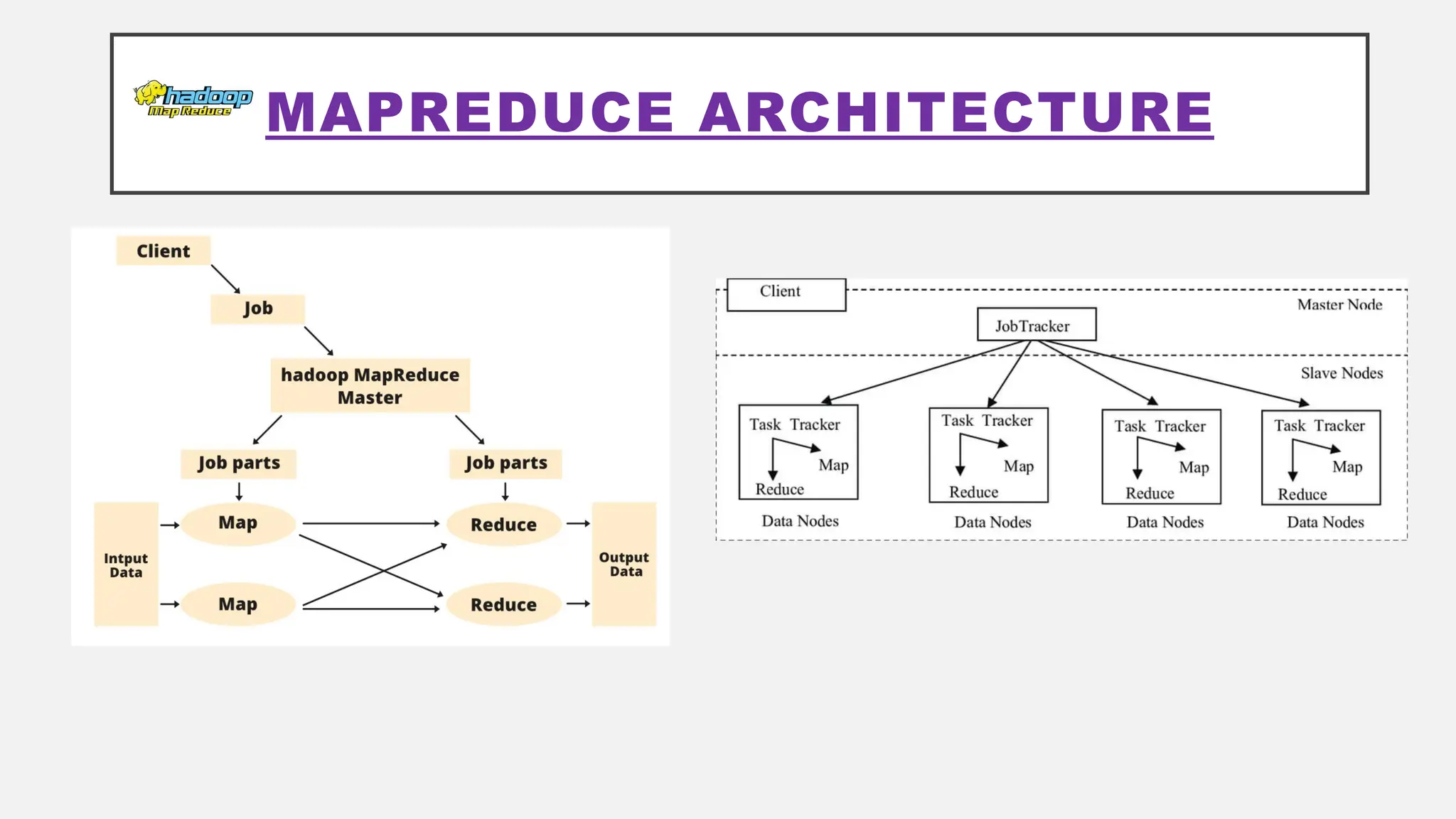
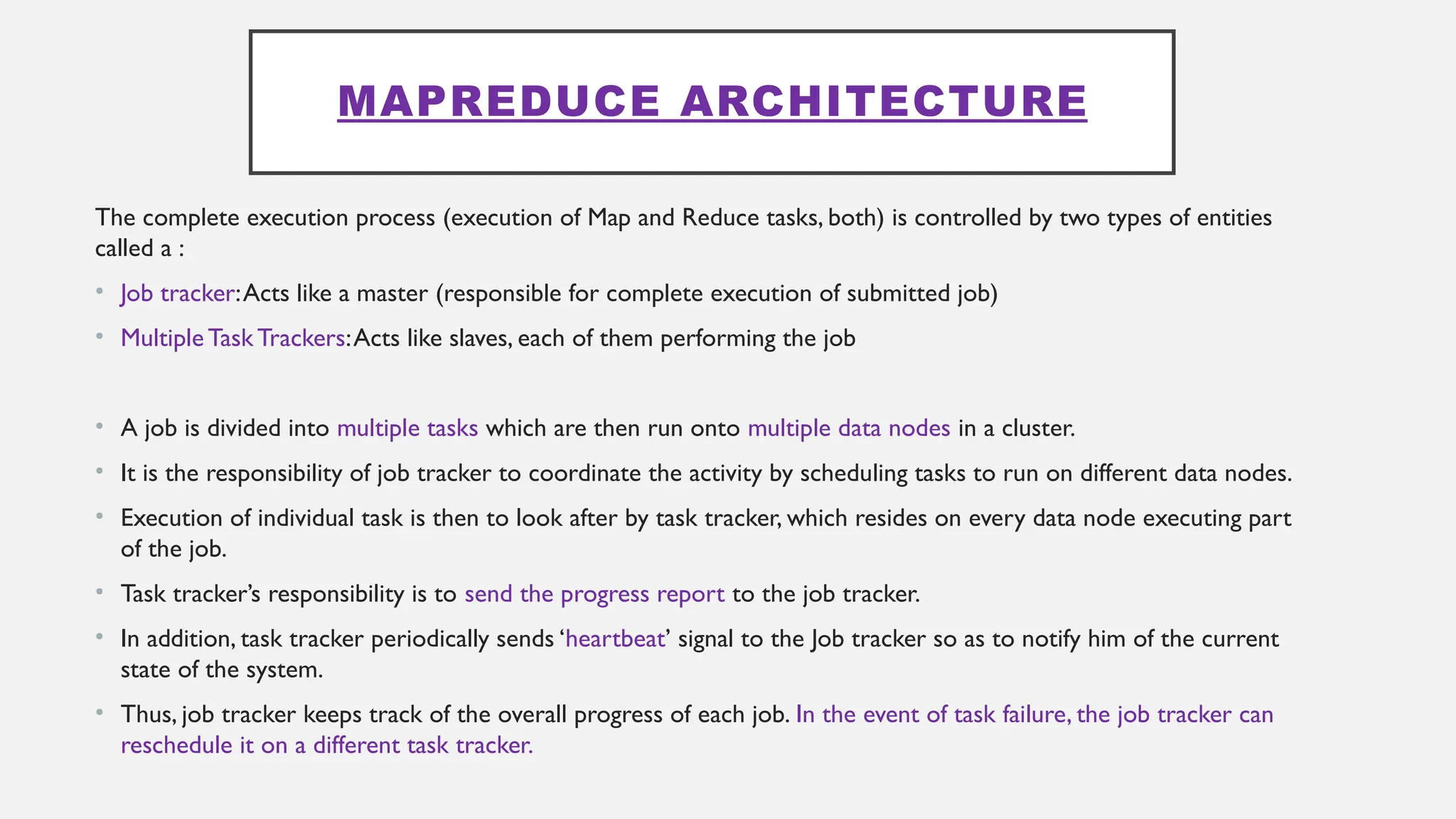
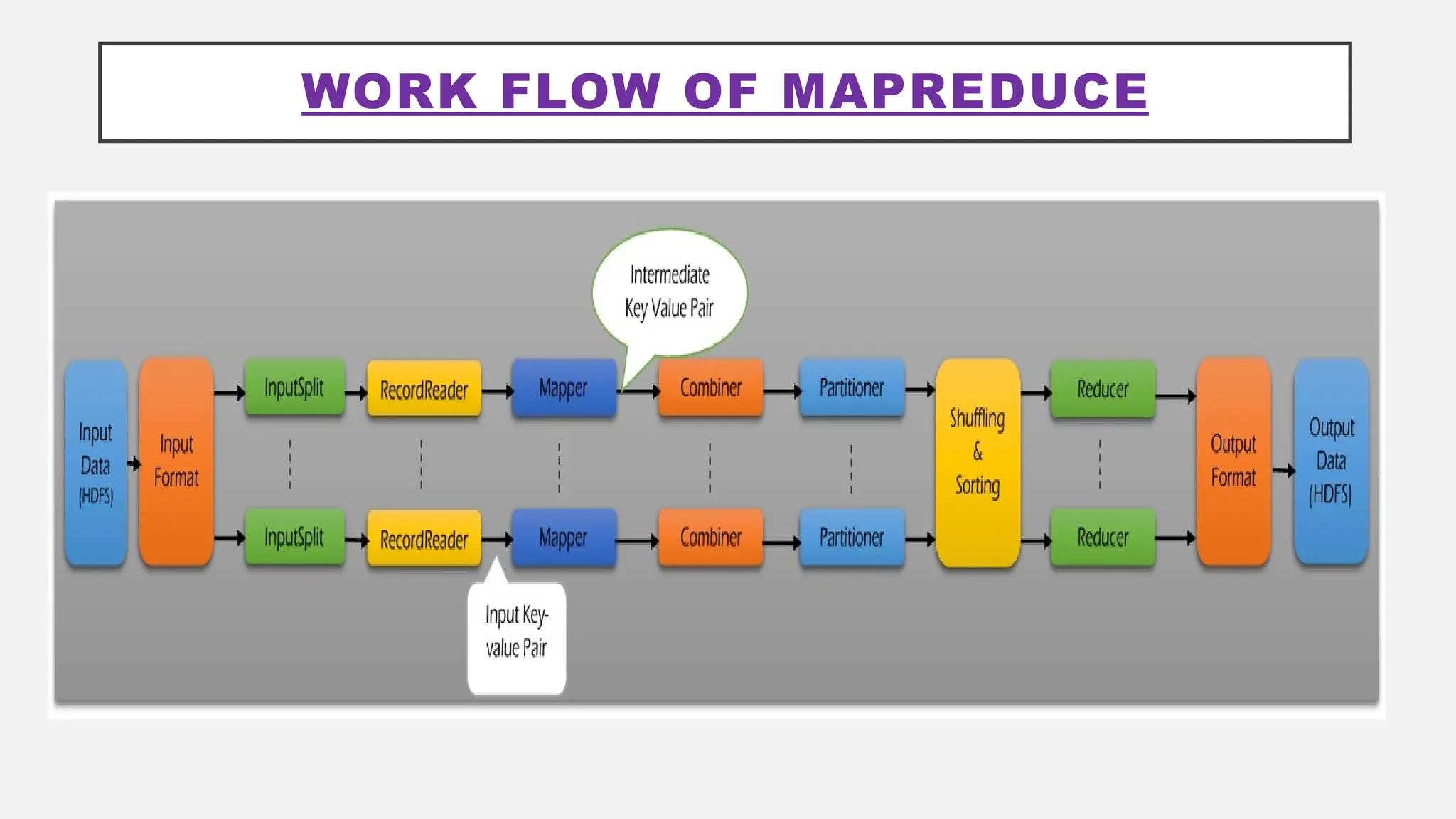
