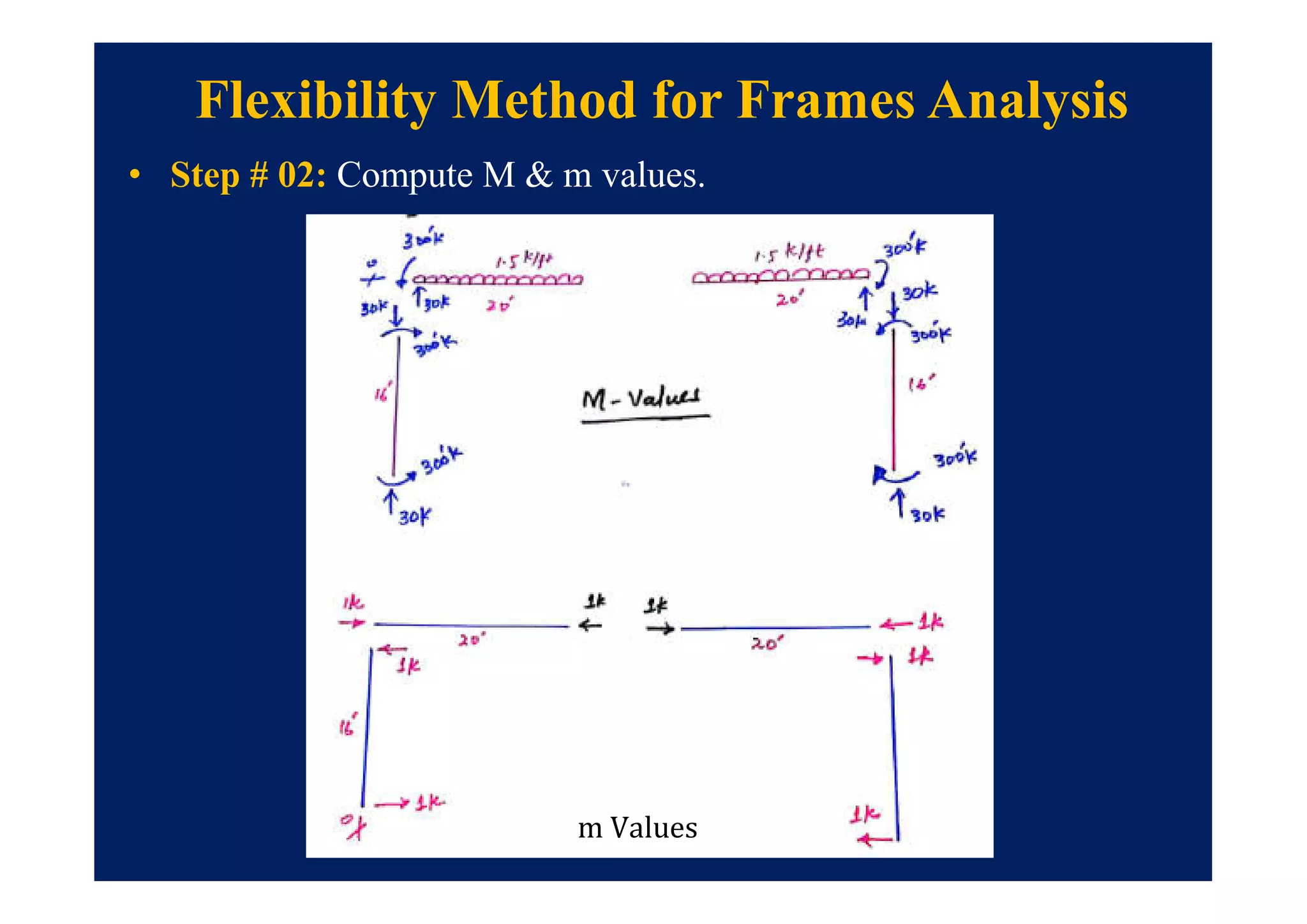
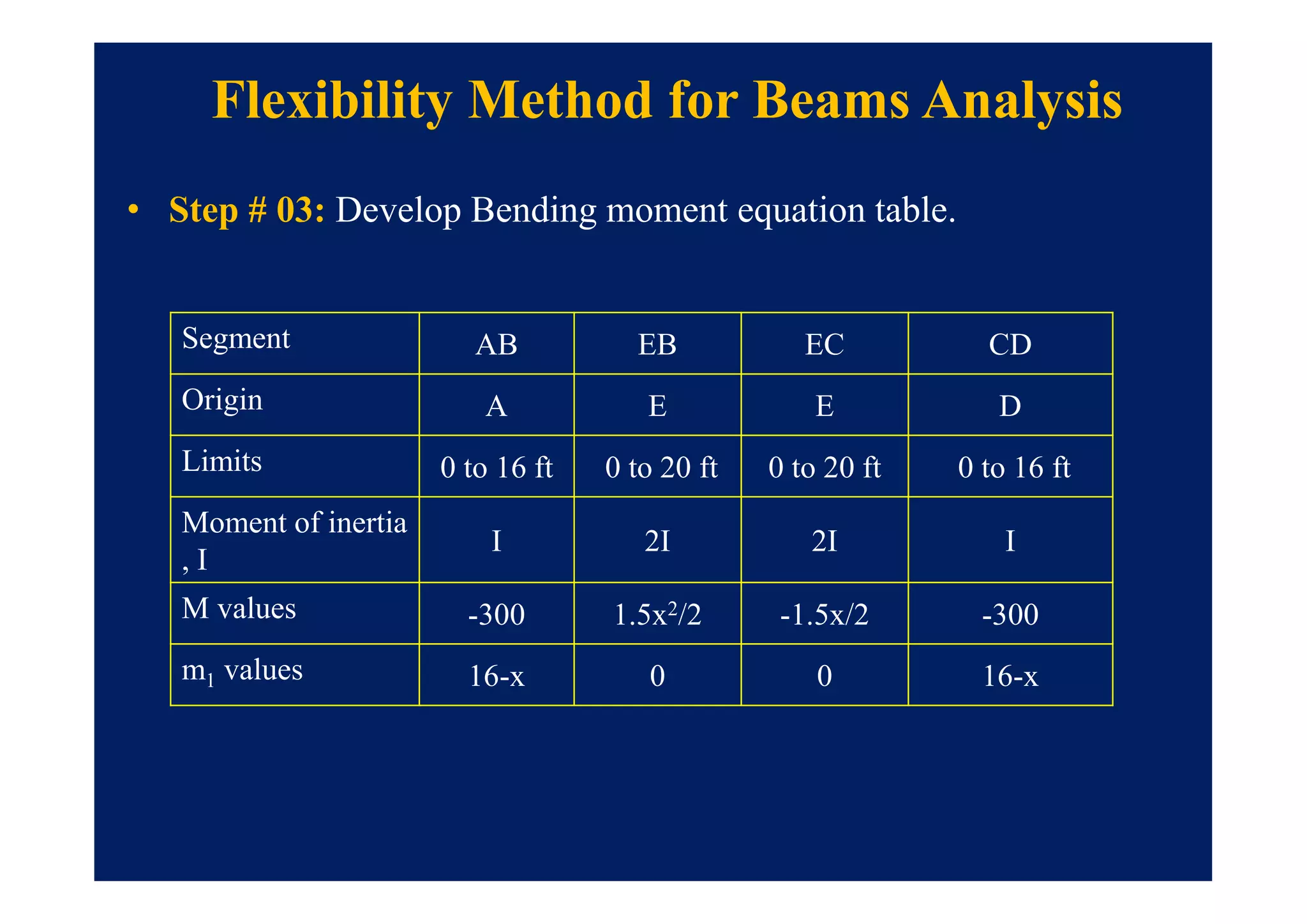
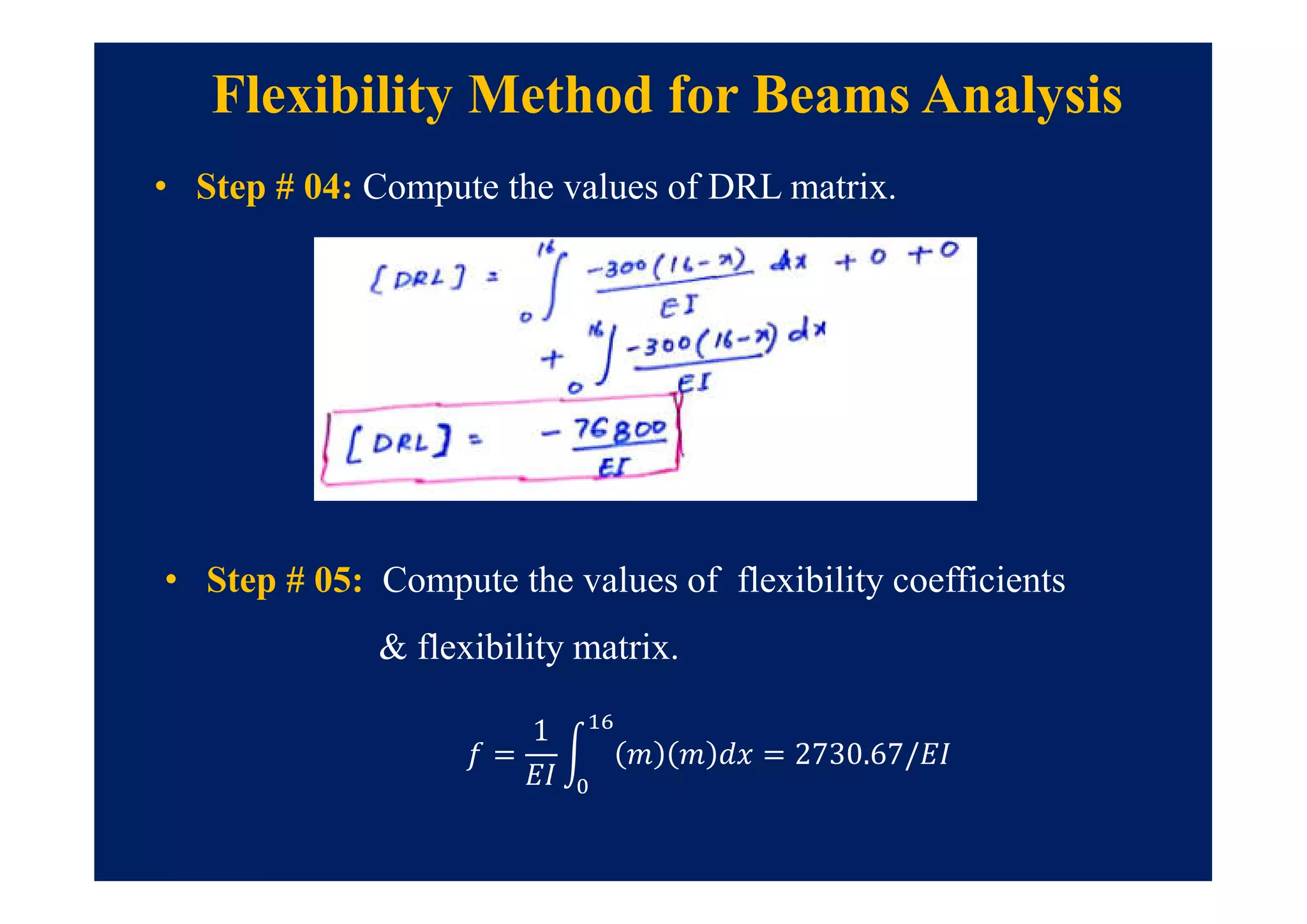
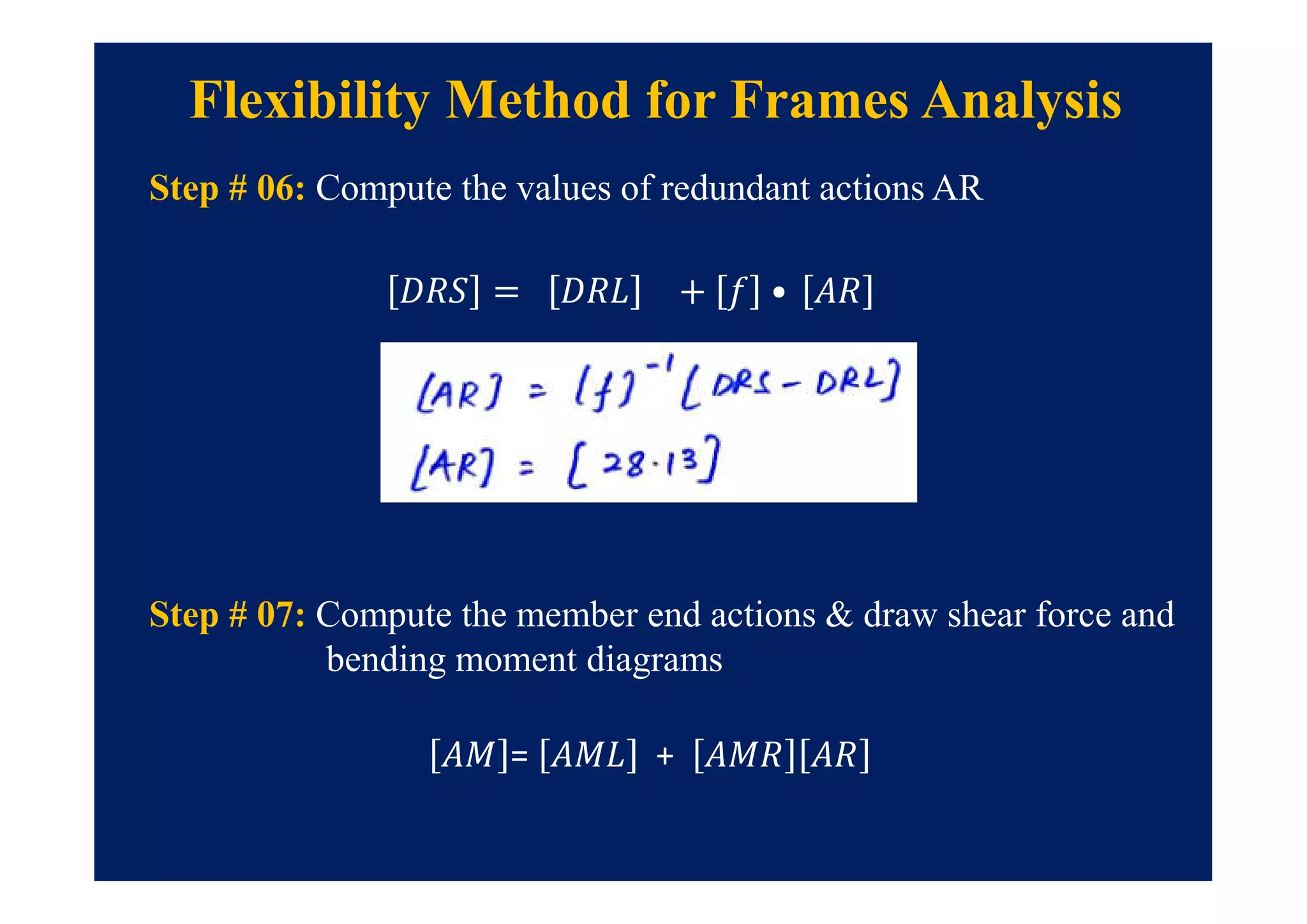
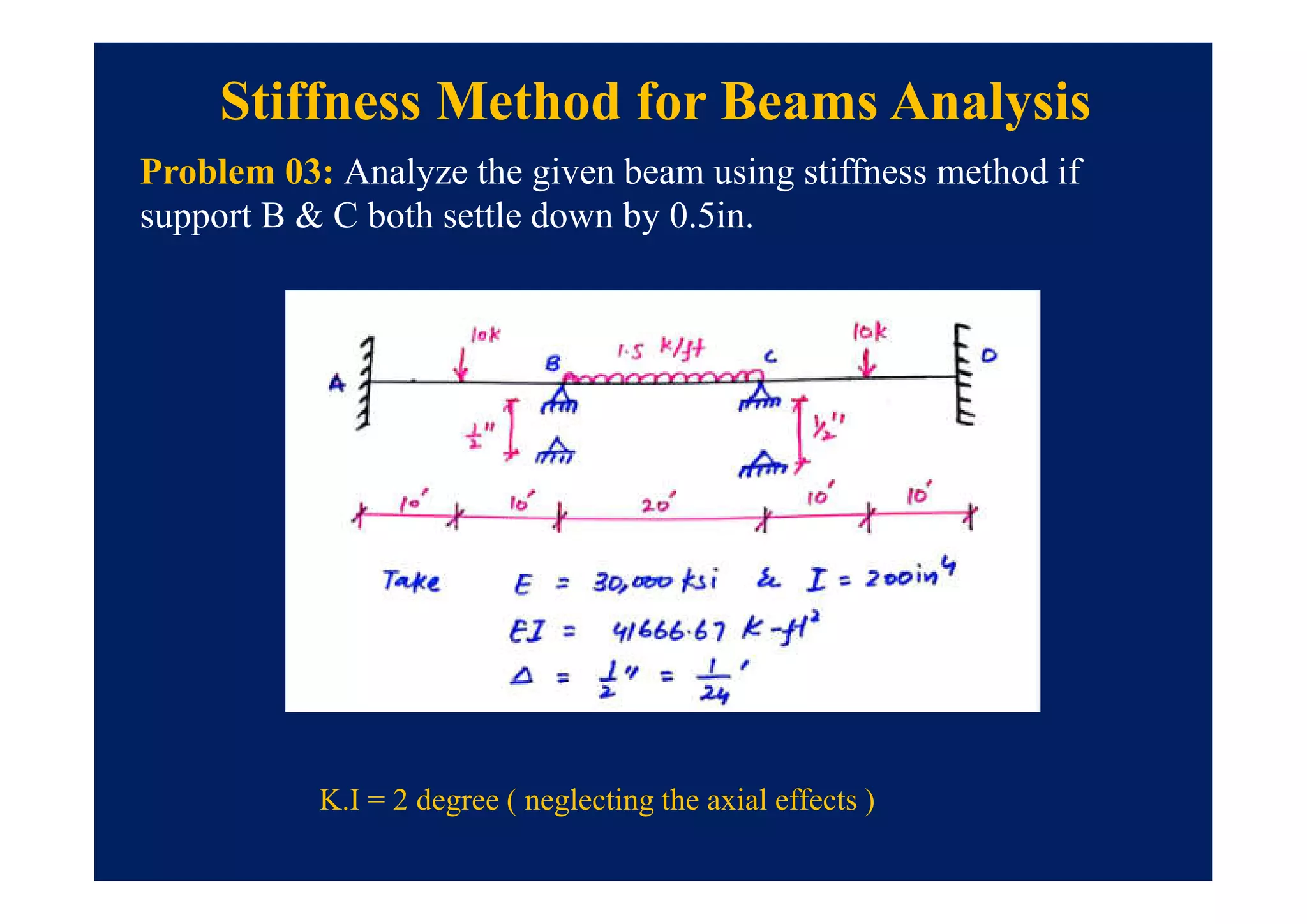
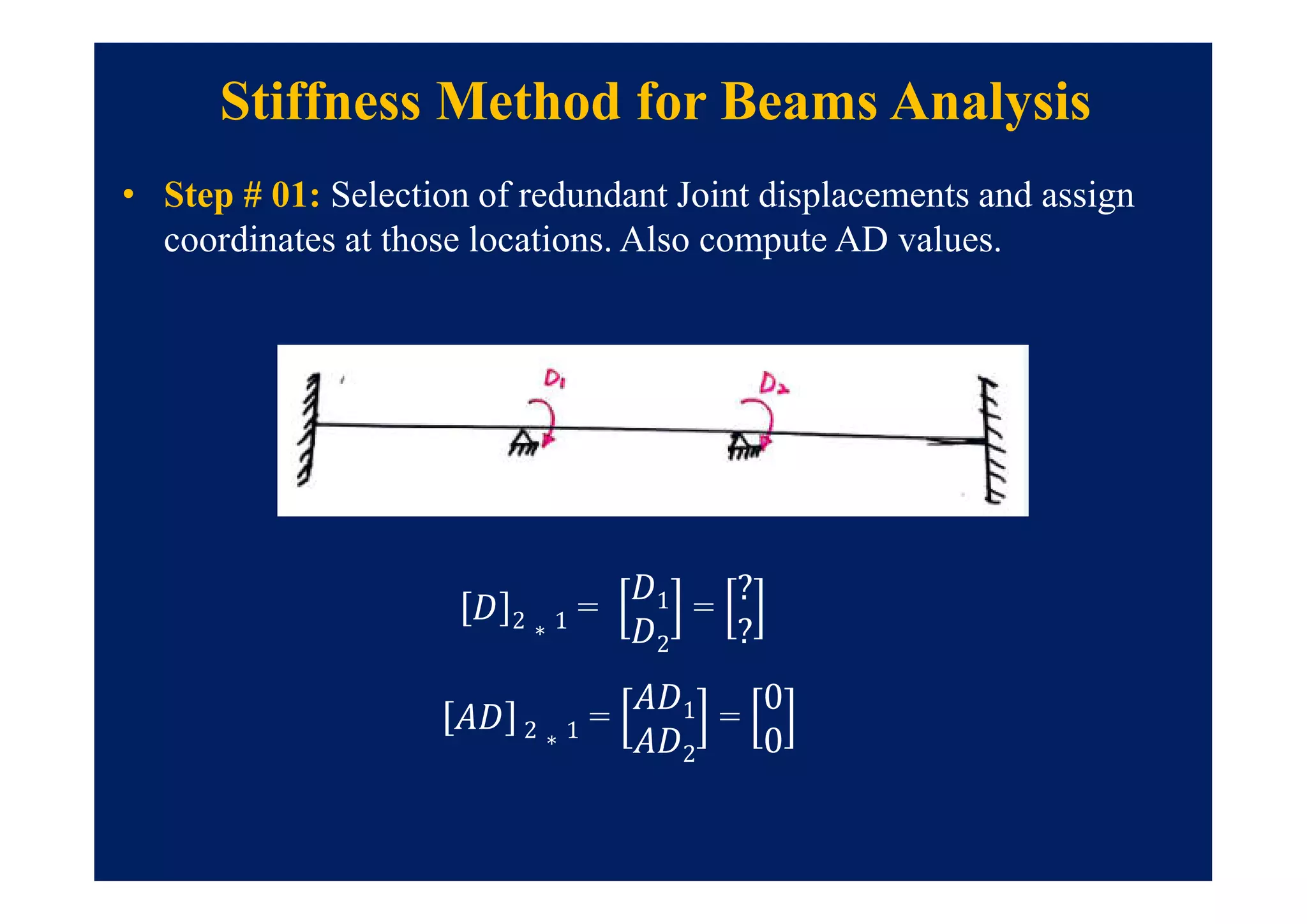
