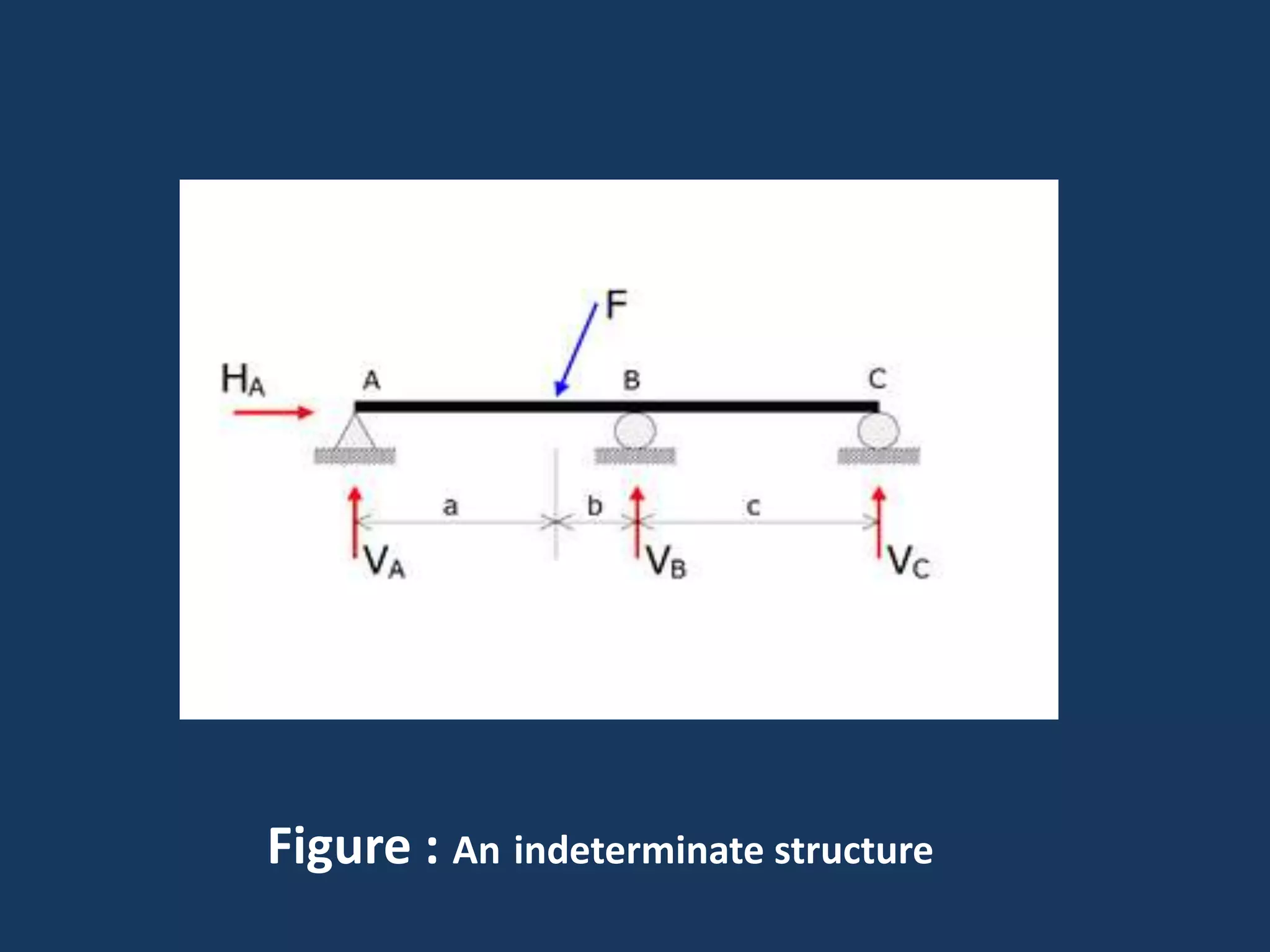
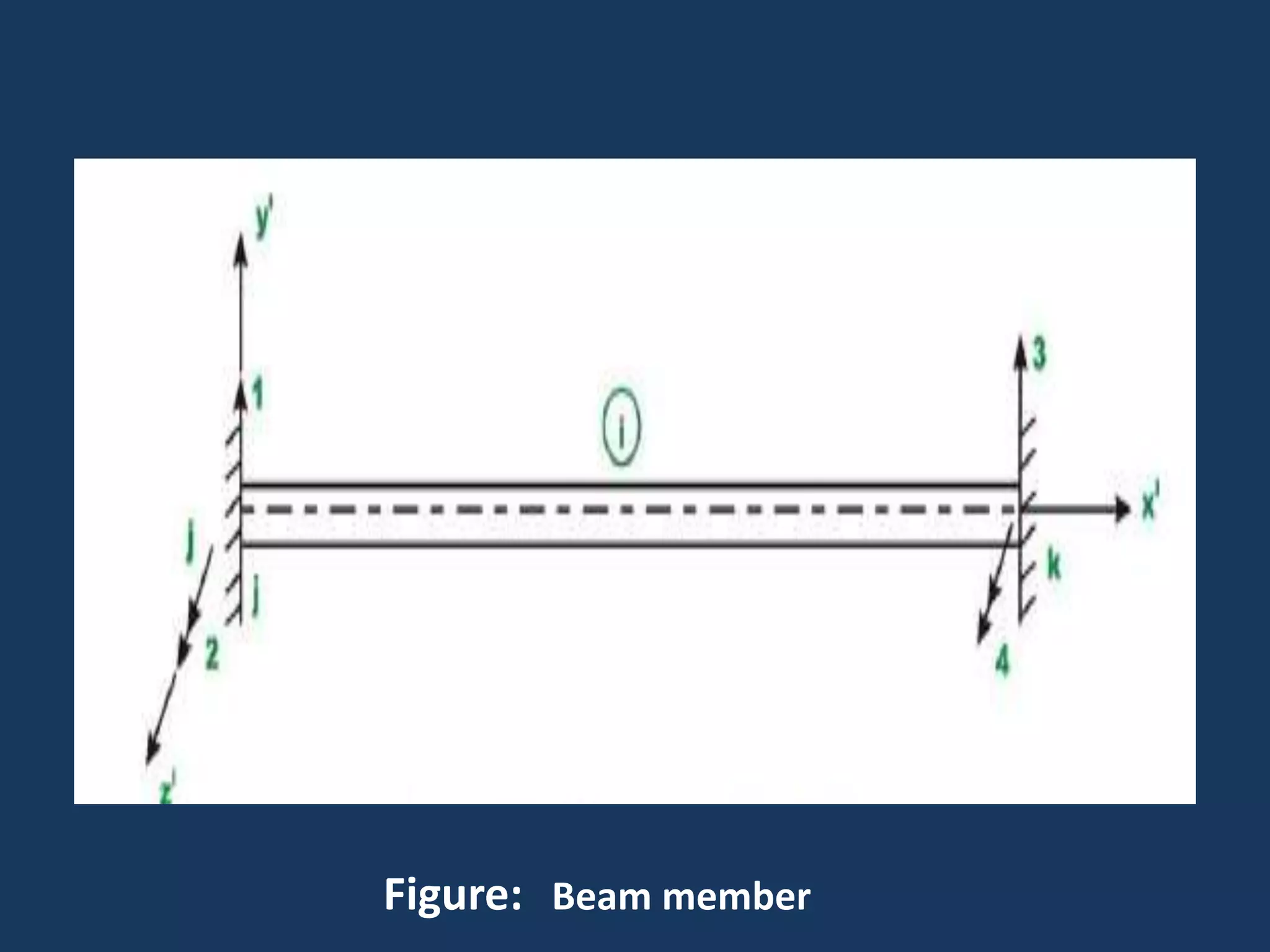
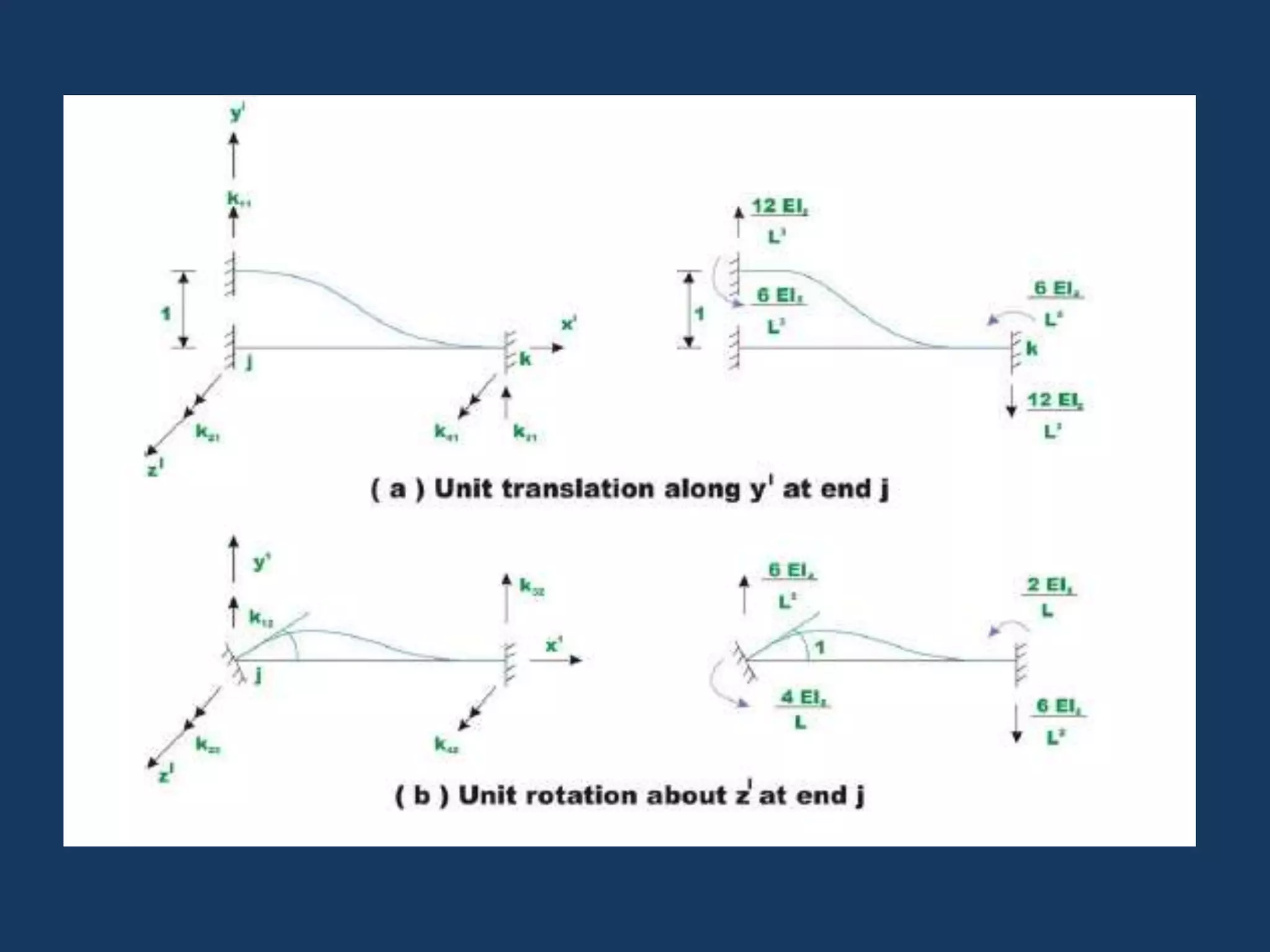
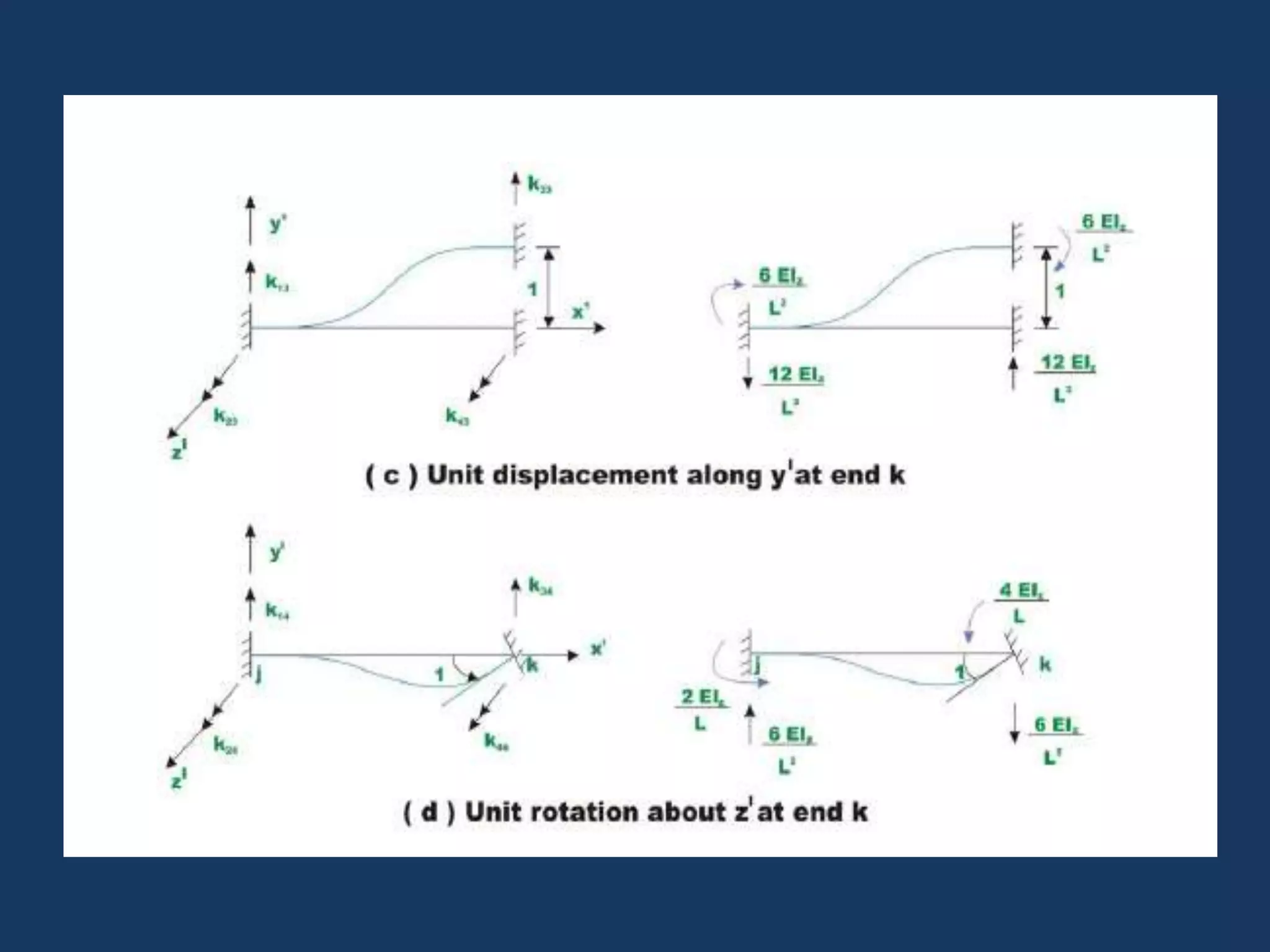