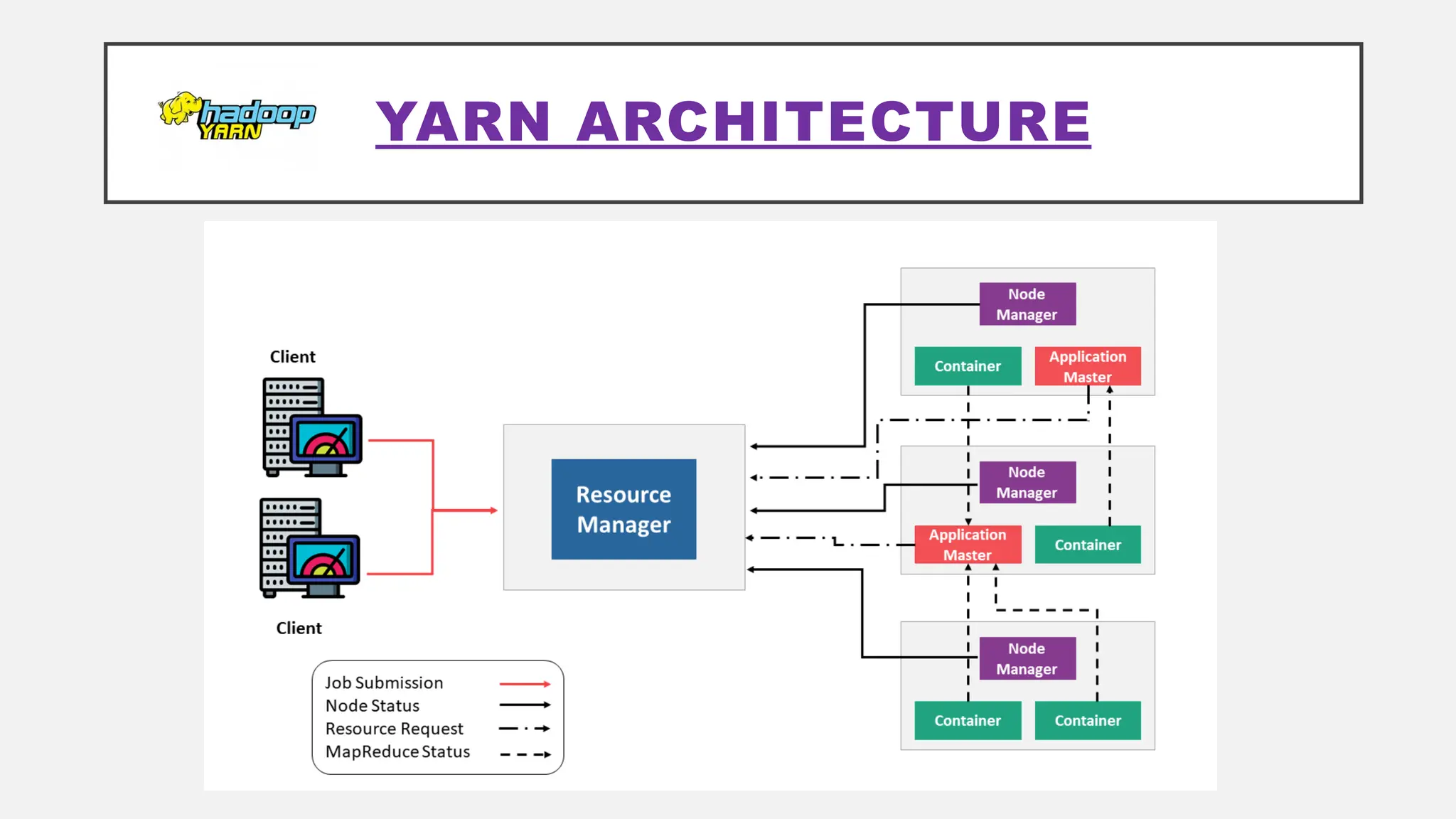
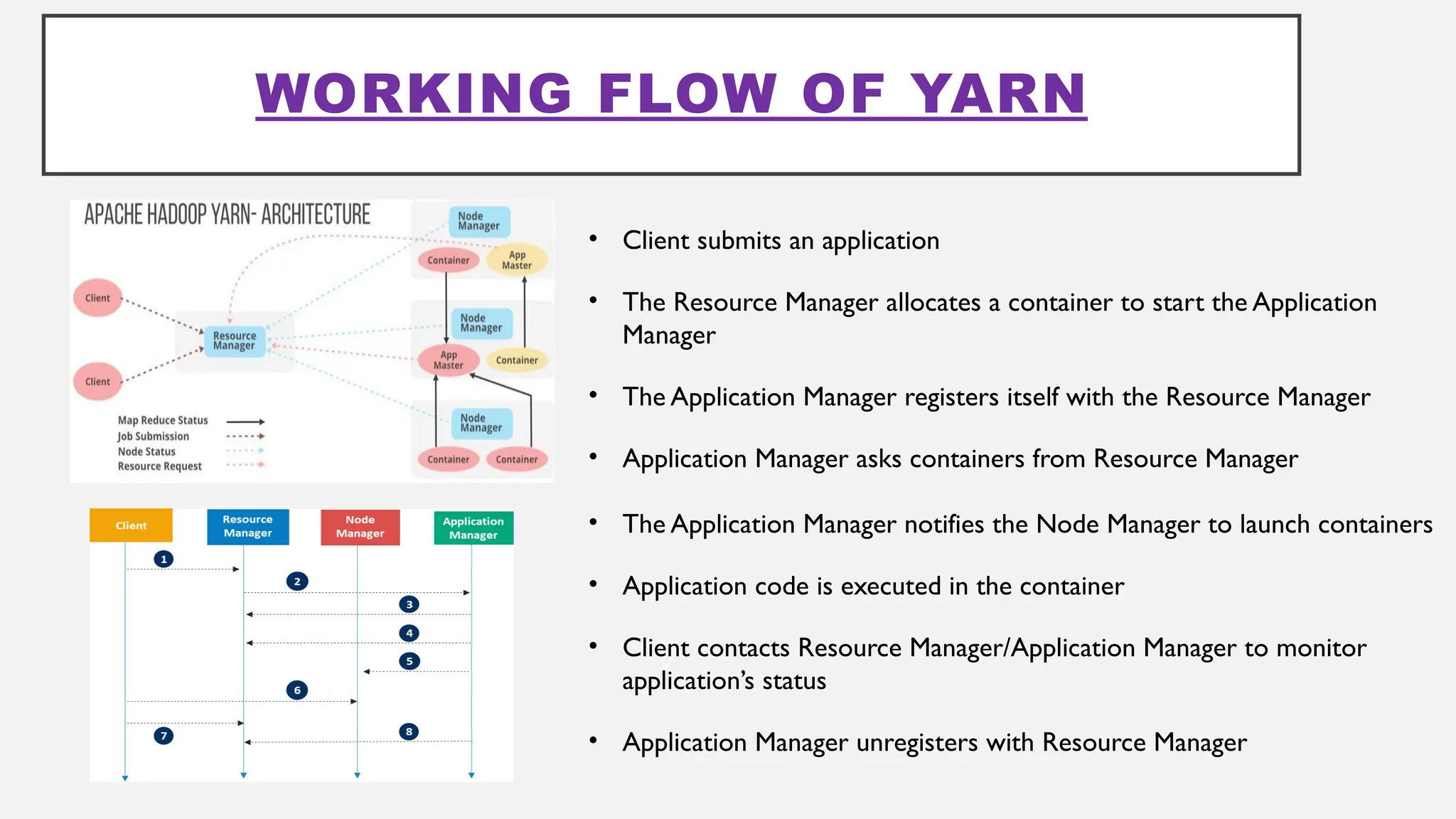
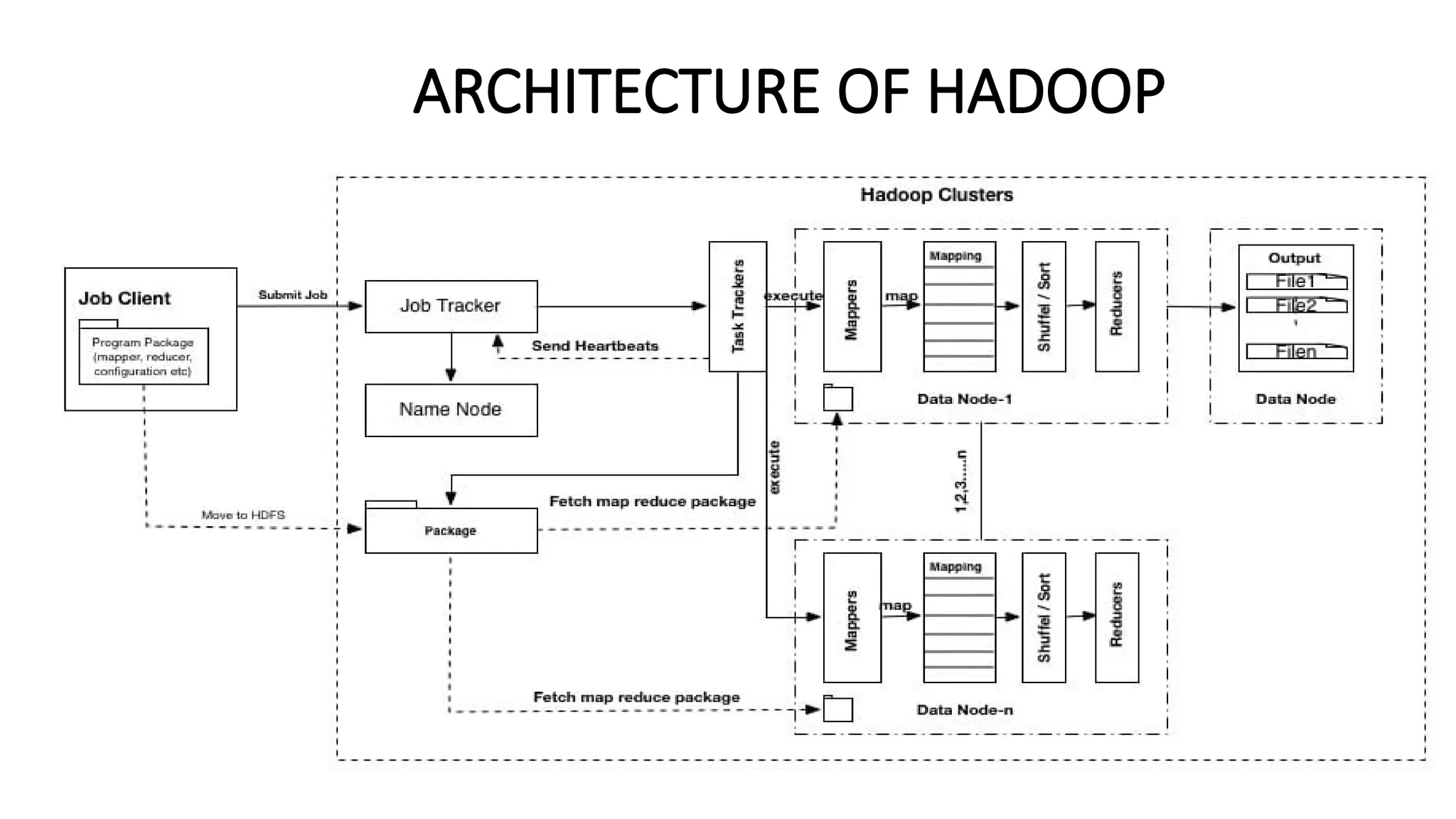