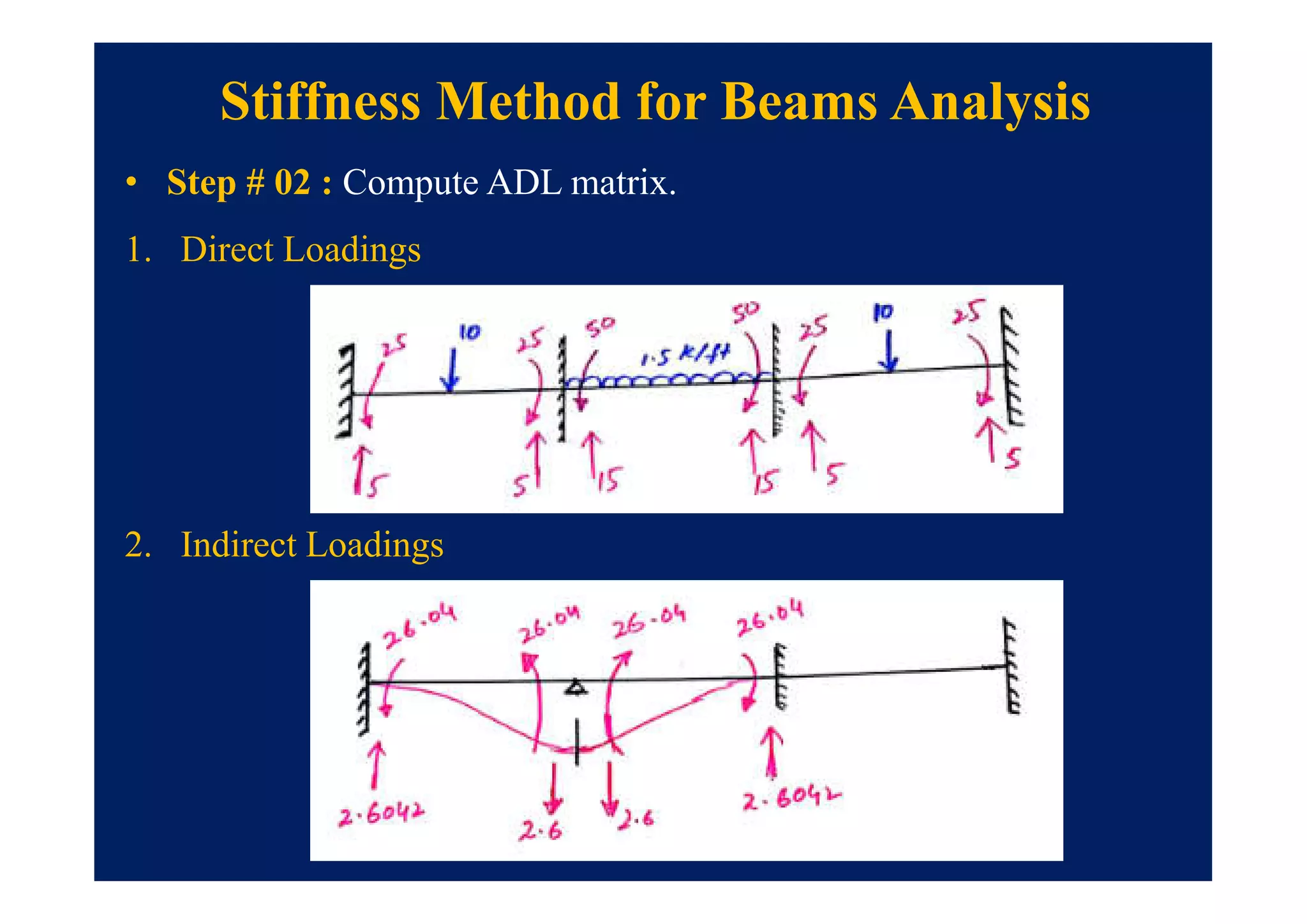
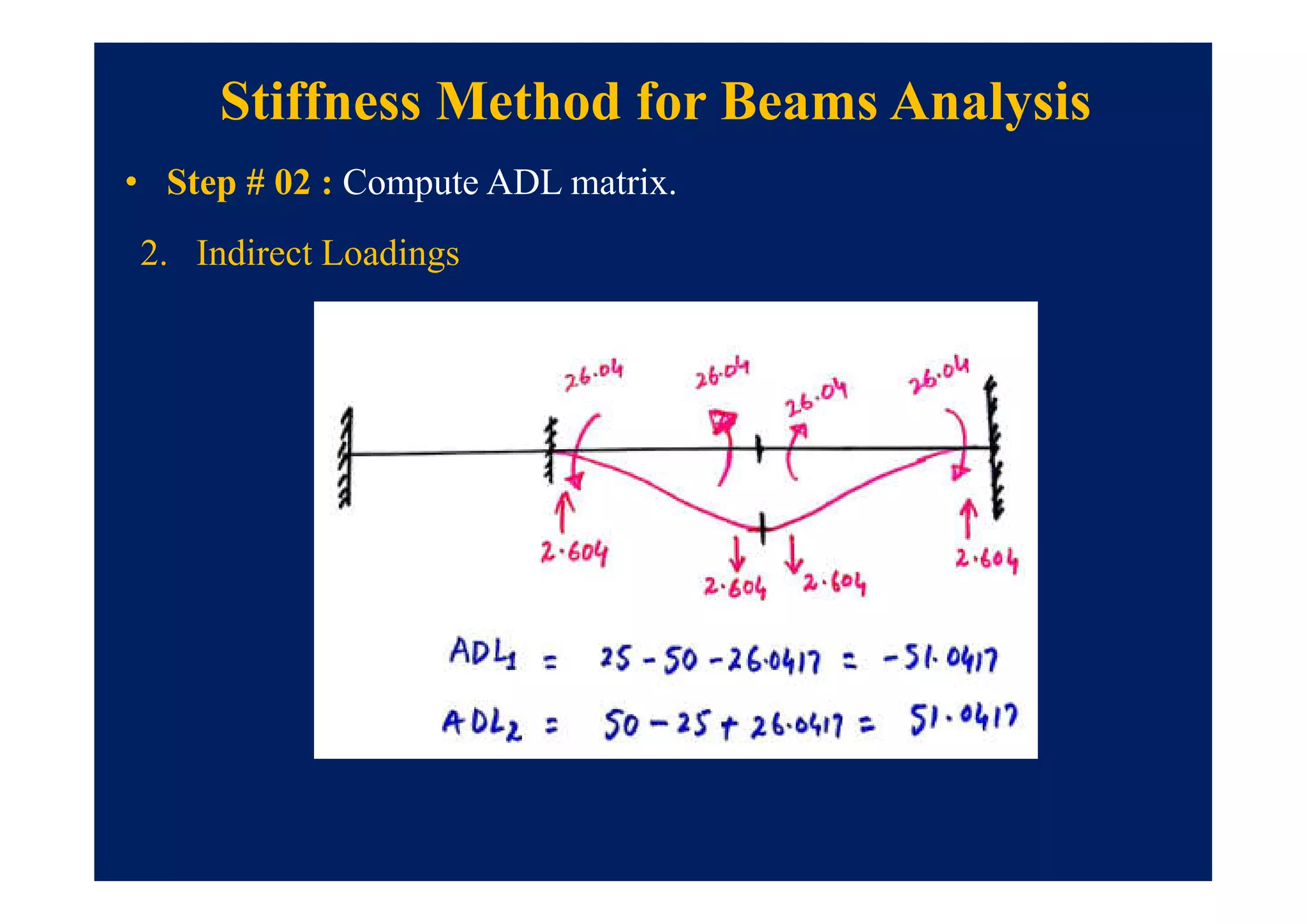
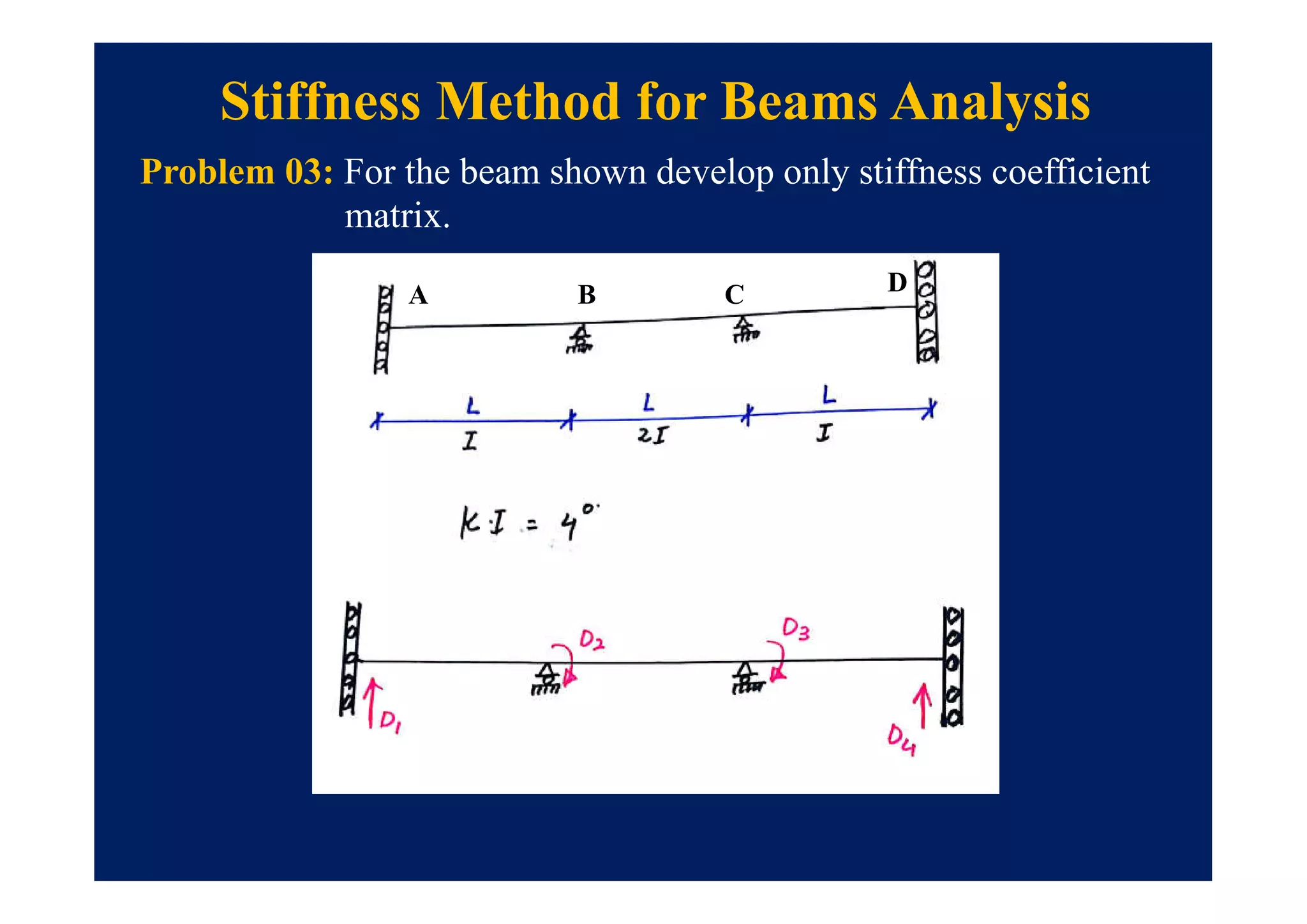
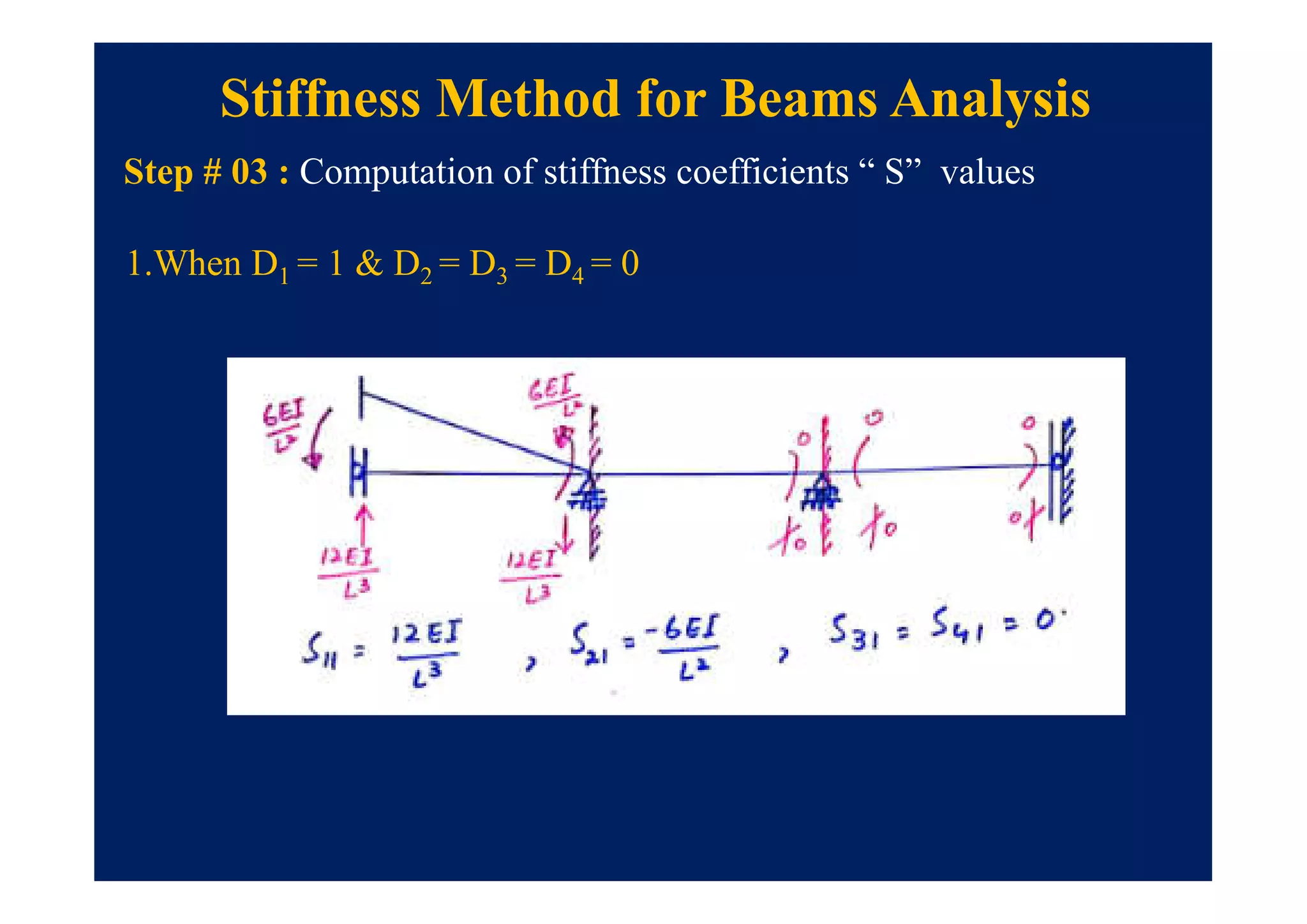
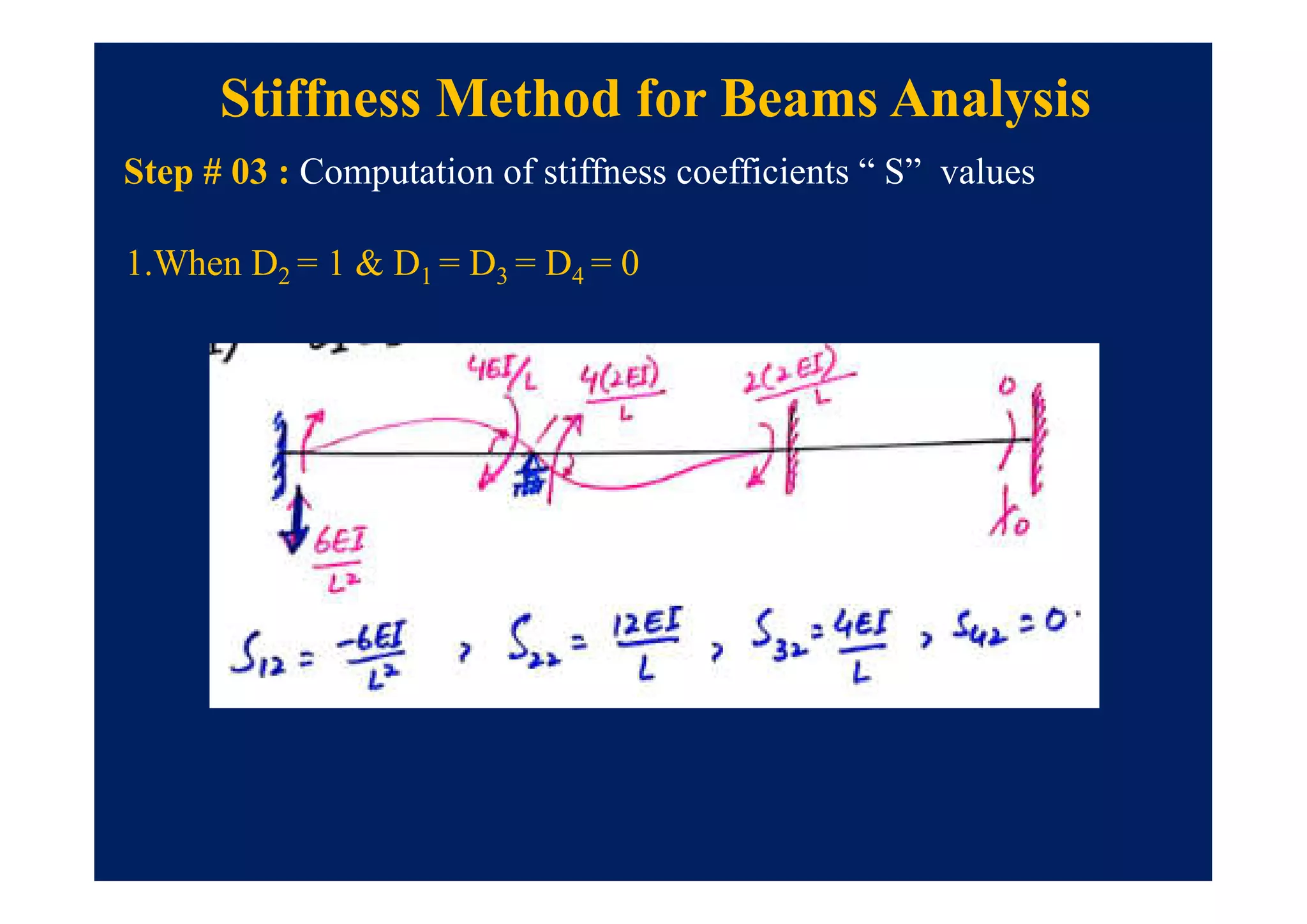
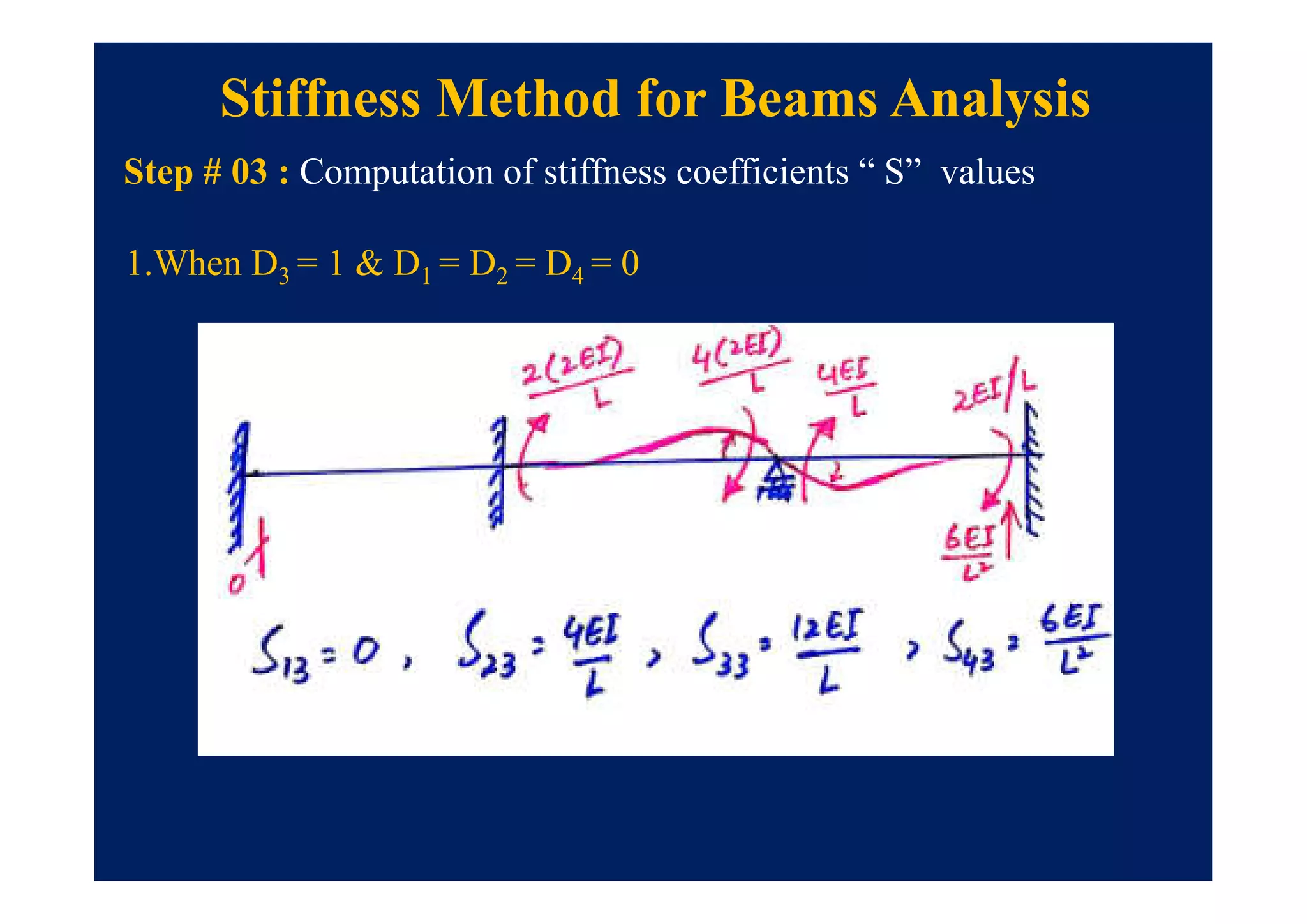
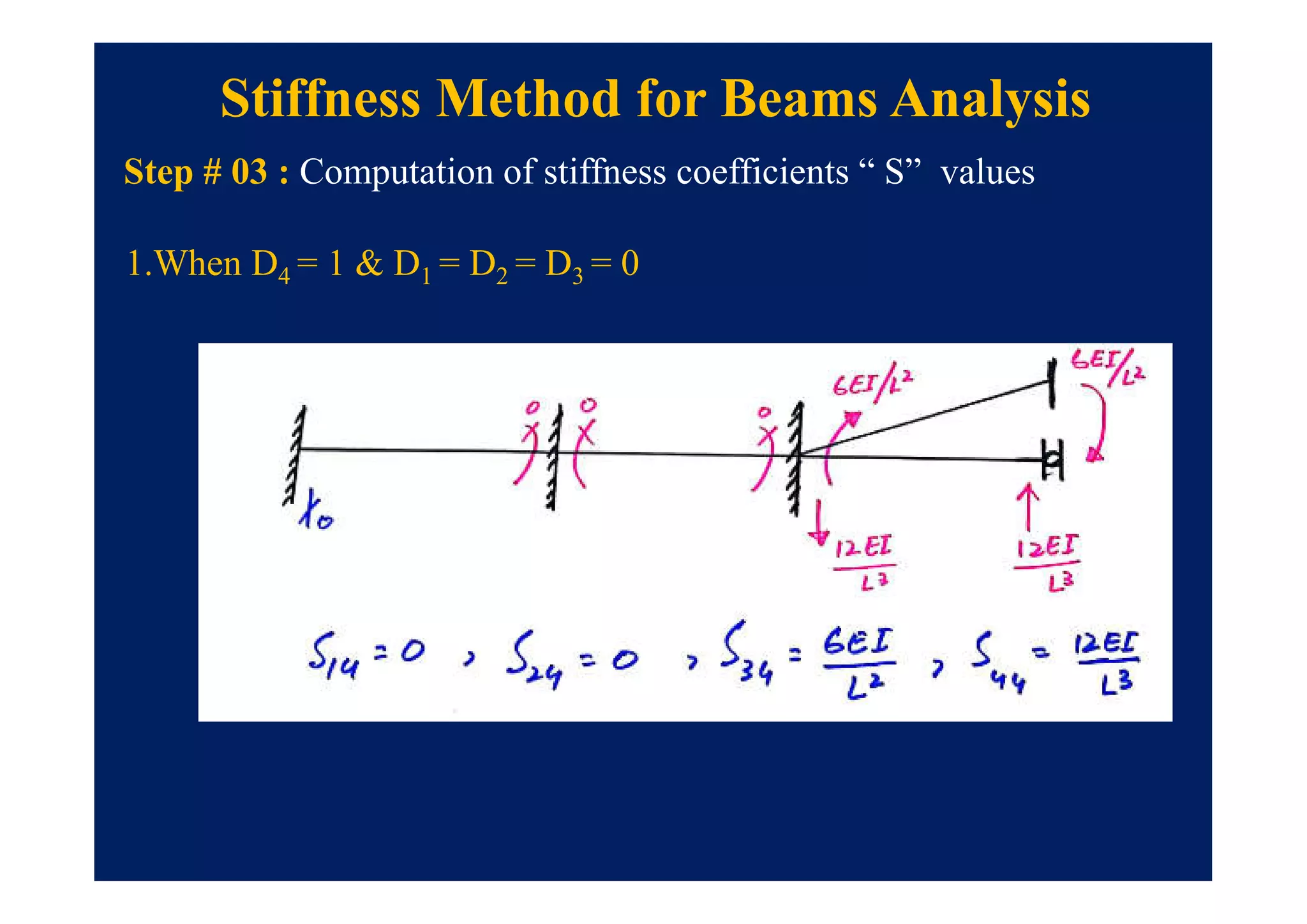
