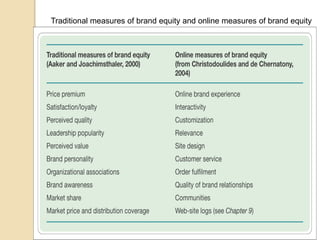
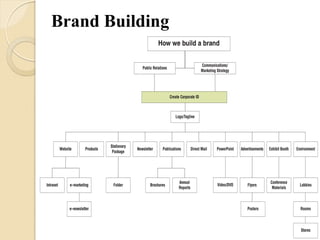
This document summarizes key concepts about branding on the web from a lecture. It defines branding and discusses the importance of developing brand identity, equity, and uniformity online. It notes challenges like protecting brands from misuse as information spreads quickly online. The document outlines best practices for building successful brands, including choosing brand elements, developing a brand strategy in steps, and maintaining consistency. It emphasizes the importance of differentiation, relevance and perceived value in online branding.