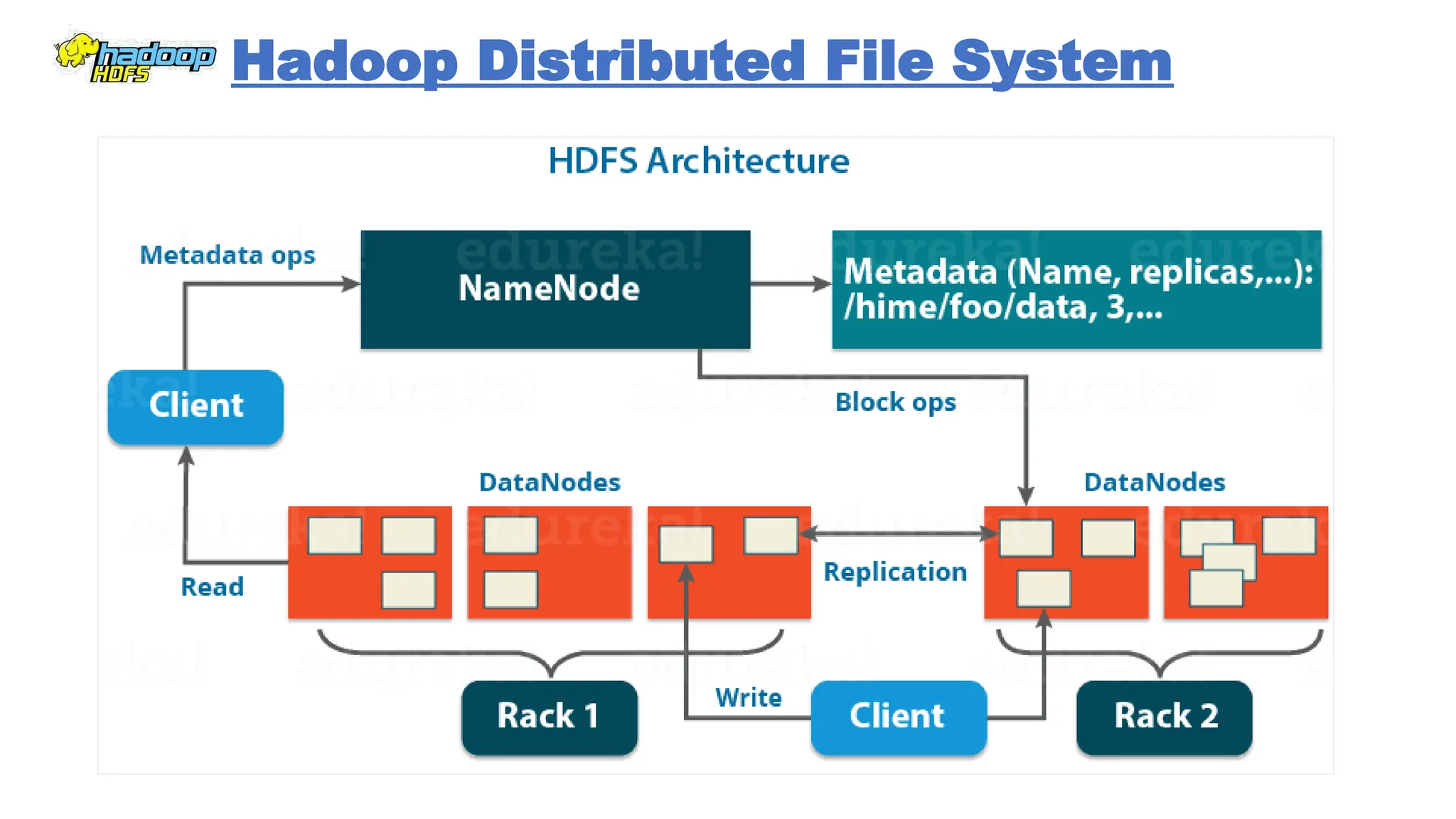
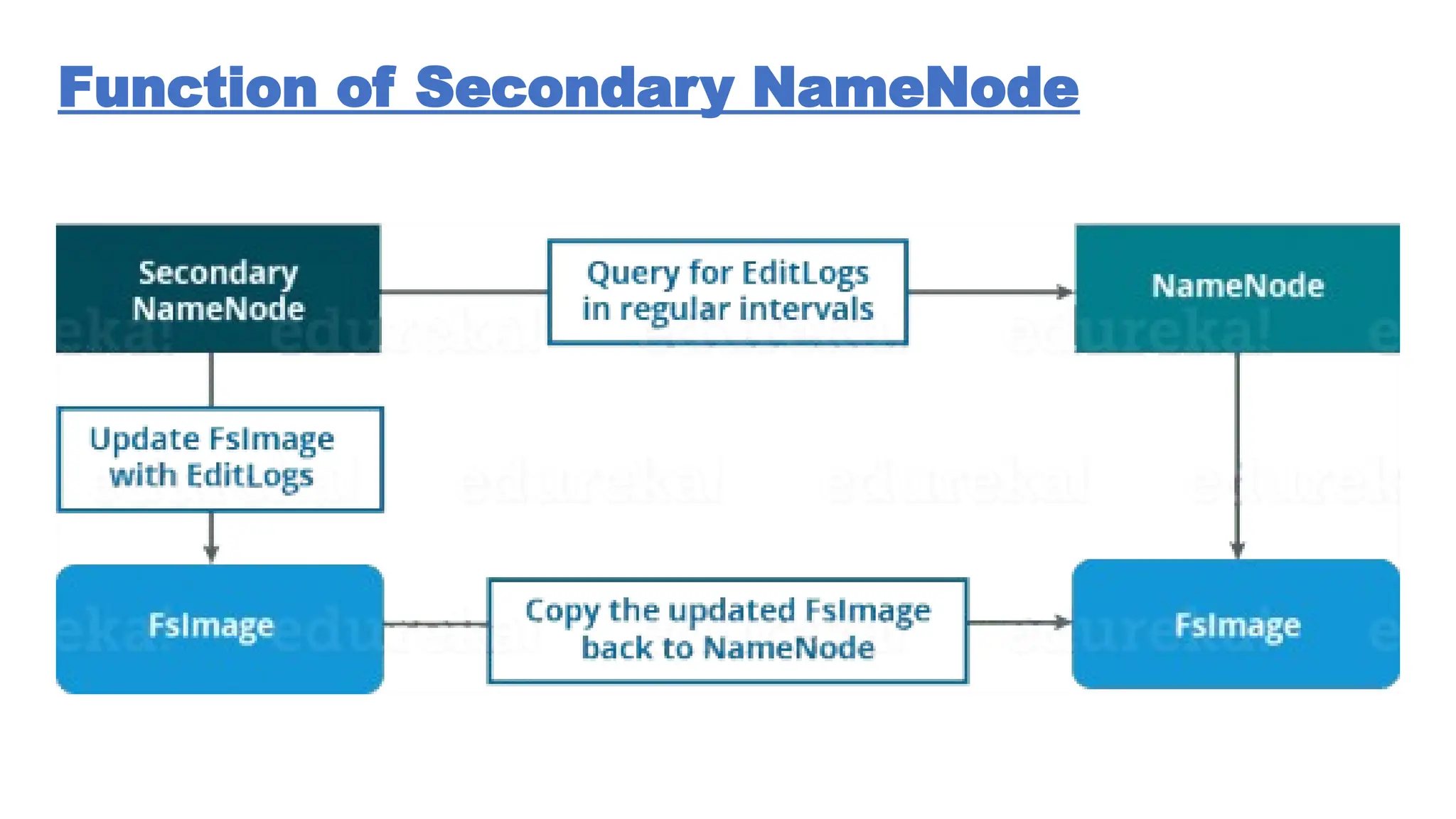