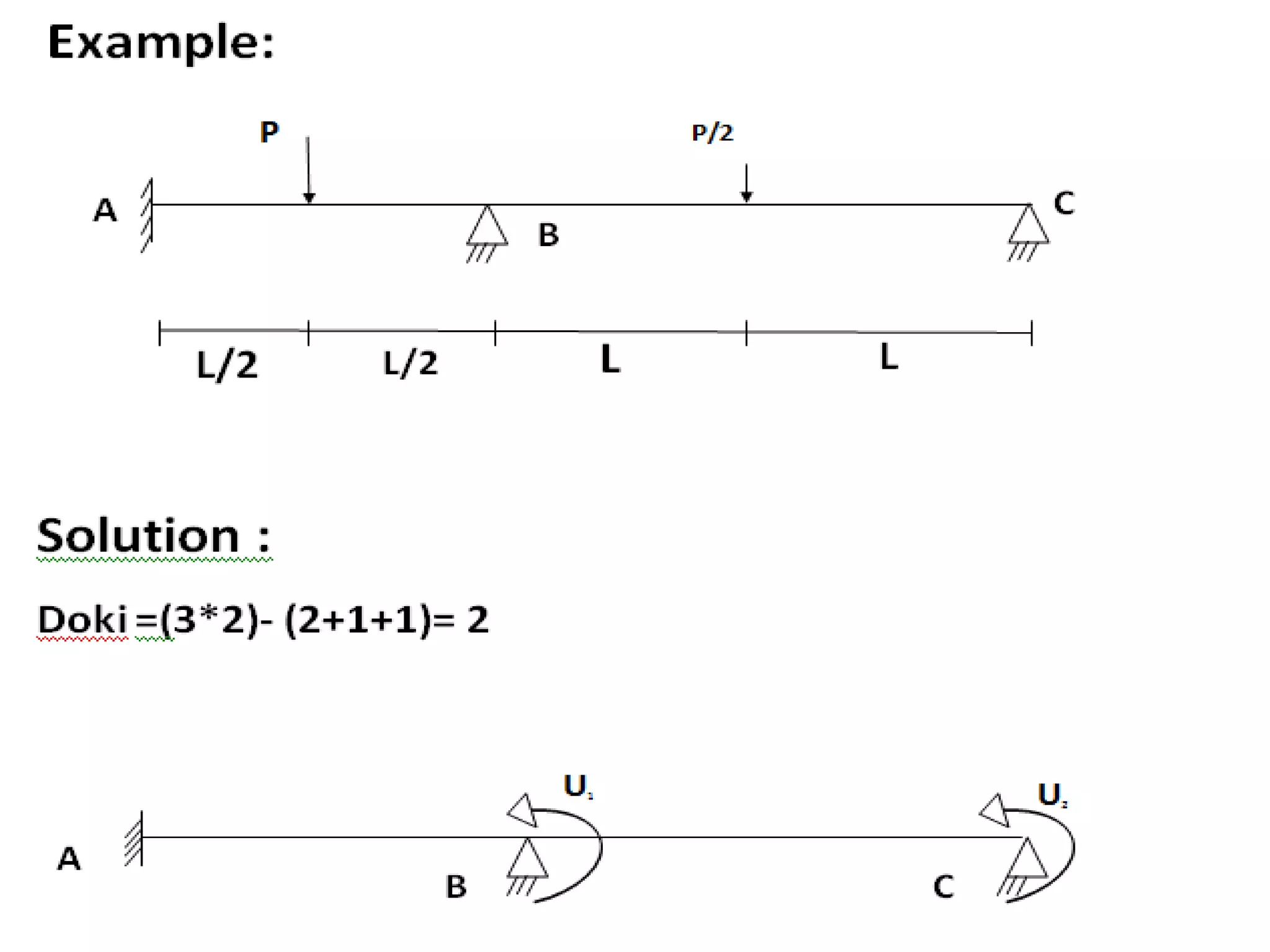
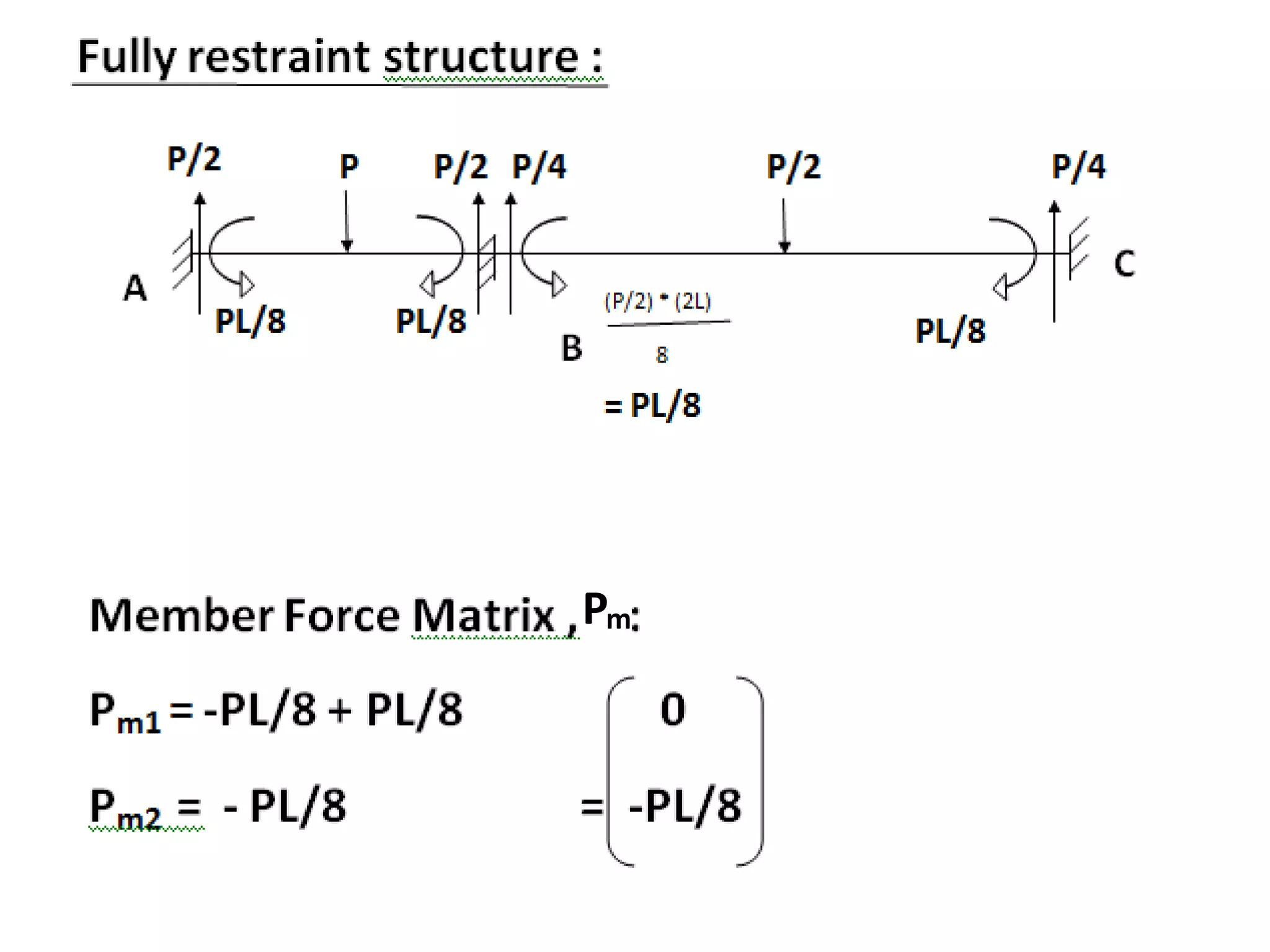
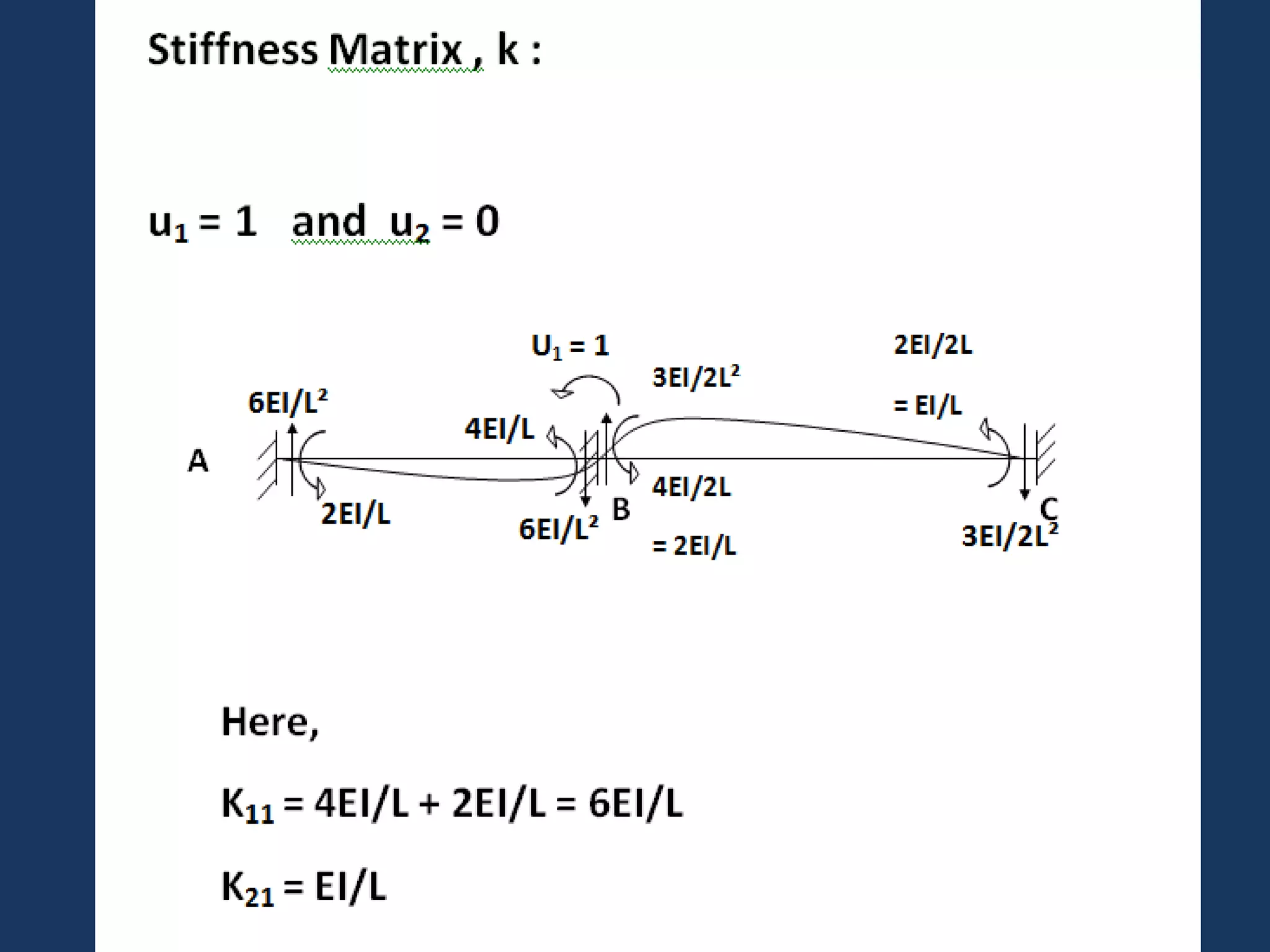
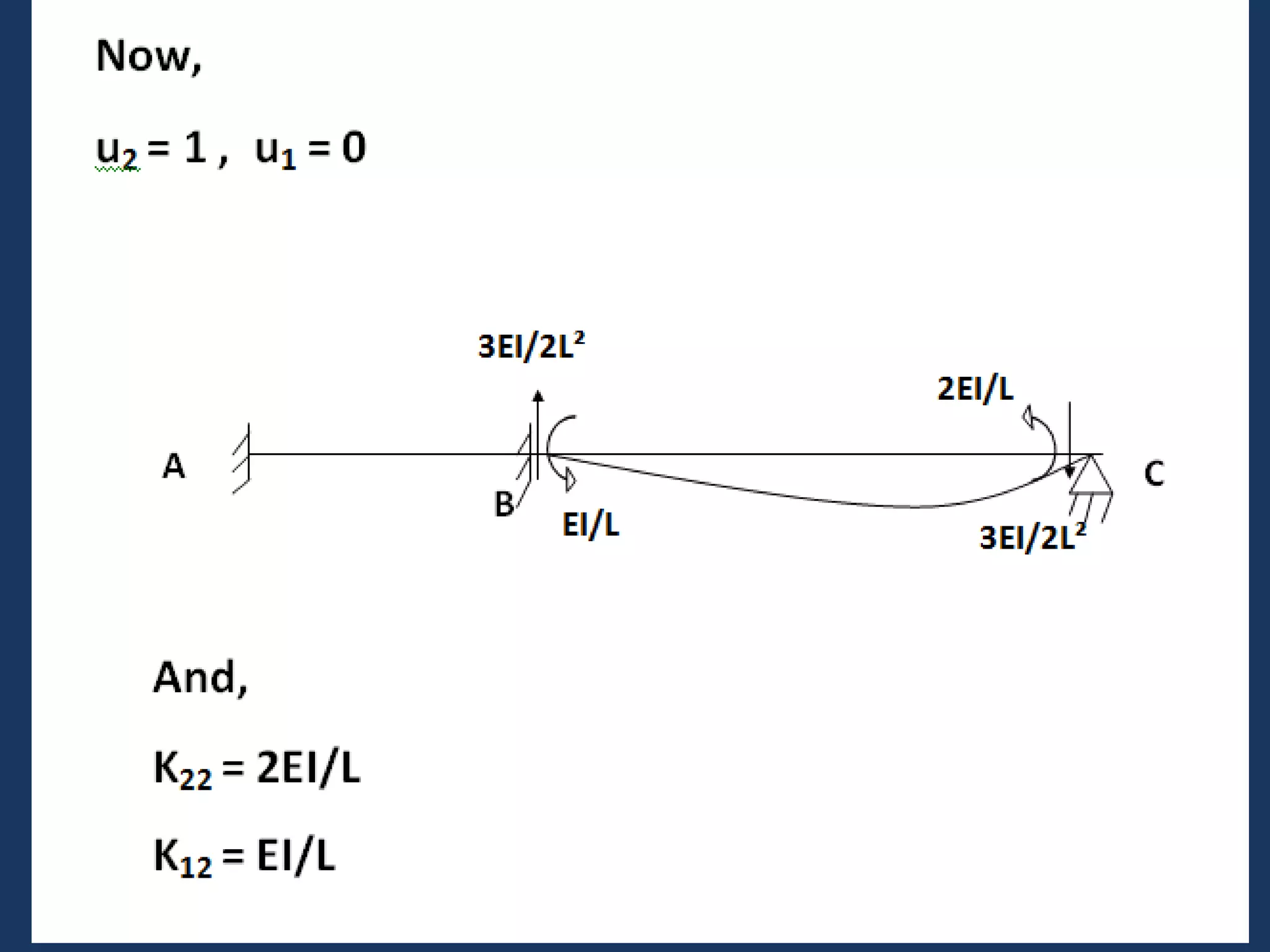
