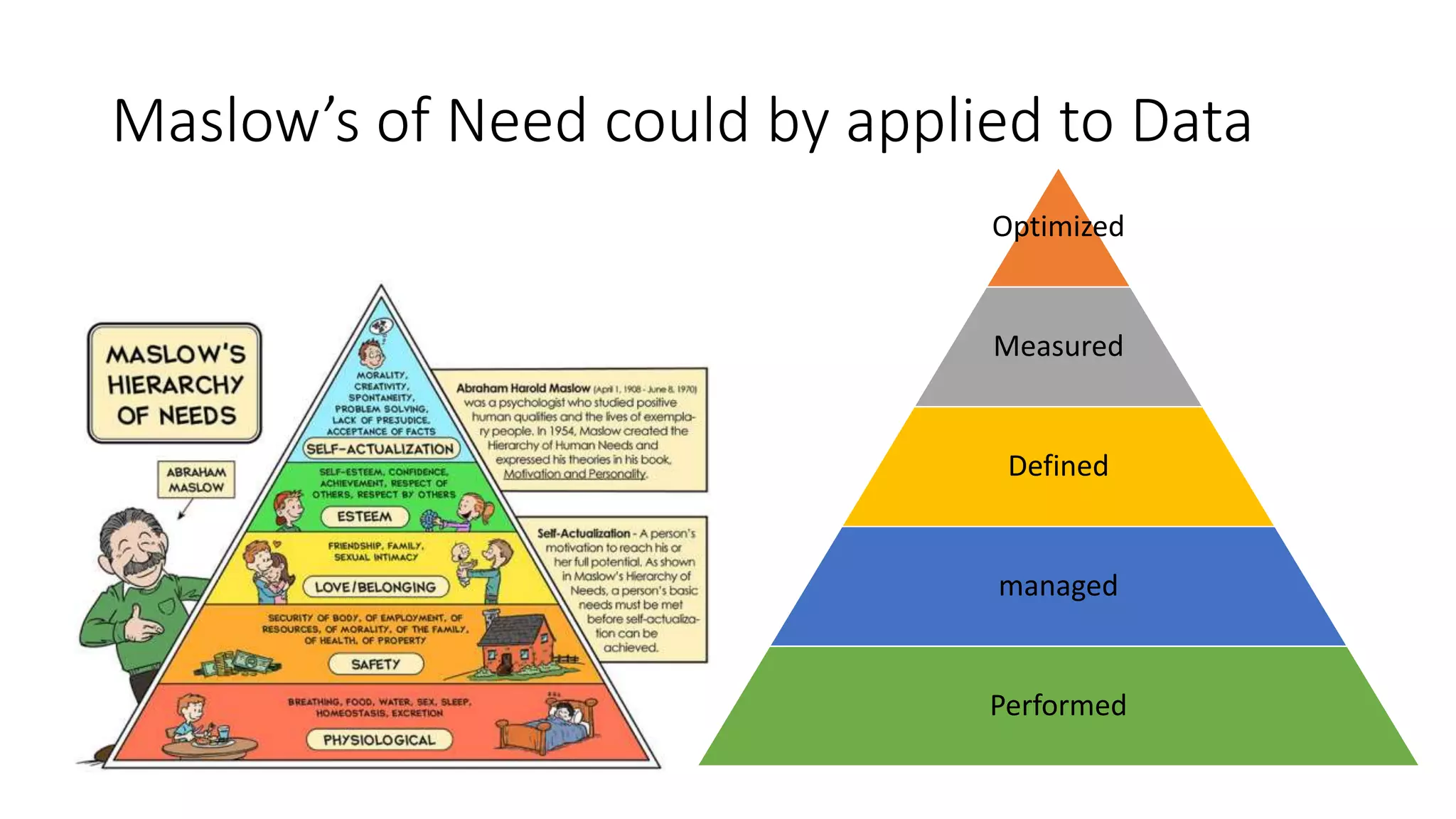
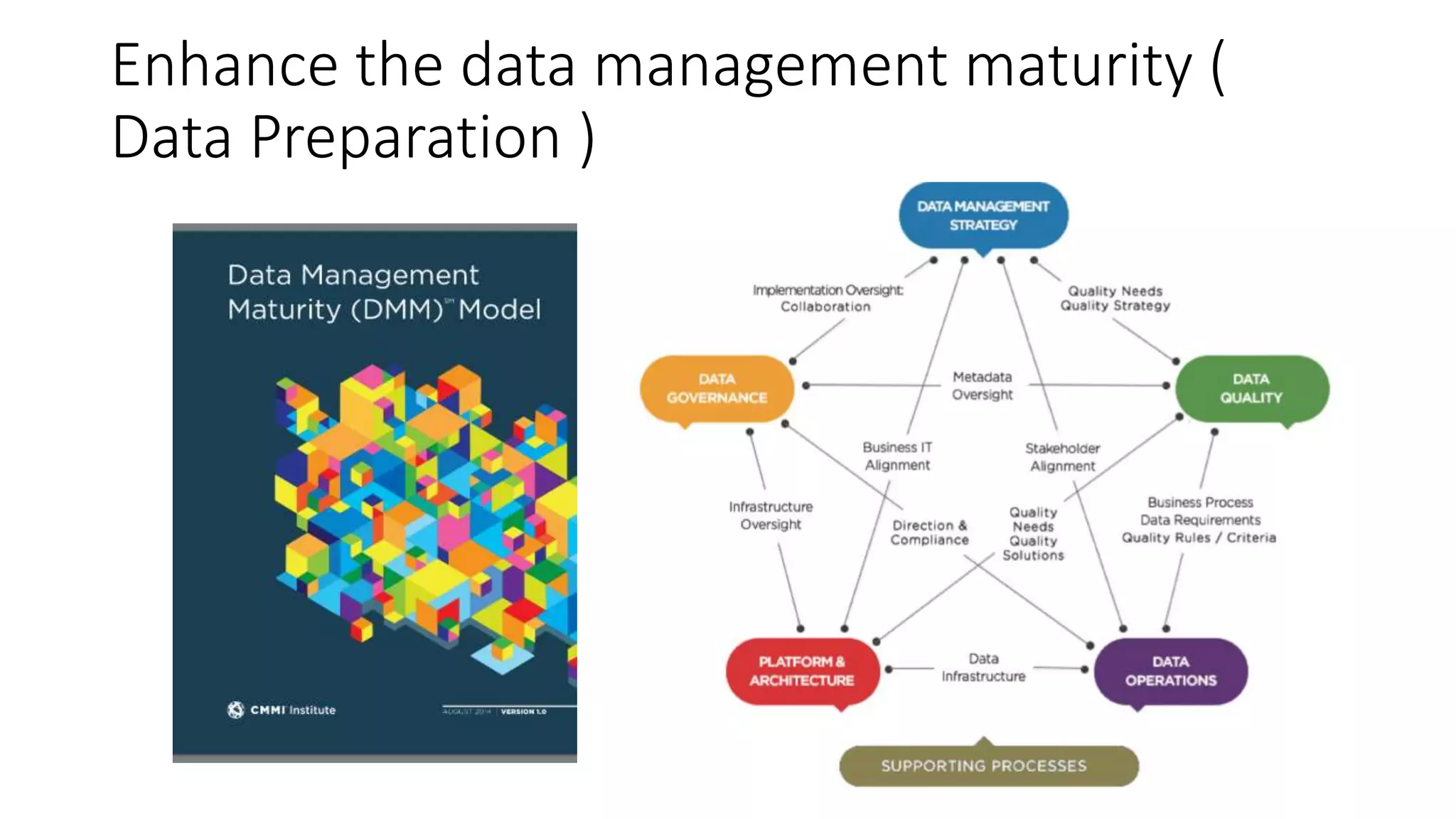
Setting up a Big Data Team requires best practices including building a team with diverse skills in areas like math, computer science, statistics and domain expertise. Data scientists fulfill key roles like generating prototypes to demonstrate ideas, decomposing problems, and communicating with stakeholders. Effective teams require data preparation, using tools like statistical systems and data management systems. Certification can increase a team's maturity, while frameworks like CRISP-DM and Six Sigma's DMAIC provide processes to optimize the data workflow. Talent management is also important to support the team over time.