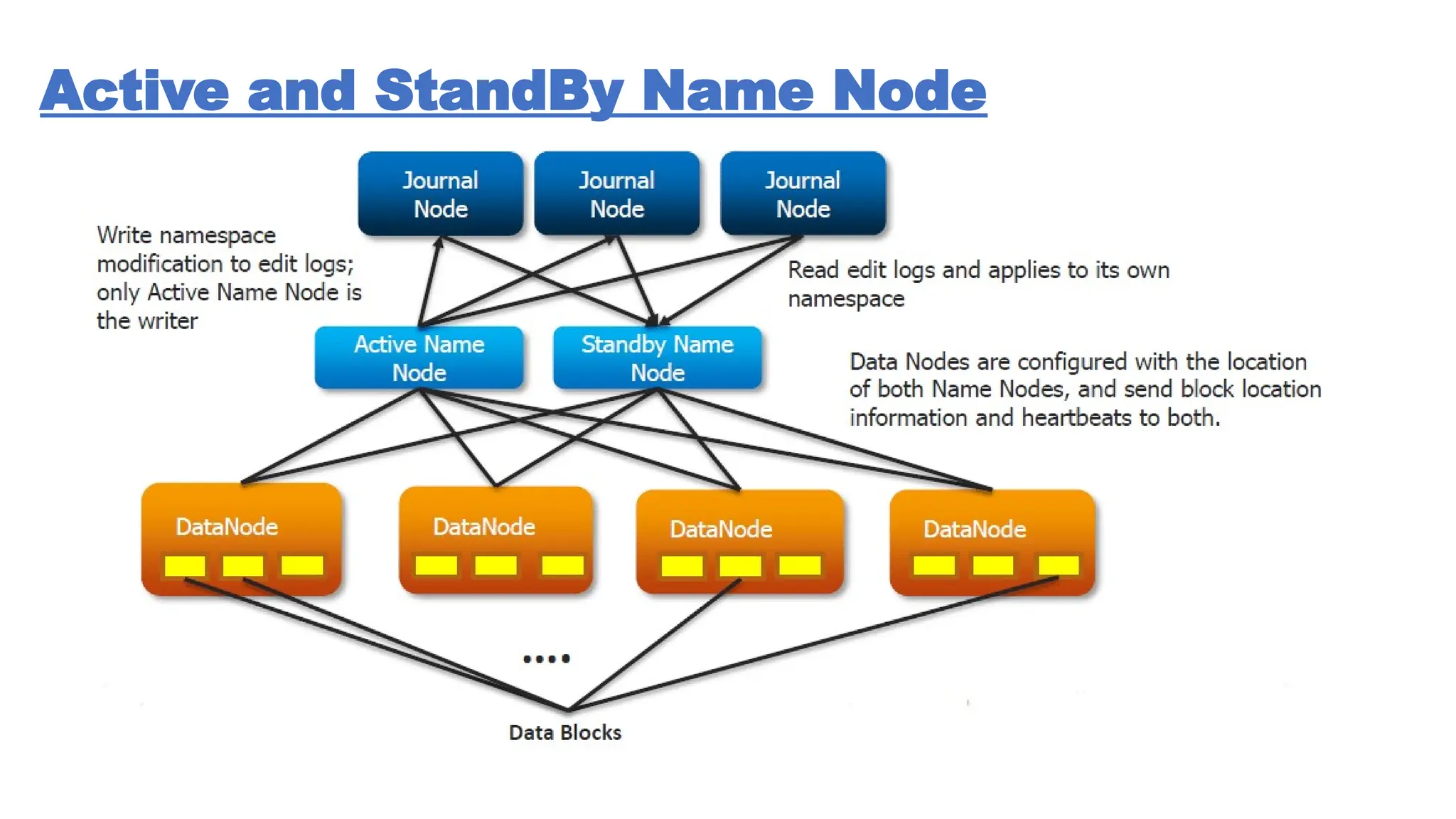
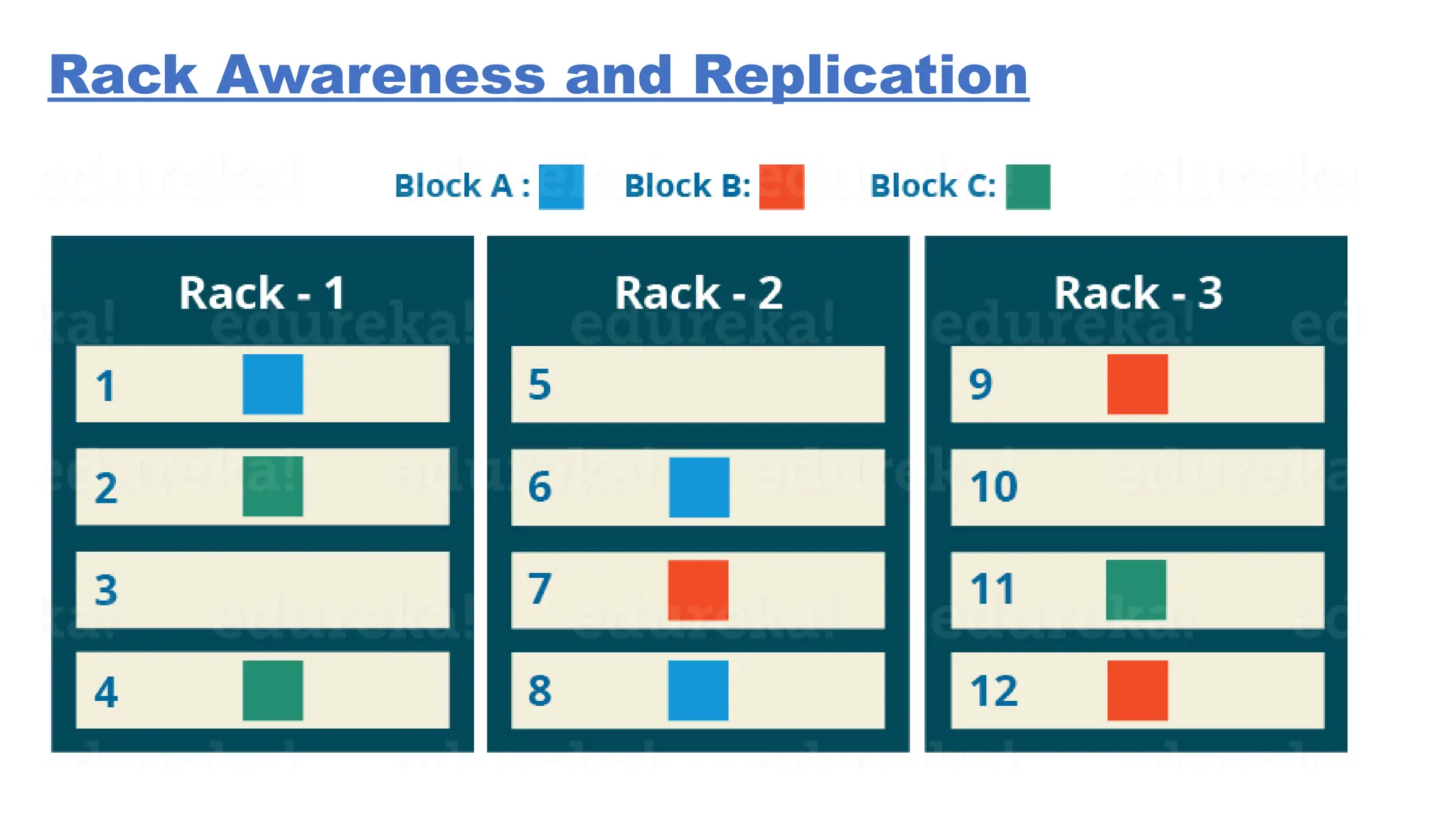
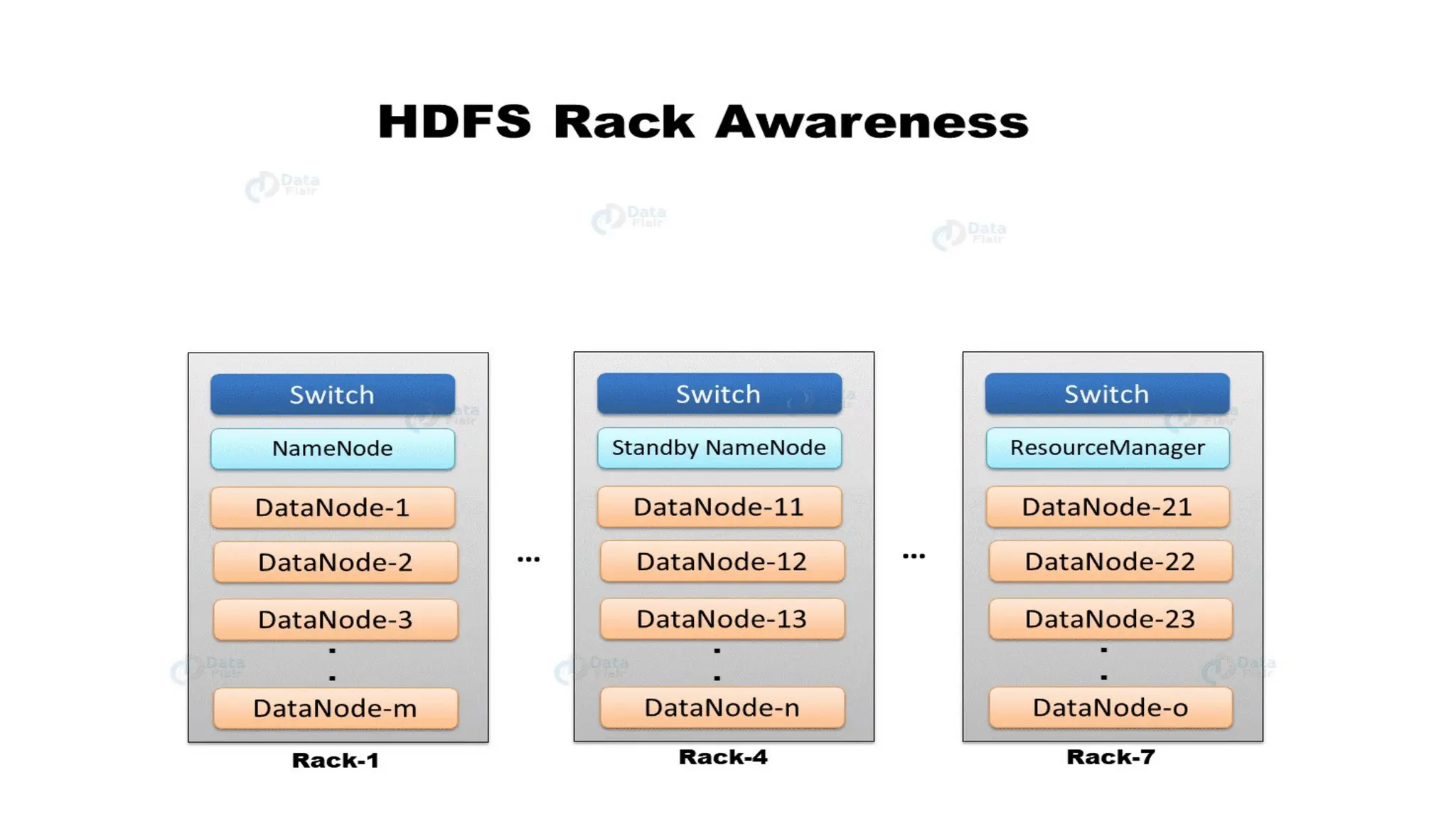
