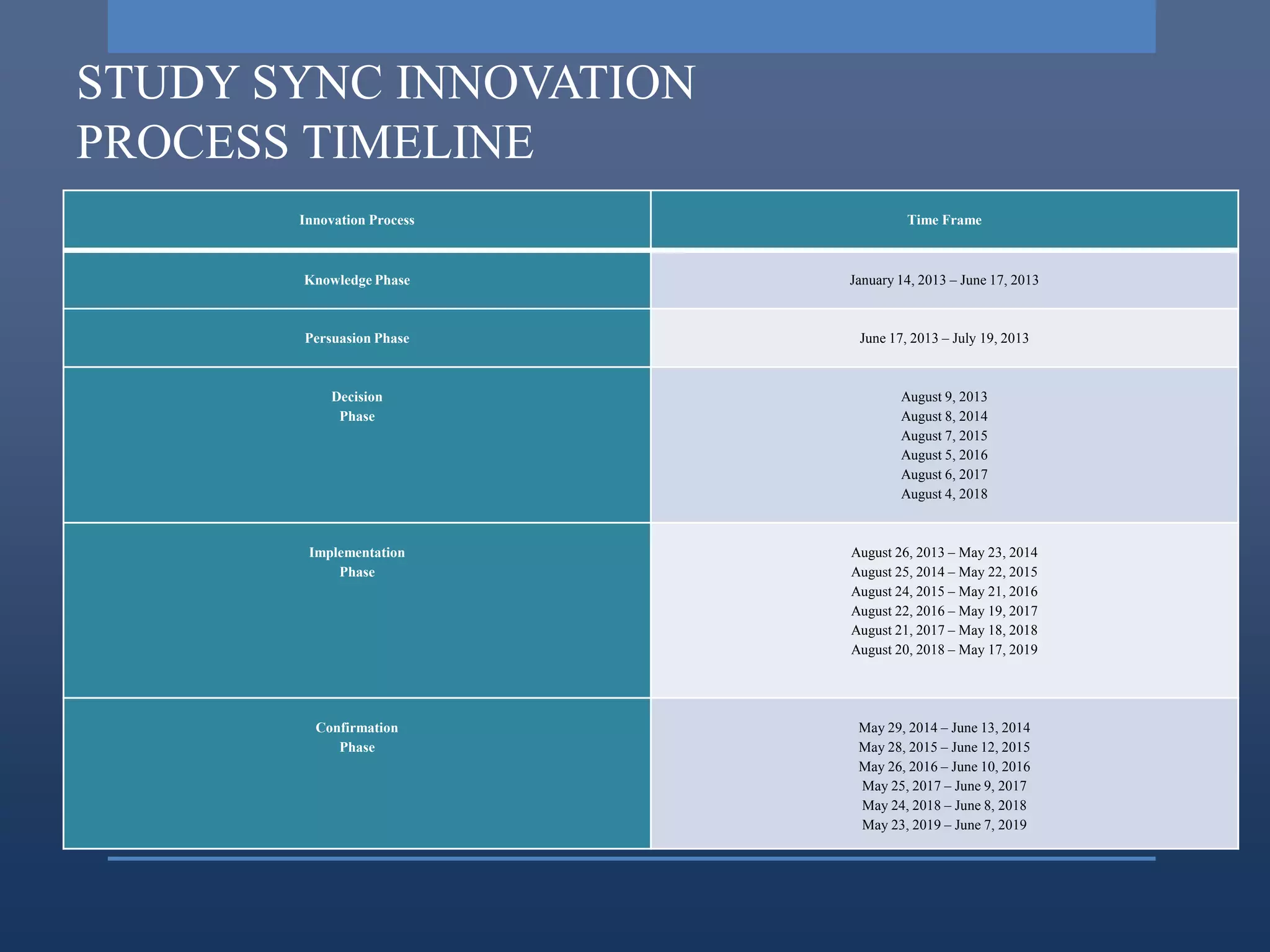
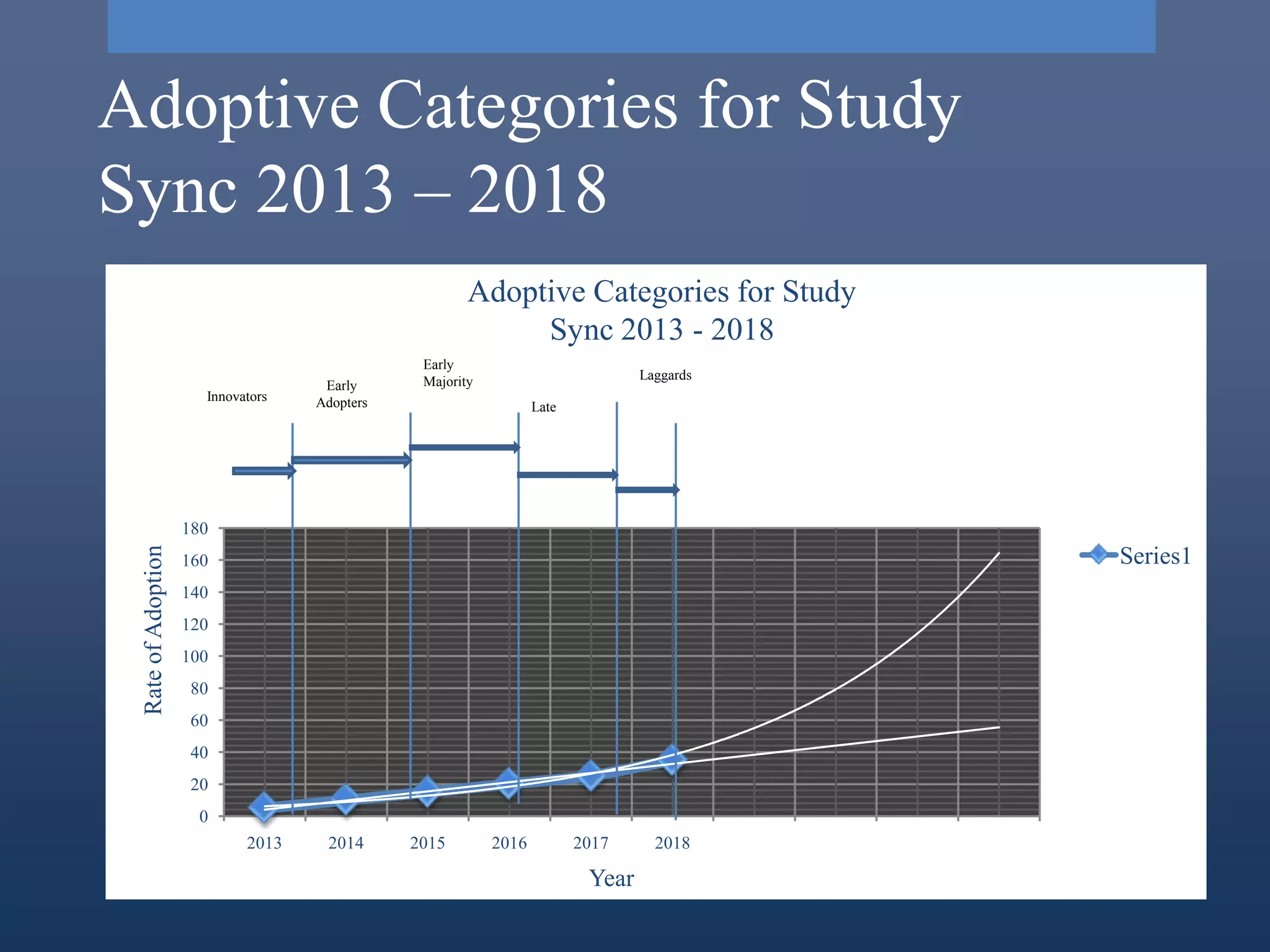
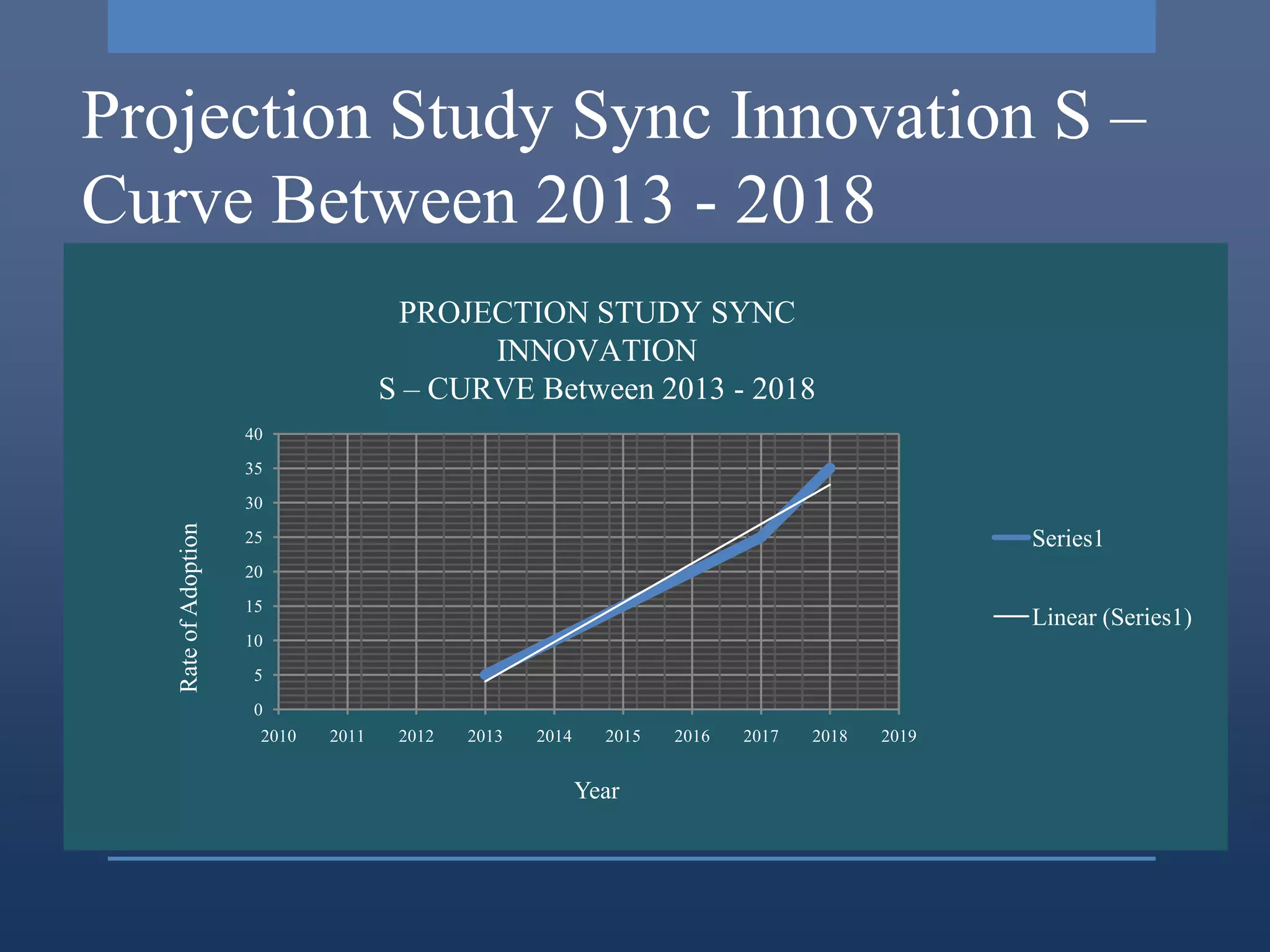
Study Sync is a learning management system that promotes literacy skills through a digital library, online writing, peer review, and other features. It addresses needs like engaging students with technology and providing flexible access. Research found that activities are time worthy and stimulate the intellect. The innovation went through stages of need identification, research, development, and commercialization. It is being implemented in phases from 2013-2018 in schools to improve students' reading, writing, and critical thinking skills.