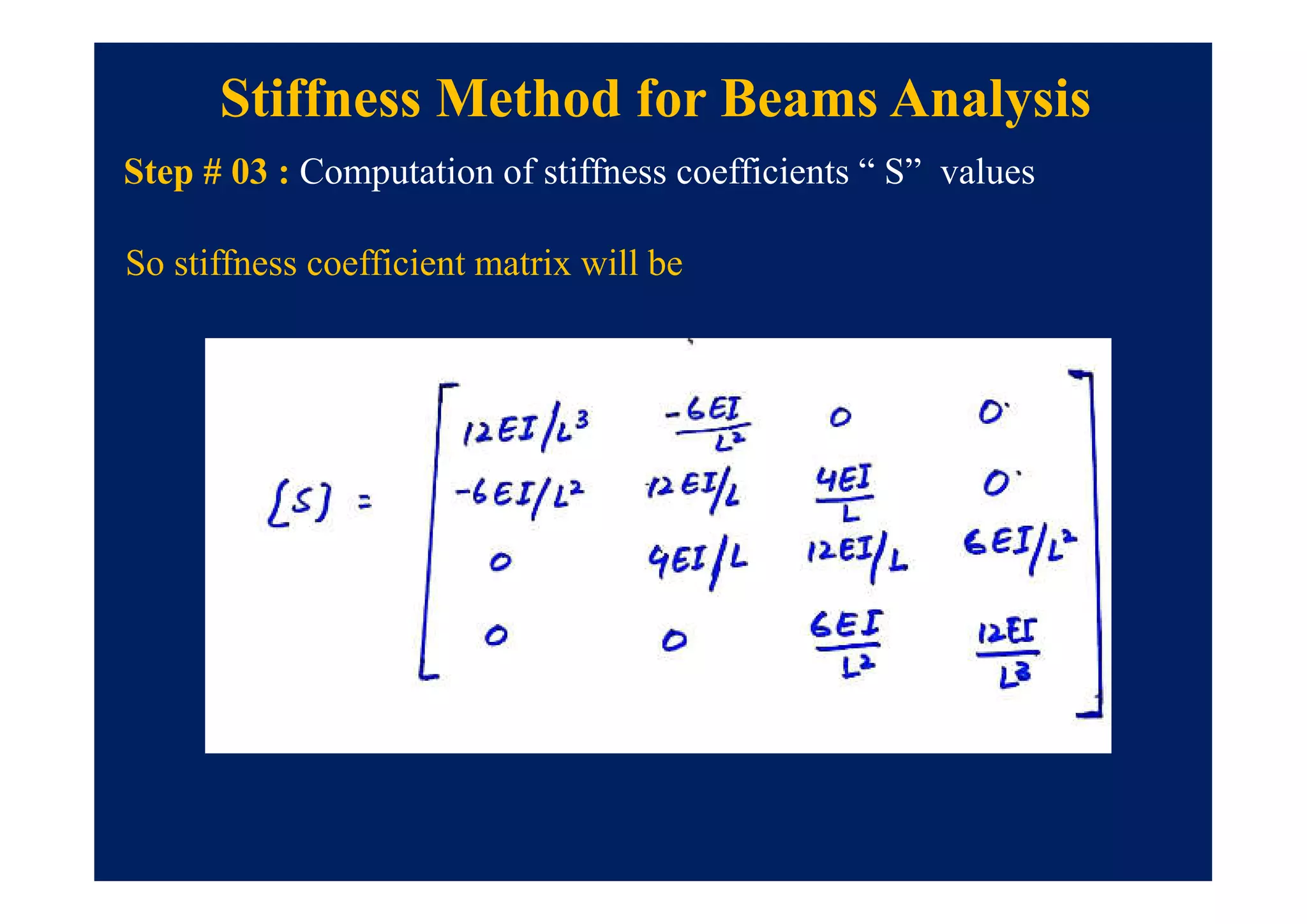
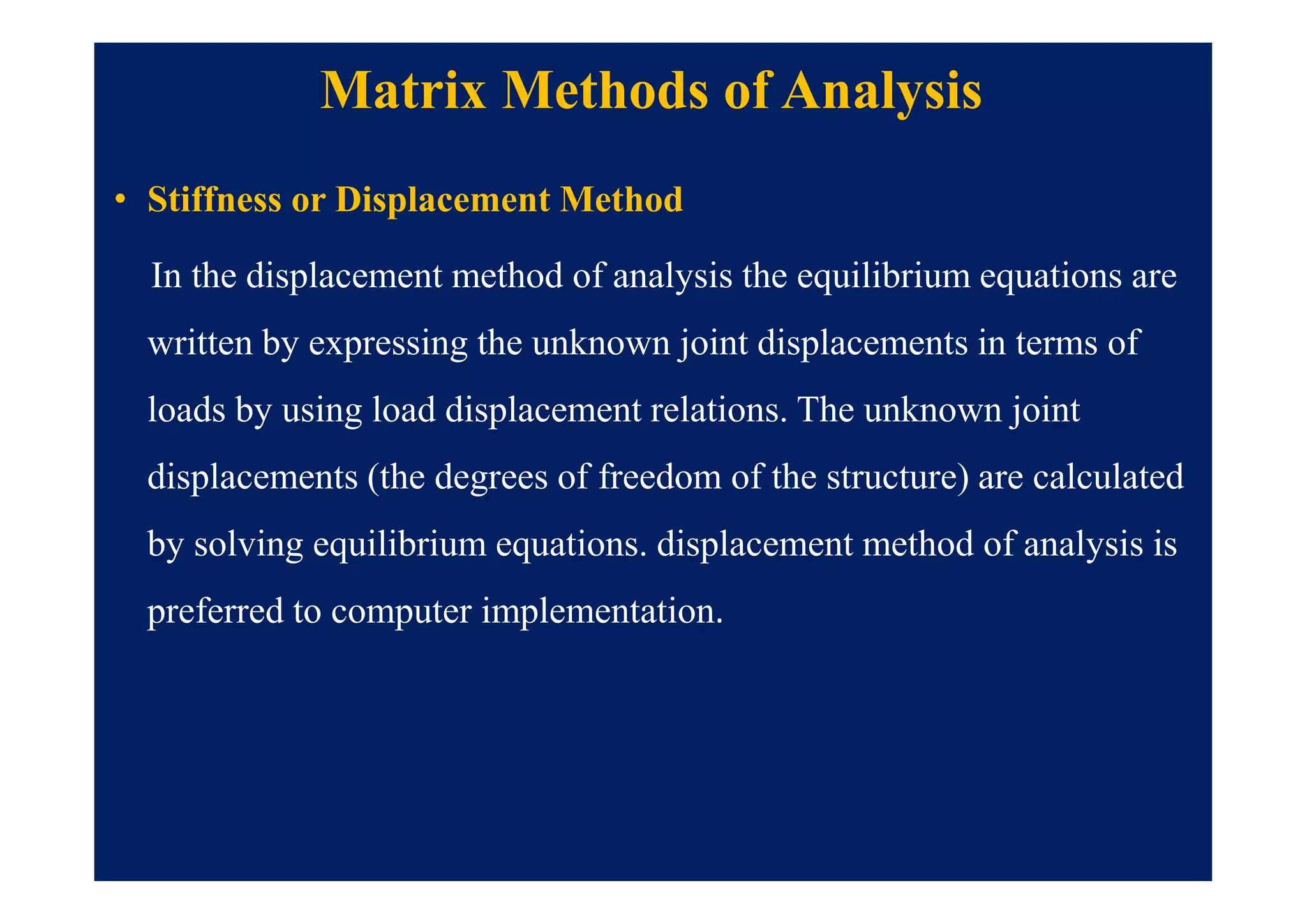
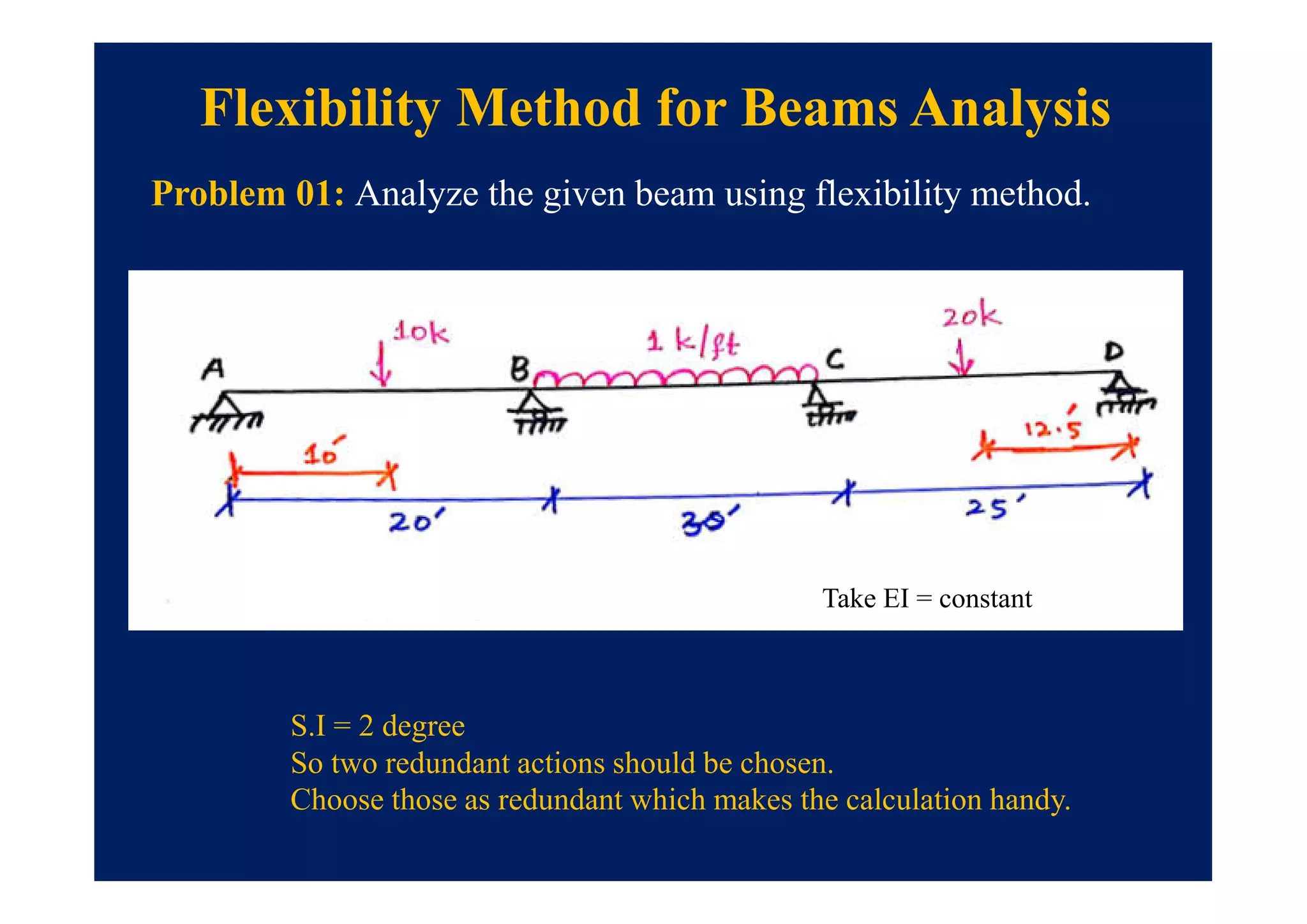
This document summarizes topics to be covered in a lecture on structure analysis using matrix methods. It will discuss the flexibility and stiffness methods. For the flexibility method, it will describe how redundant constraints are removed and equations of compatibility are written in terms of redundant actions and displacements. It will then show examples of applying the flexibility method to analyze beams and frames. For the stiffness method, it will explain how equilibrium equations are written using load-displacement relations and joint displacements are solved. Examples of applying the stiffness method to analyze beams are also provided.


![• Step # 02 : Compute the values of [DRL].
Flexibility Method for Beams Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module7-221102150327-0da88919/75/Module-7-pdf-8-2048.jpg)
![• Step # 02 : Compute the values of [DRL].