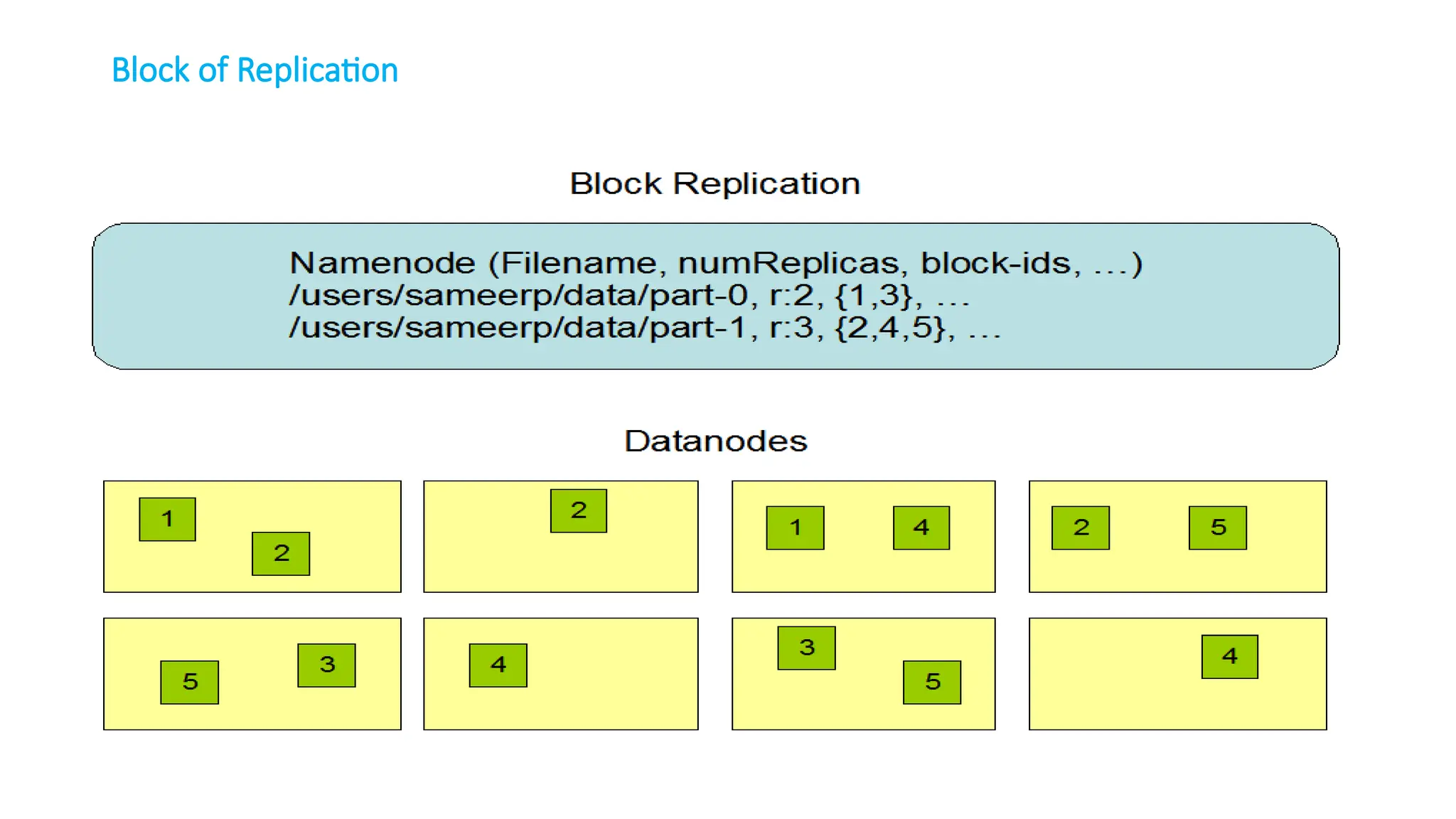
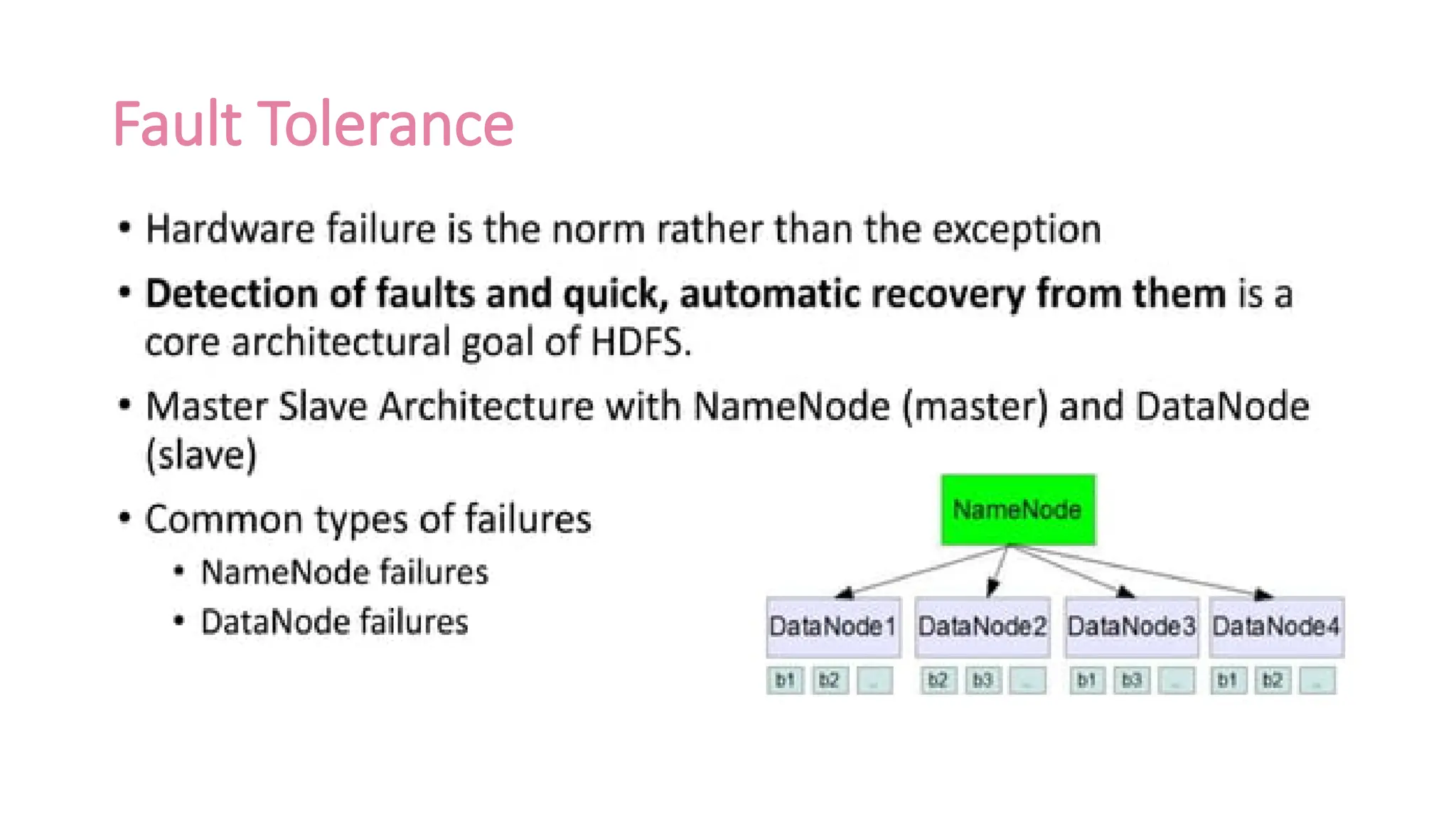
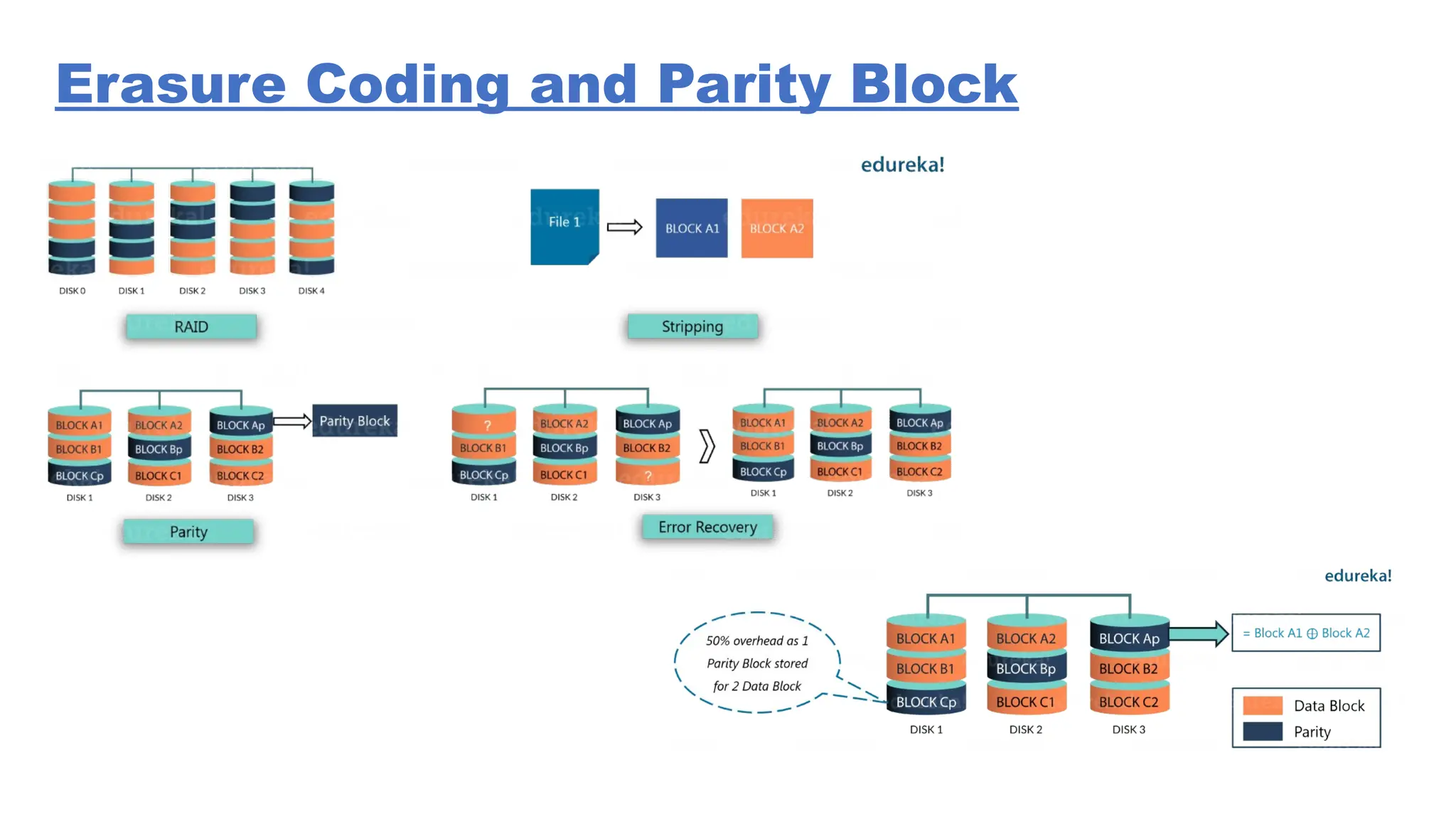
