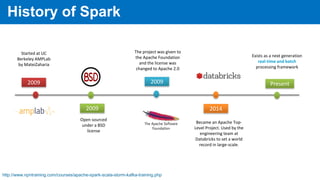
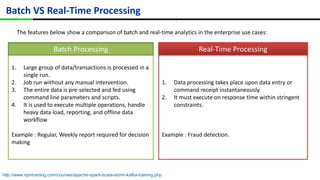
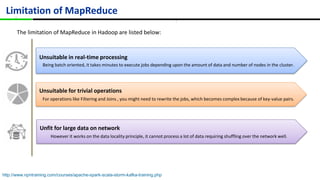
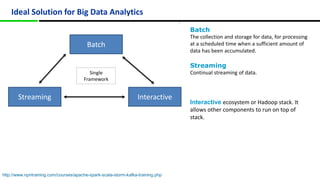
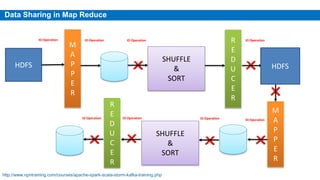
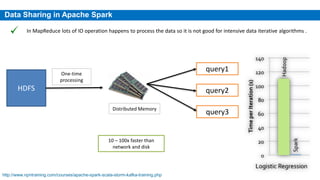
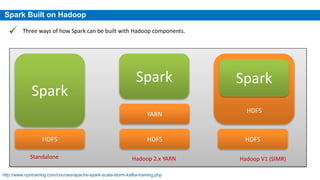
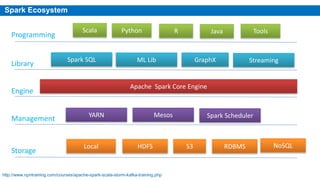
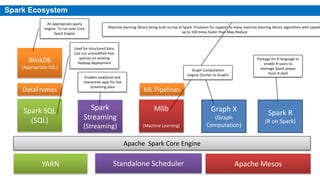
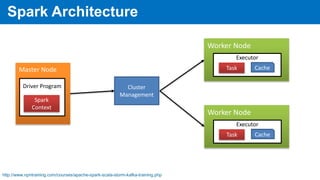
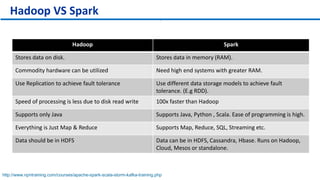
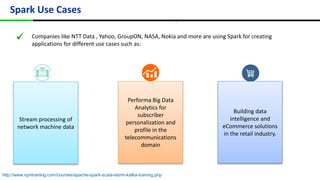
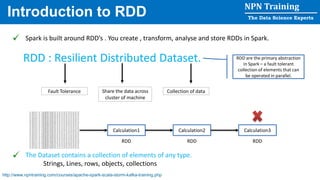
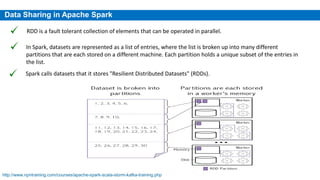
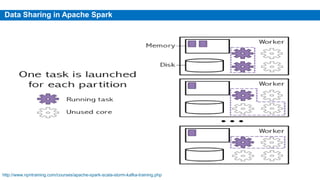
This document provides an overview of Apache Spark, including its history, features, architecture and use cases. Spark started in 2009 at UC Berkeley and was later adopted by the Apache Foundation. It provides faster processing than Hadoop by keeping data in memory. Spark supports batch, streaming and interactive processing on large datasets using its core abstraction called resilient distributed datasets (RDDs).