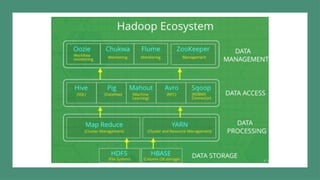
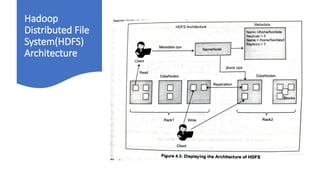
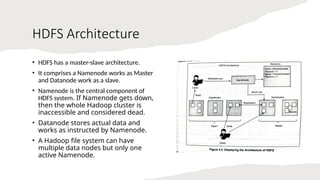
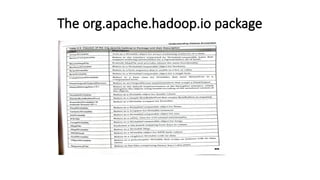
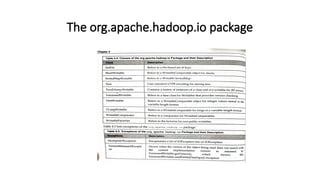
The document provides an overview of the Hadoop ecosystem, emphasizing its role in processing large datasets through distributed computing. It highlights the architecture of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), detailing the functions of the namenode and datanodes, and how the system manages data replication and node failure. Additionally, it discusses the necessity of various components within the ecosystem to effectively deal with big data challenges.