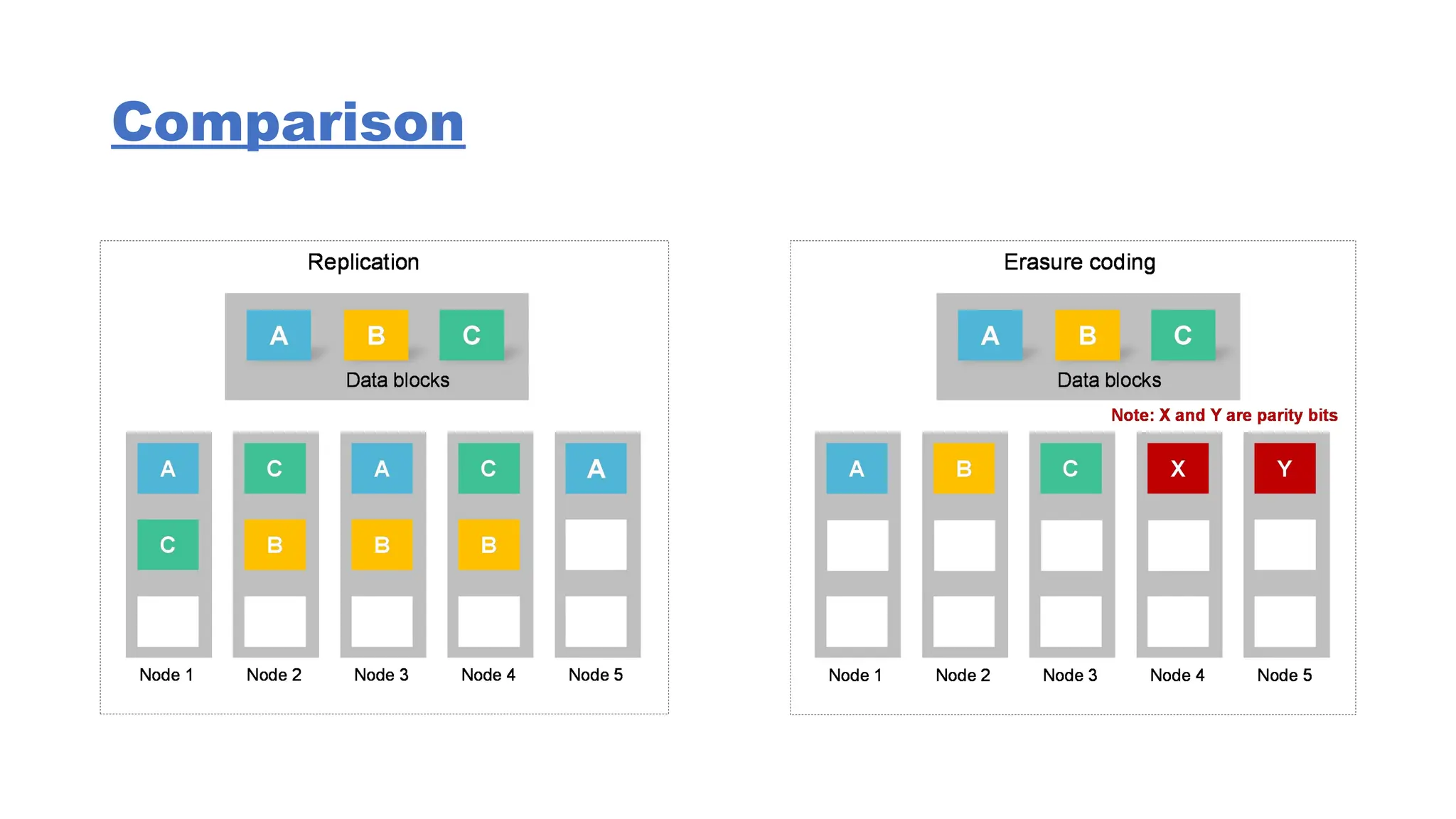
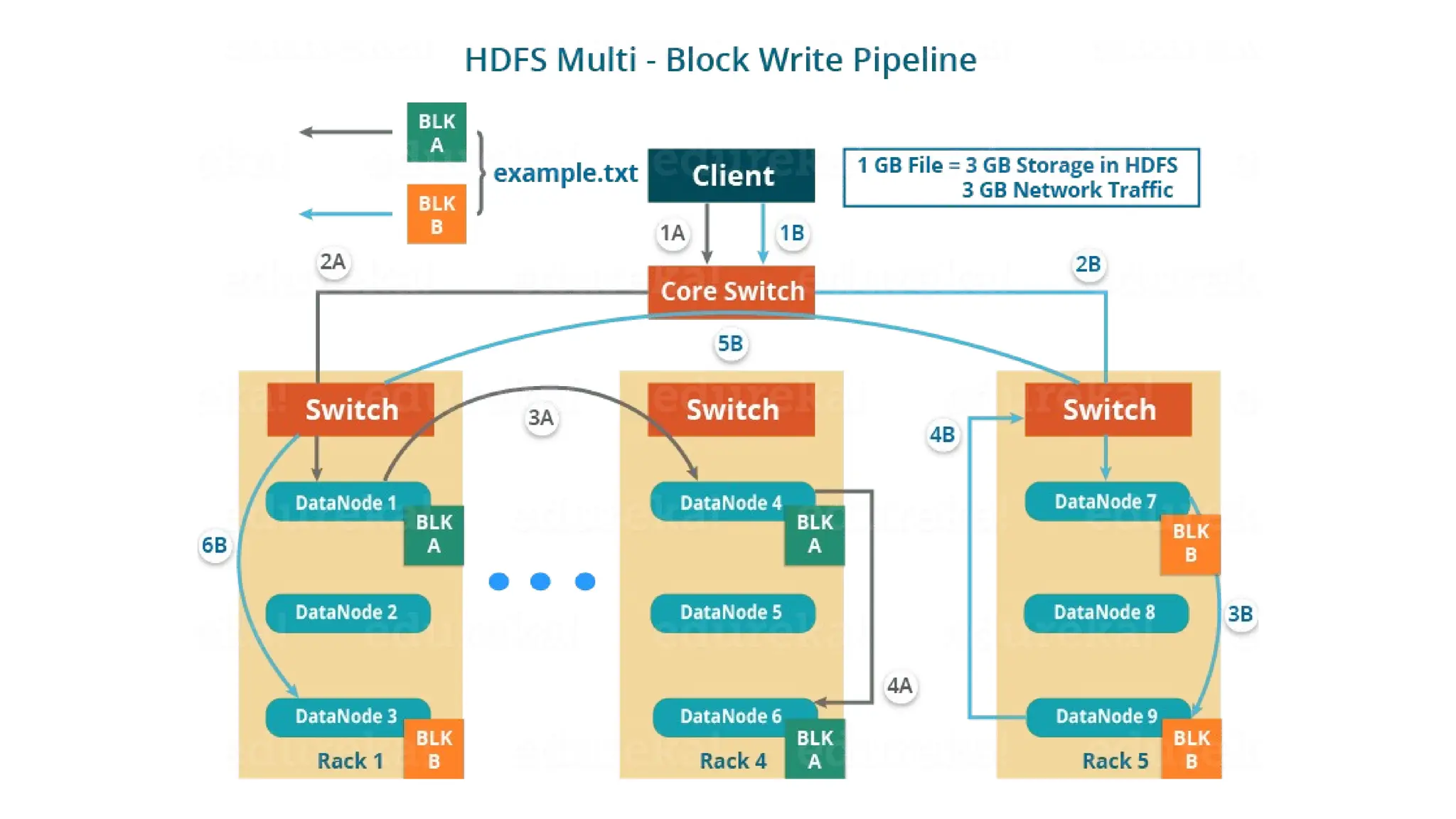
