Embed presentation



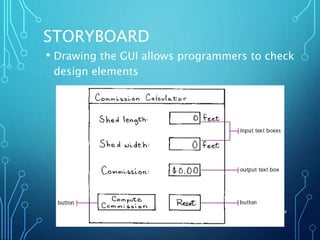

This document discusses graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and user interface (UI) design. It explains that GUIs use visual elements like windows, icons and menus to provide a point-and-click experience to users. The document also outlines important principles for UI design, such as prioritizing functionality over aesthetics, following consistent design patterns, and creating intuitive experiences based on real-world analogies familiar to users. Storyboarding is presented as a way to plan and check the design elements of a GUI before development.