This document discusses solving statically indeterminate structures using the direct stiffness method. It begins with an introduction that defines statically indeterminate structures as those that cannot be analyzed using static equilibrium equations alone, consisting of more members and/or supports than needed for static determinacy.
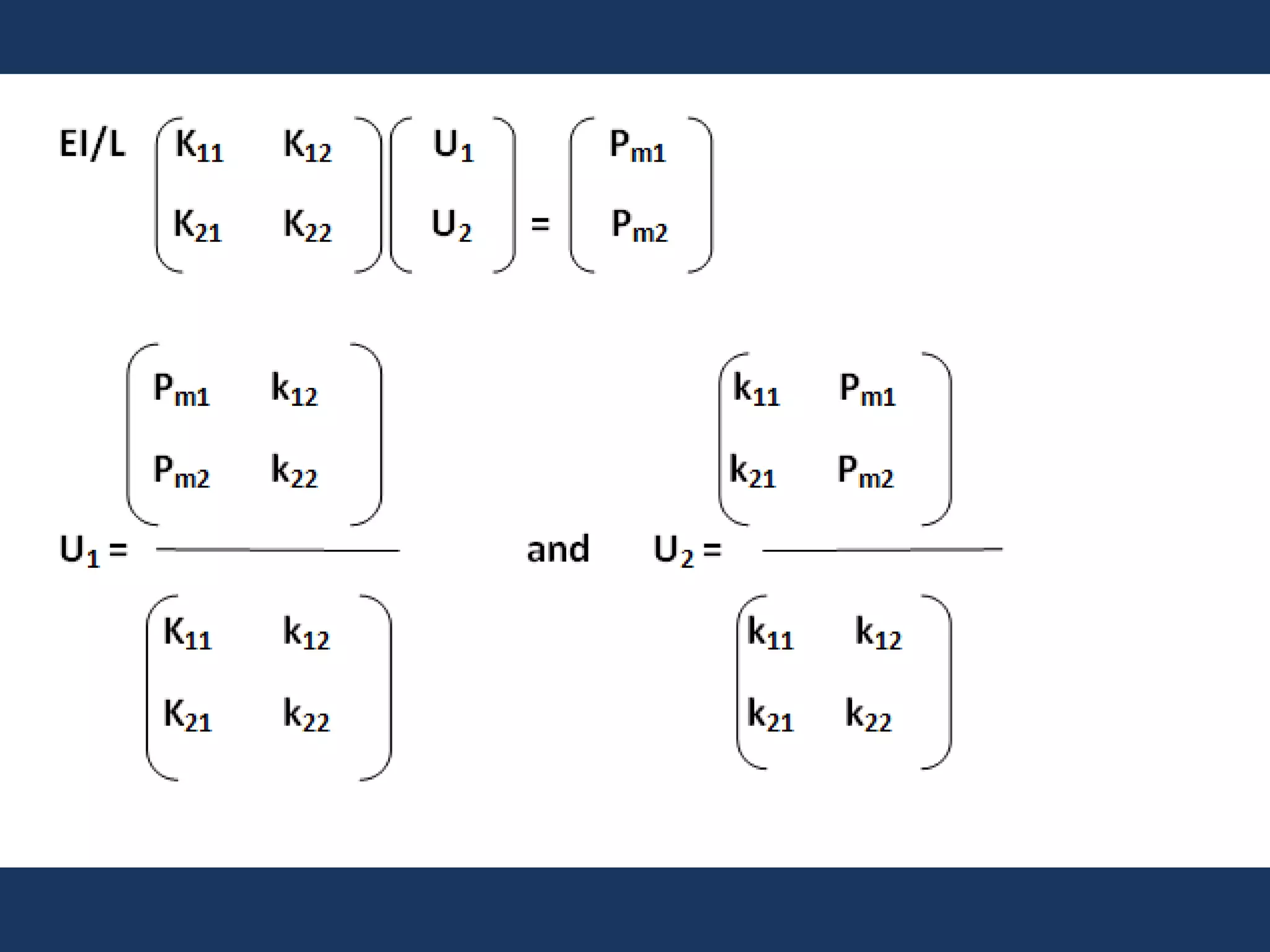
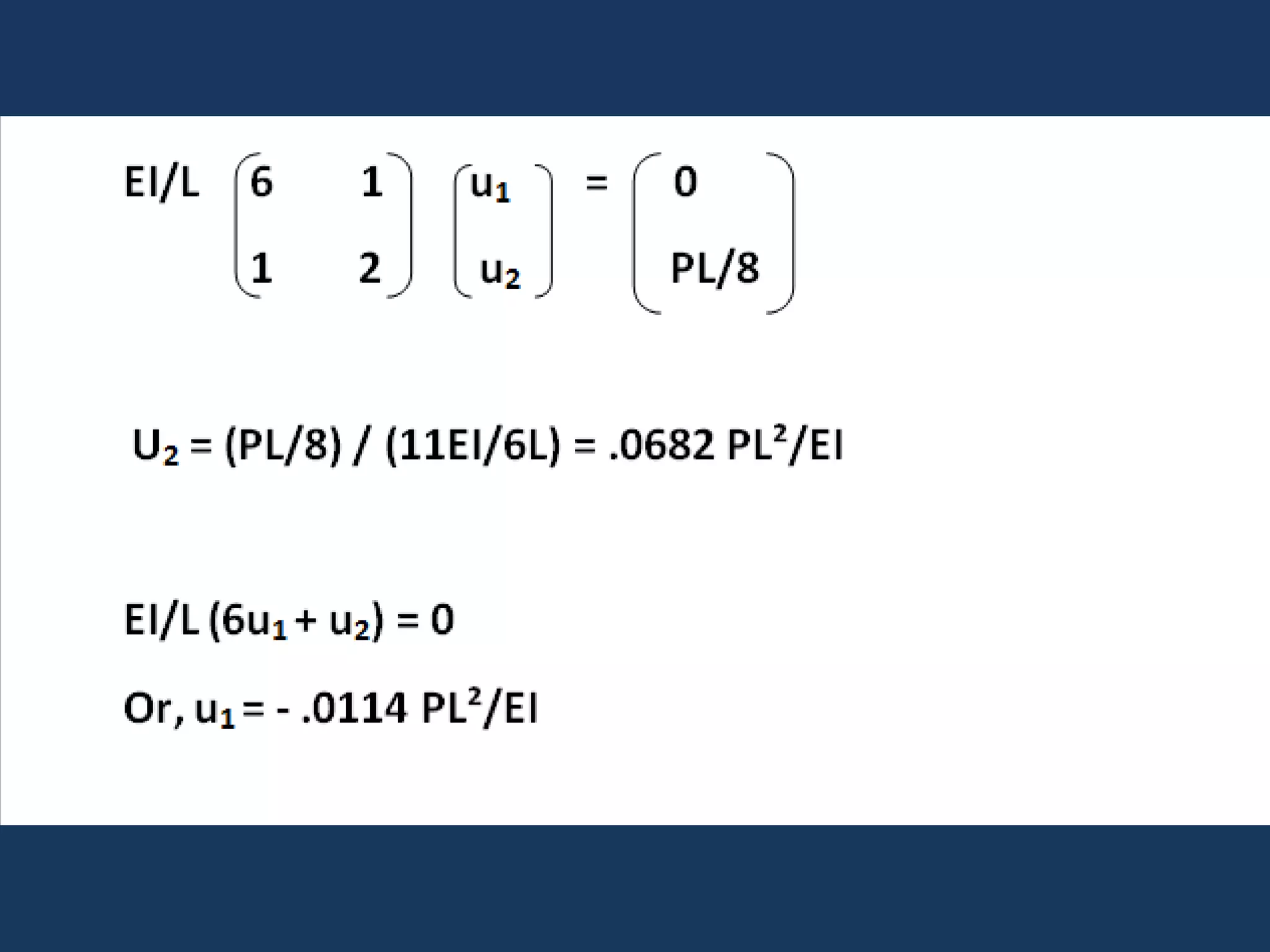
It then explains that the direct stiffness method is a matrix method that uses member stiffness relations to compute member forces and displacements. It involves adding restraints to make the structure determinate, applying loads to calculate forces, applying displacements one at a time to determine corresponding forces, writing equilibrium equations, and solving the matrix equation to obtain displacements and subsequently other reactions.
The benefits of the direct stiffness method are that it can effectively and