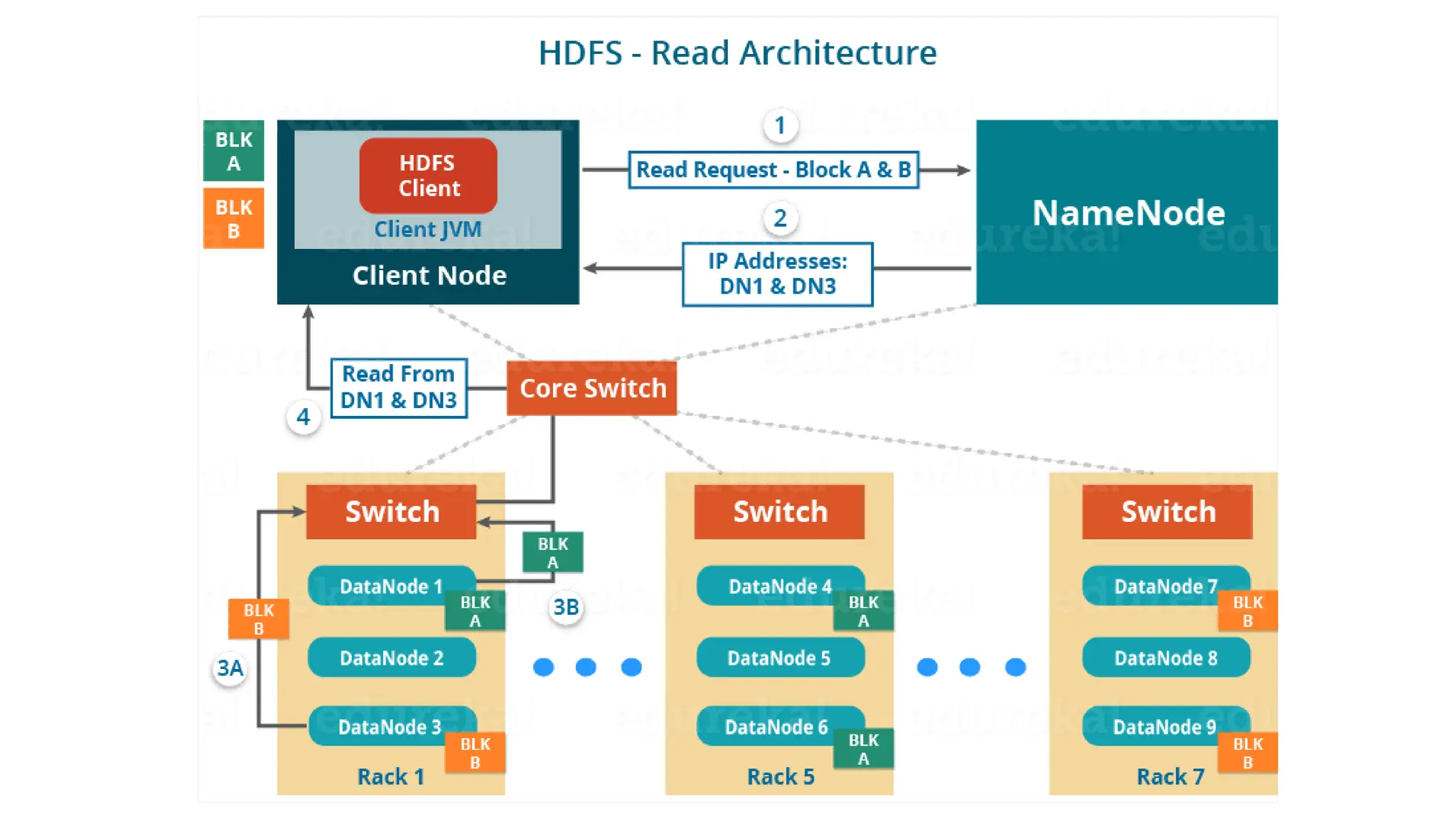
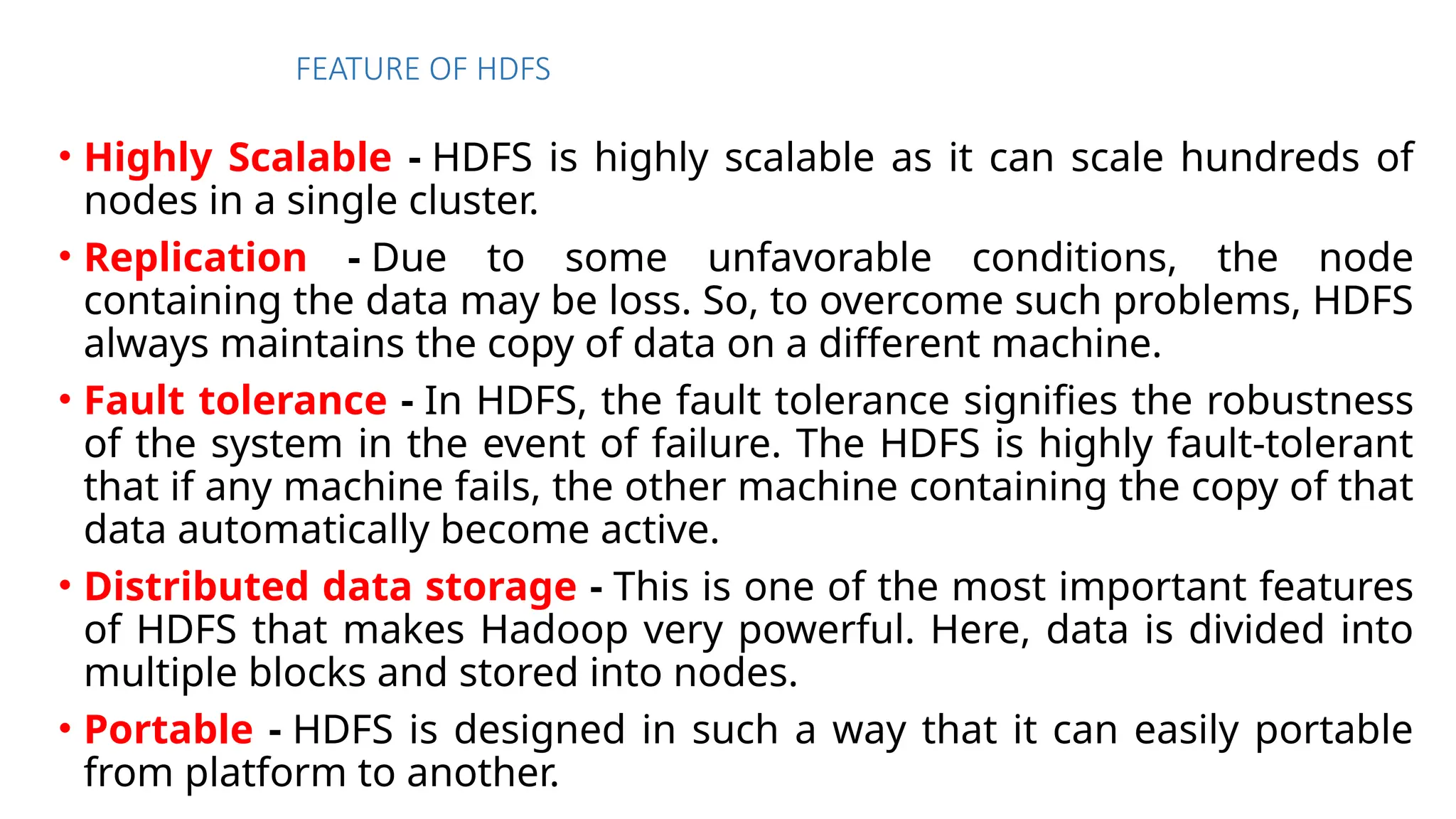
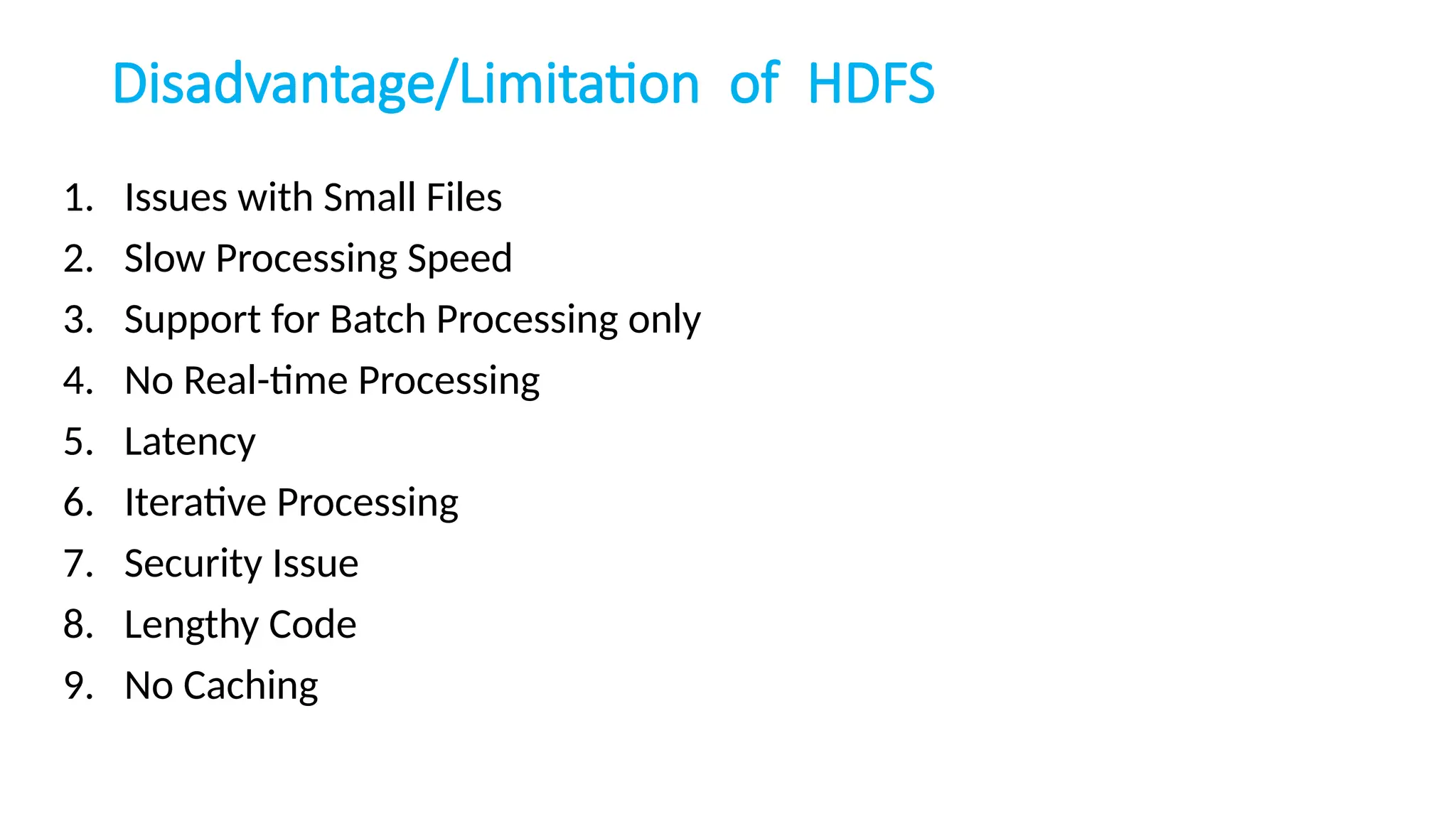