Flexibility Method for Beams Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module7-221102150327-0da88919/75/Module-7-pdf-9-2048.jpg)
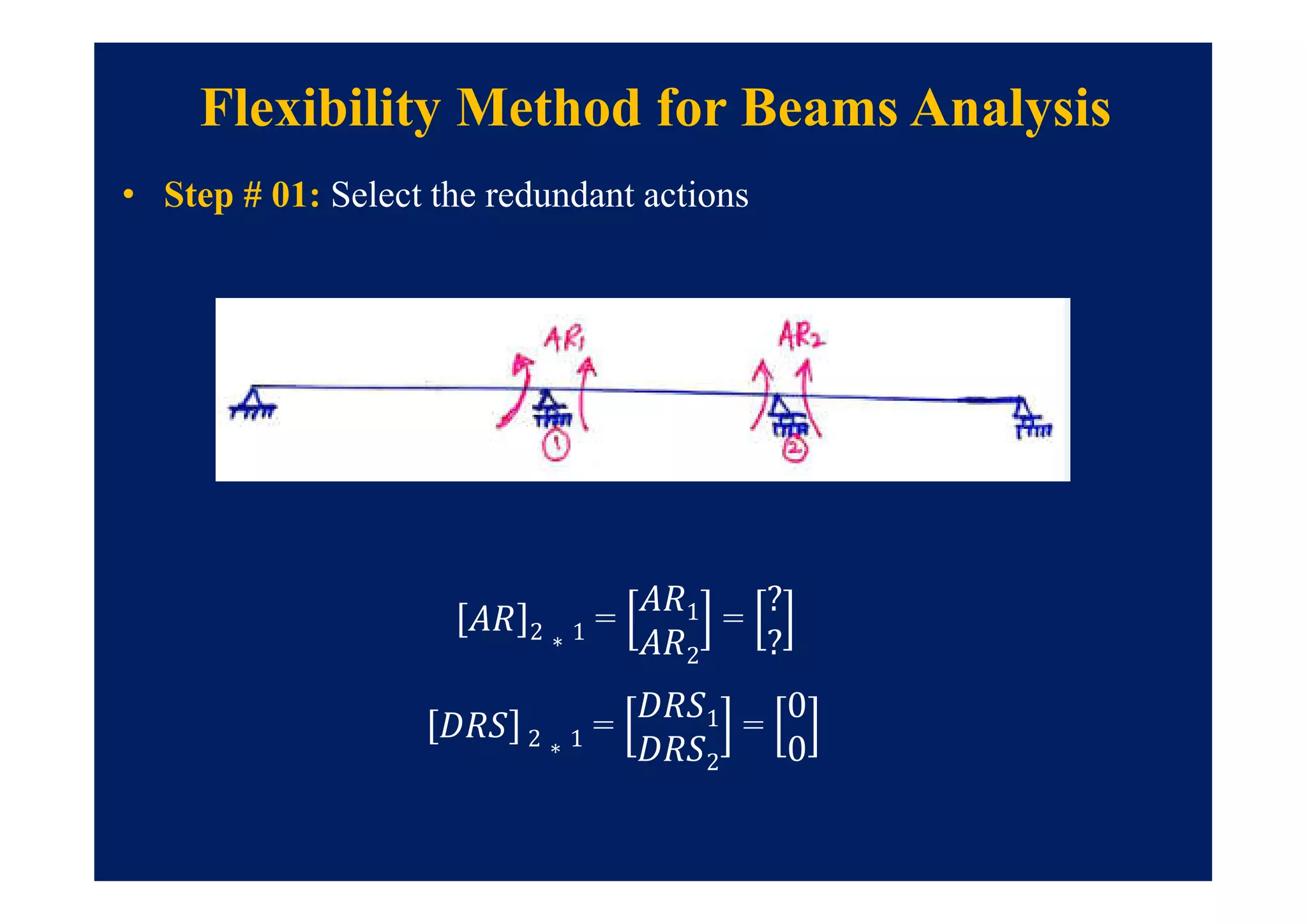
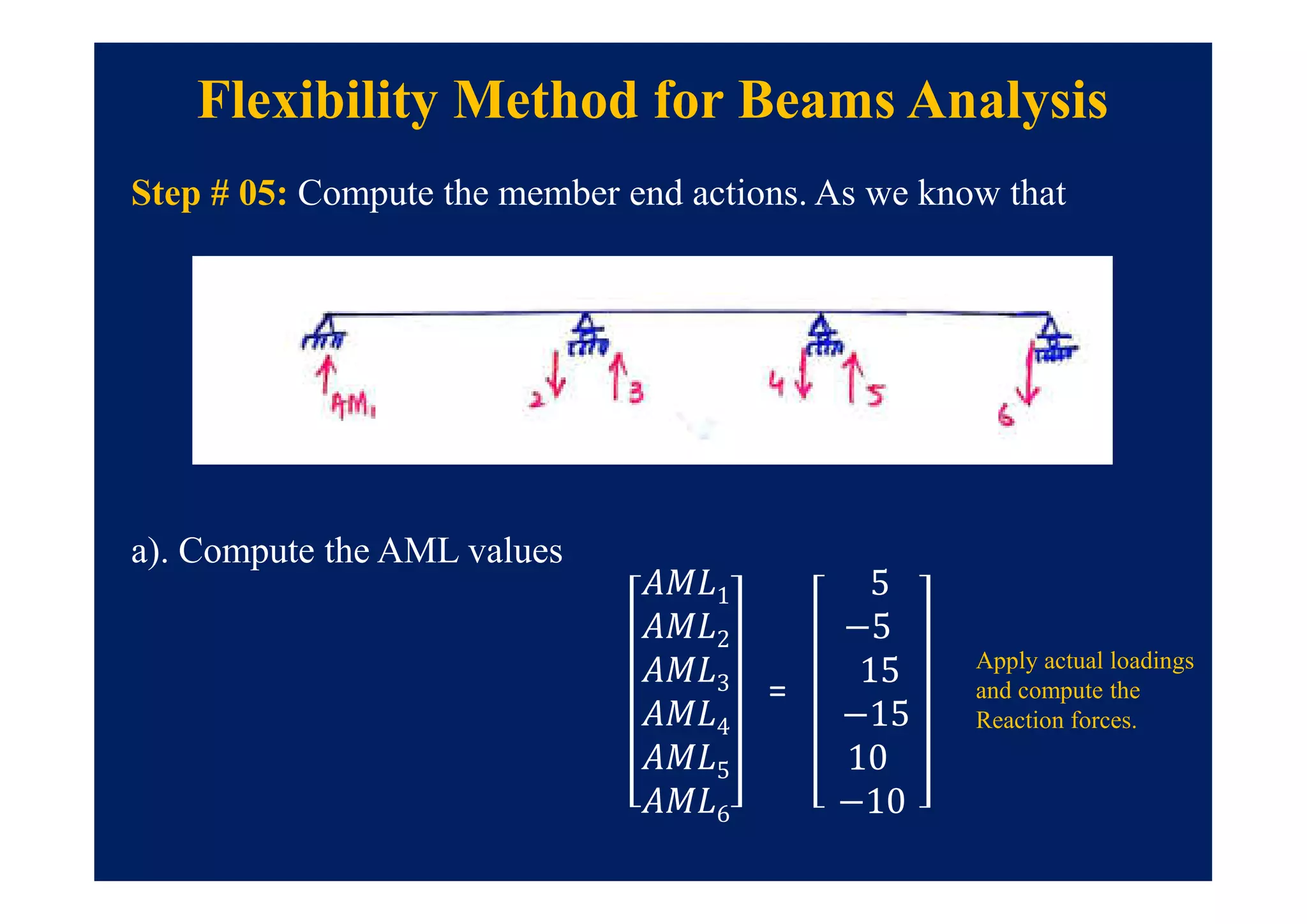
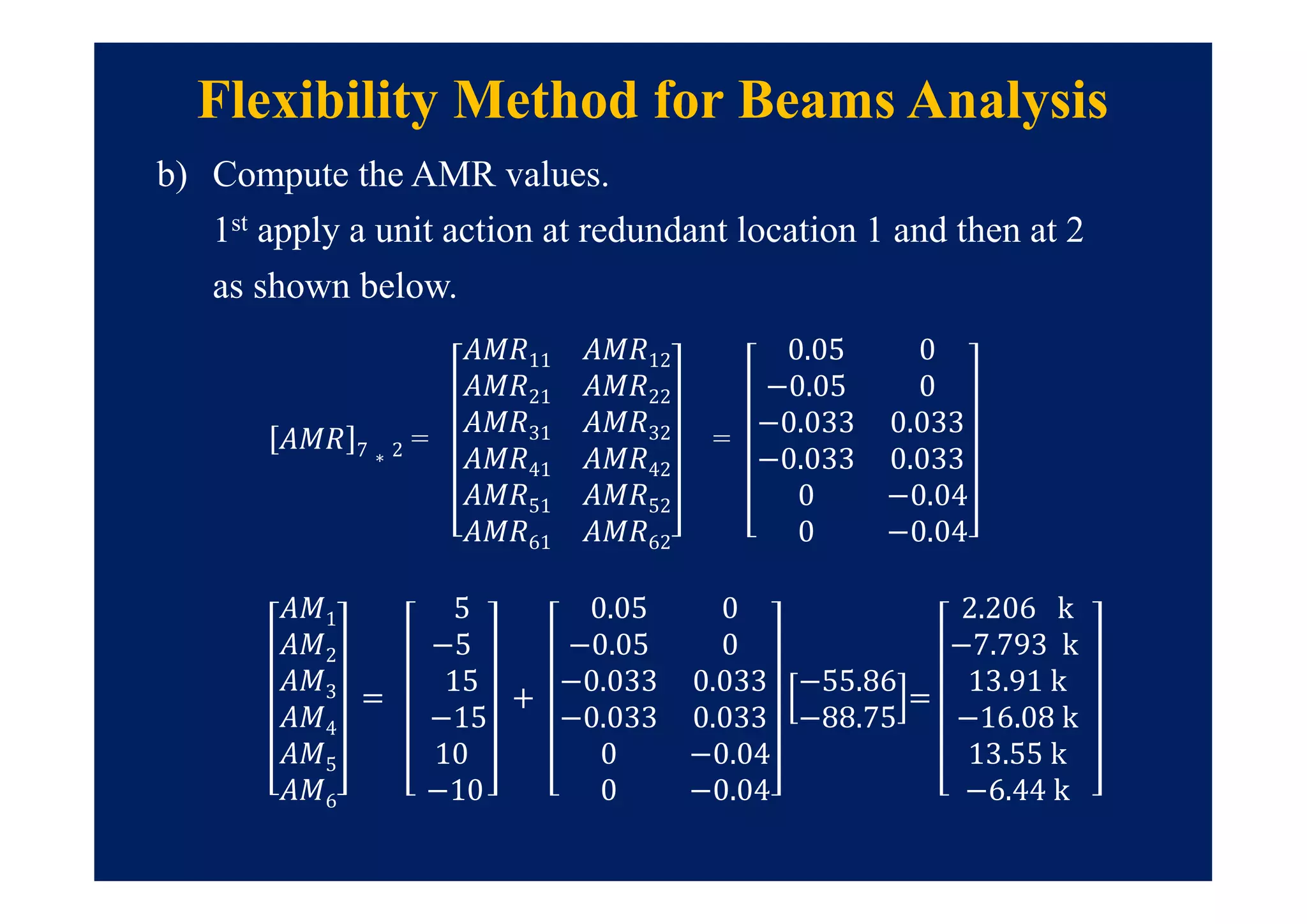
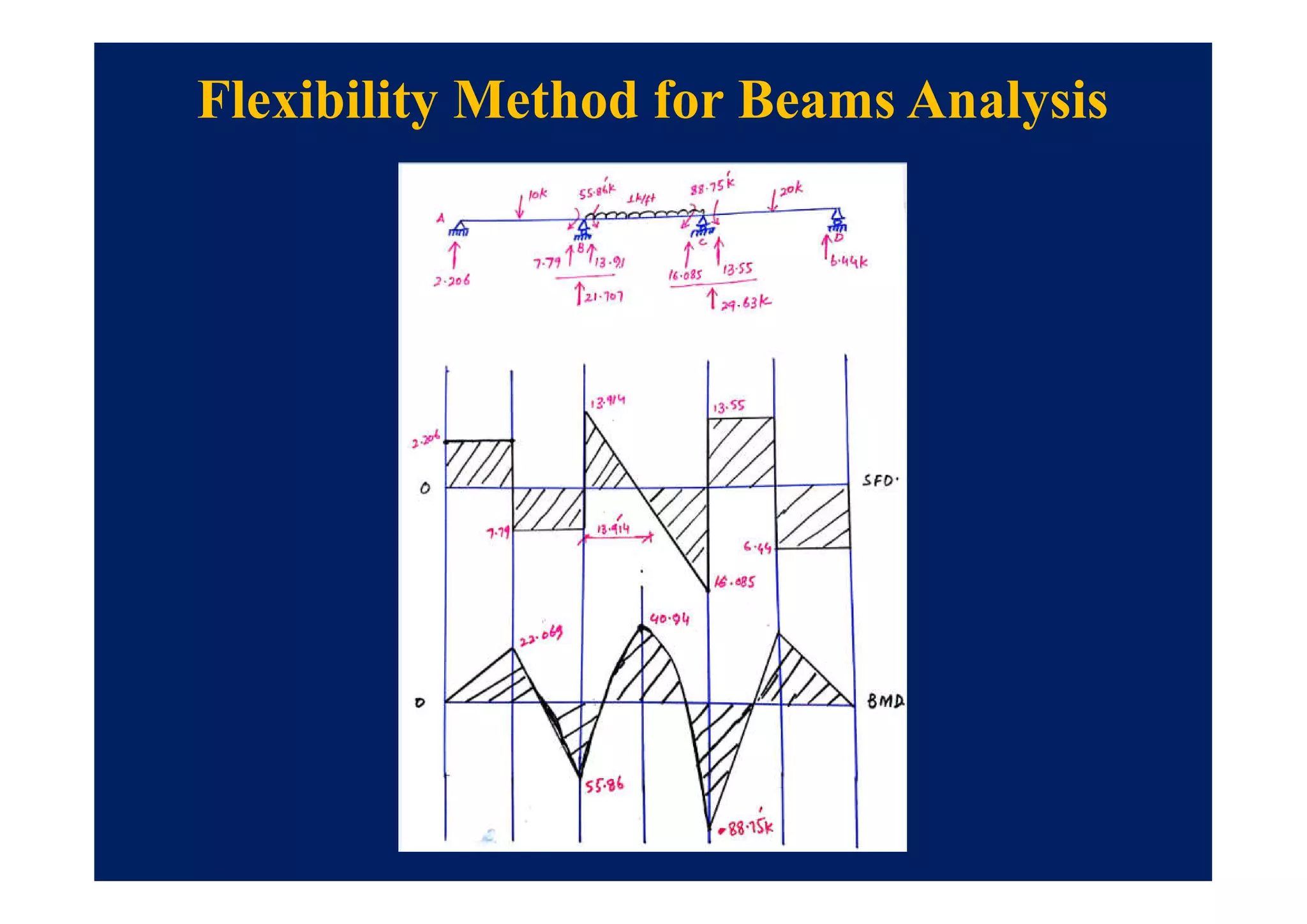
![Flexibility Method for Beams Analysis
• Step # 03 : Compute the values of flexibility matrix [ f ].
i. 1st apply a unit value of AR1 at reference point 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module7-221102150327-0da88919/75/Module-7-pdf-10-2048.jpg)
![Flexibility Method for Beams Analysis
• Step # 03 : Compute the values of flexibility matrix [ f ].
i. Now apply a unit value of AR2 at reference point 2
= 11 12
21 22
=
16.67 5
5 18.33
EI = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module7-221102150327-0da88919/75/Module-7-pdf-11-2048.jpg)
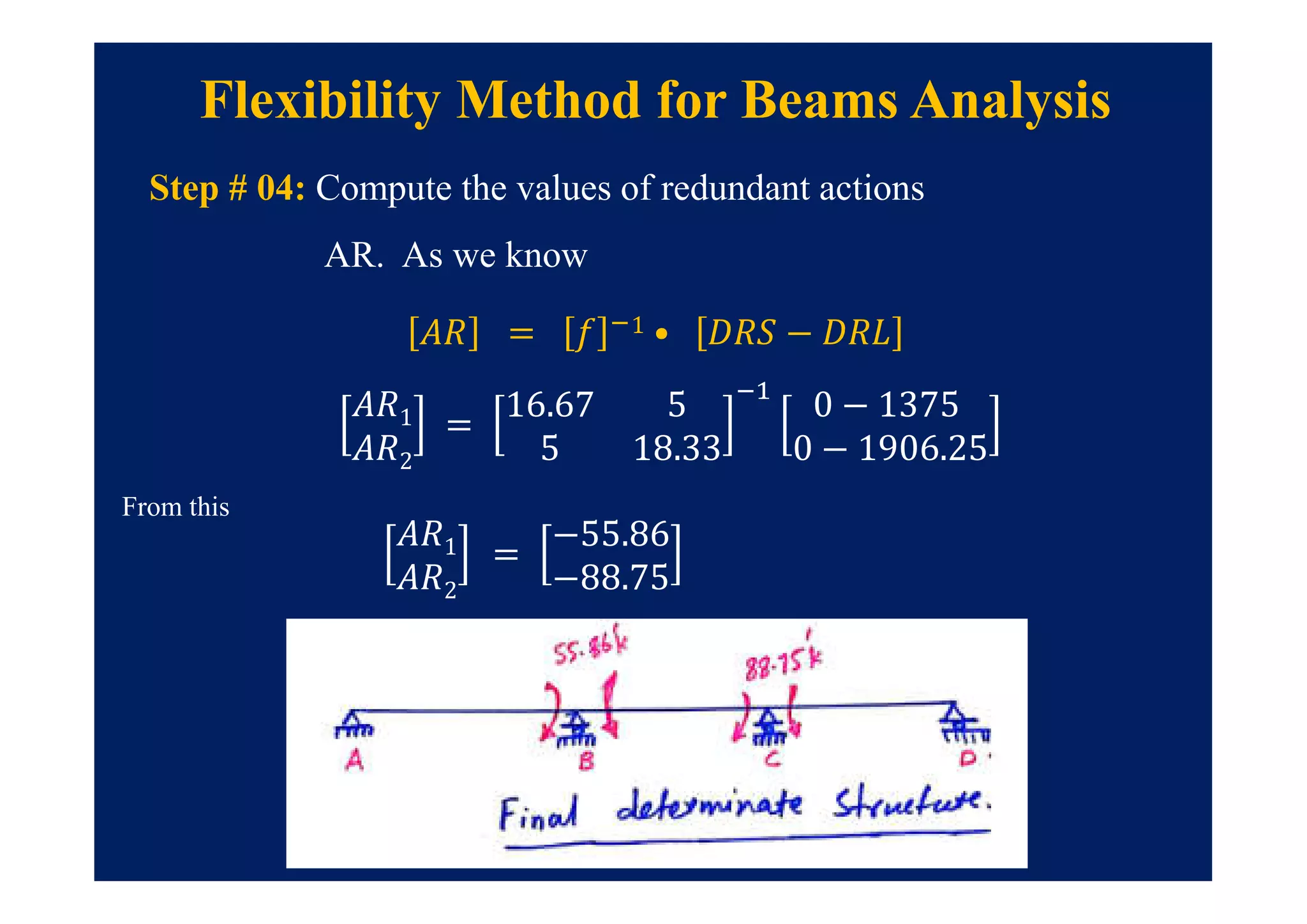
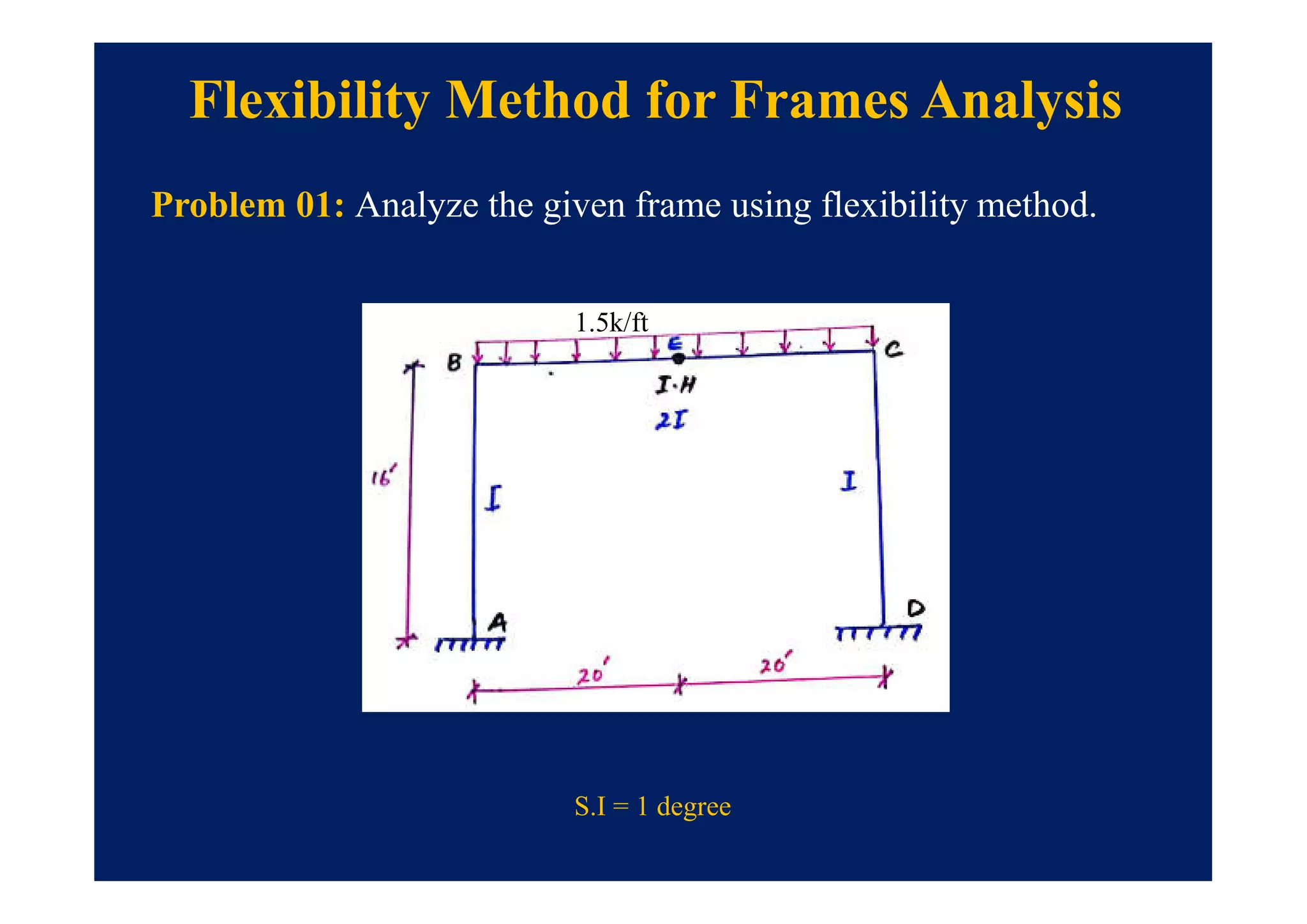
![• Step # 01: Identify the redundants and obtain BDS also compute
[DRS] values.
Flexibility Method for Frames Analysis
= ?
= 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module7-221102150327-0da88919/75/Module-7-pdf-17-2048.jpg)