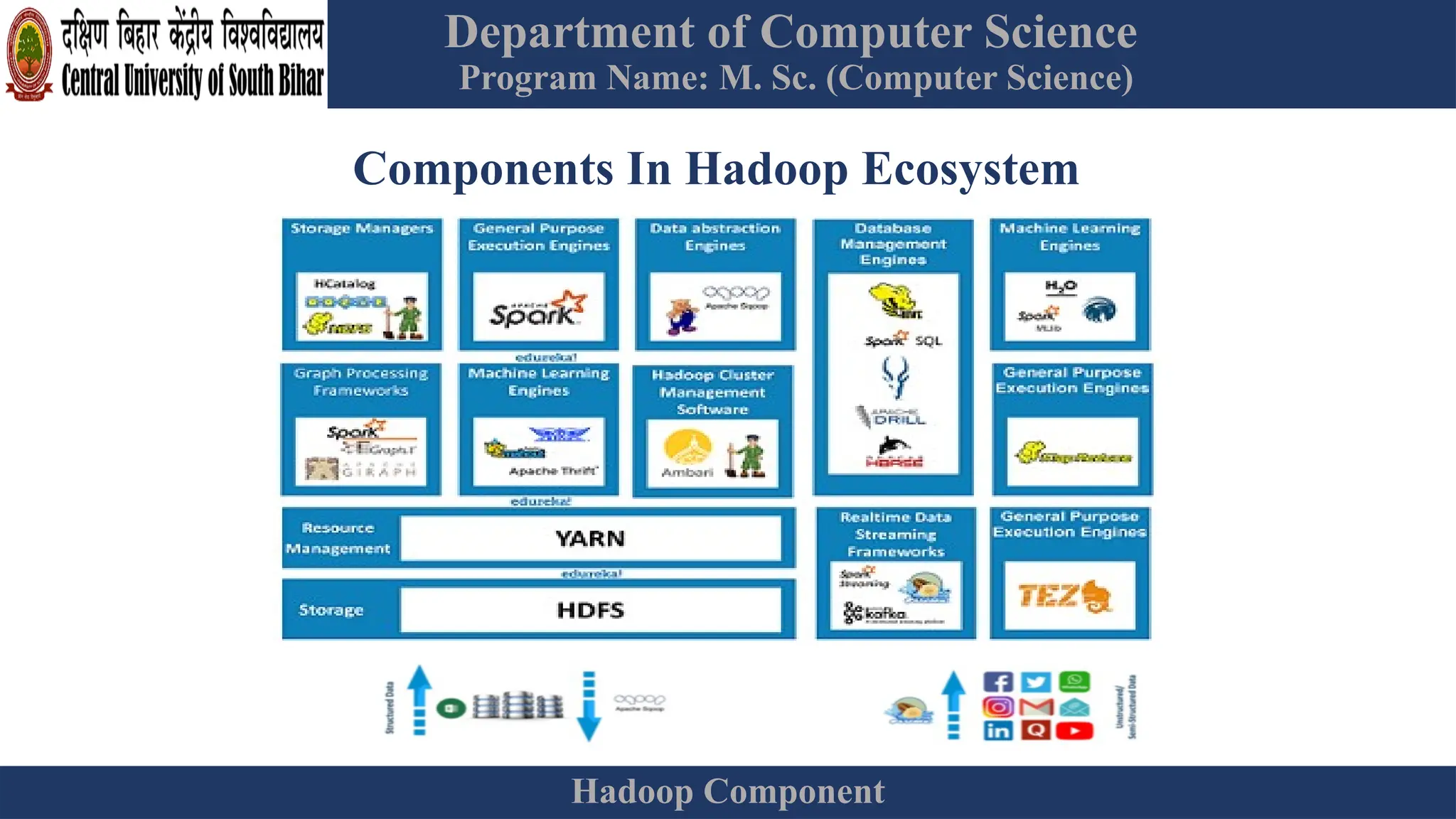
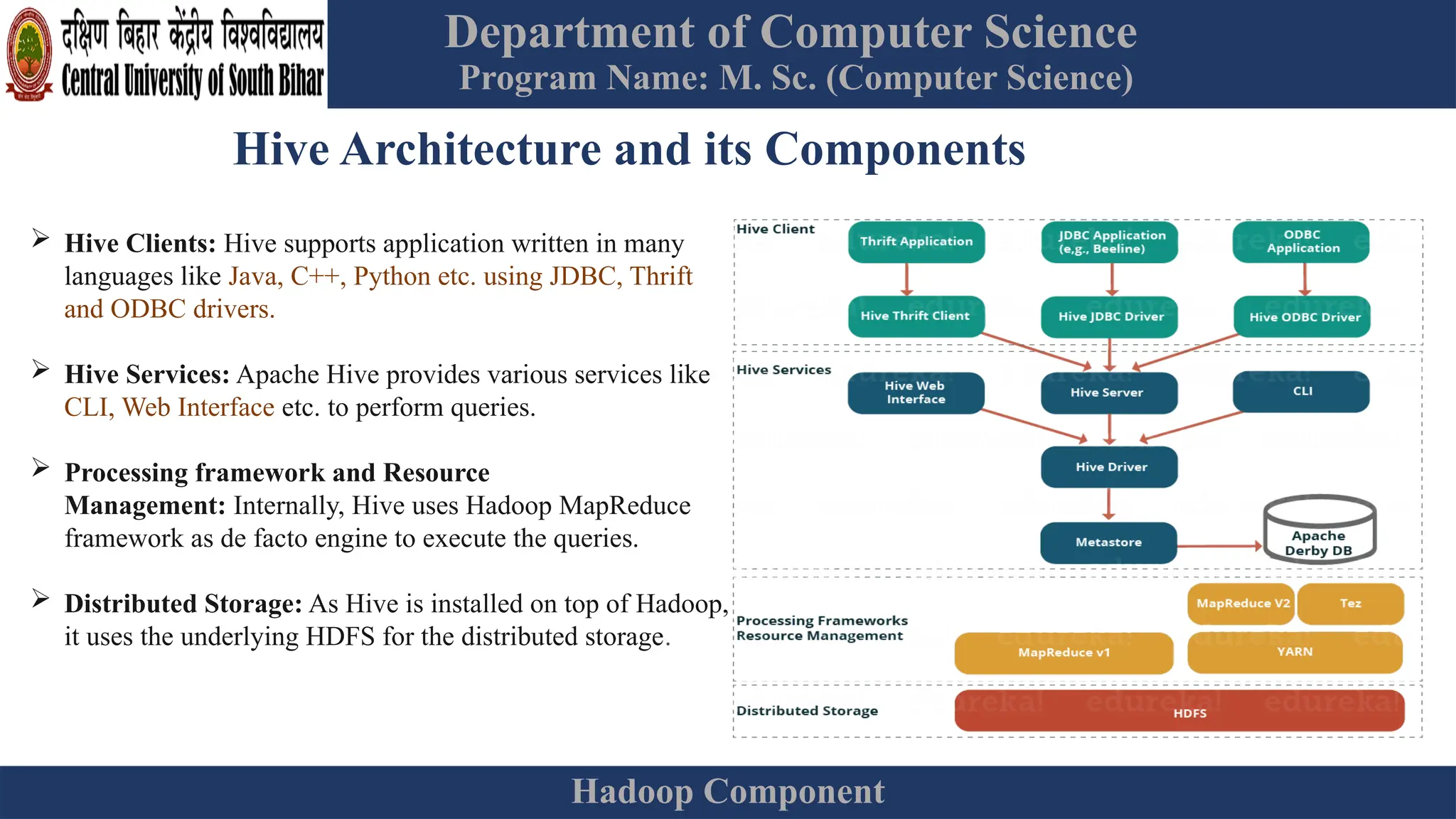
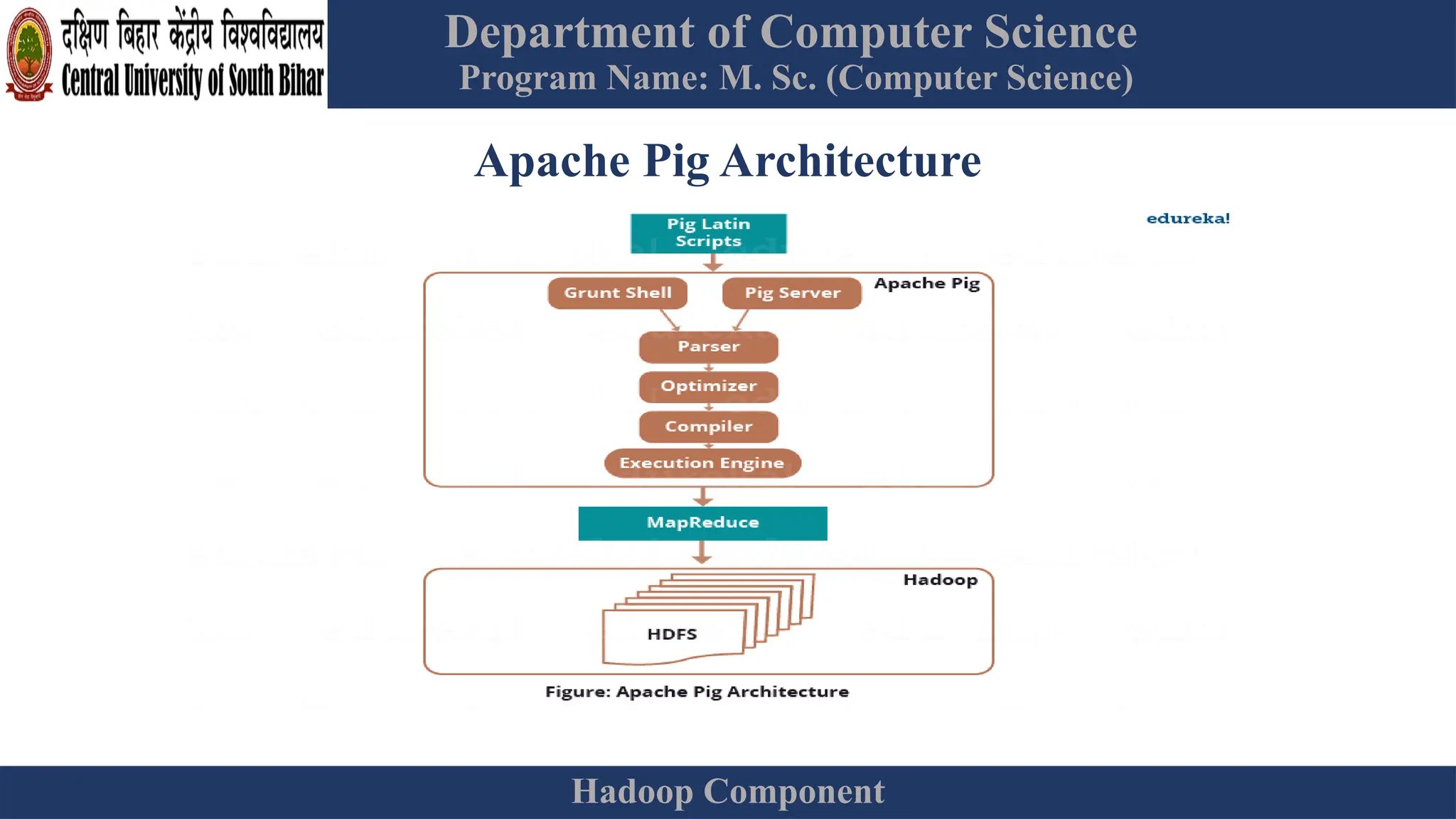
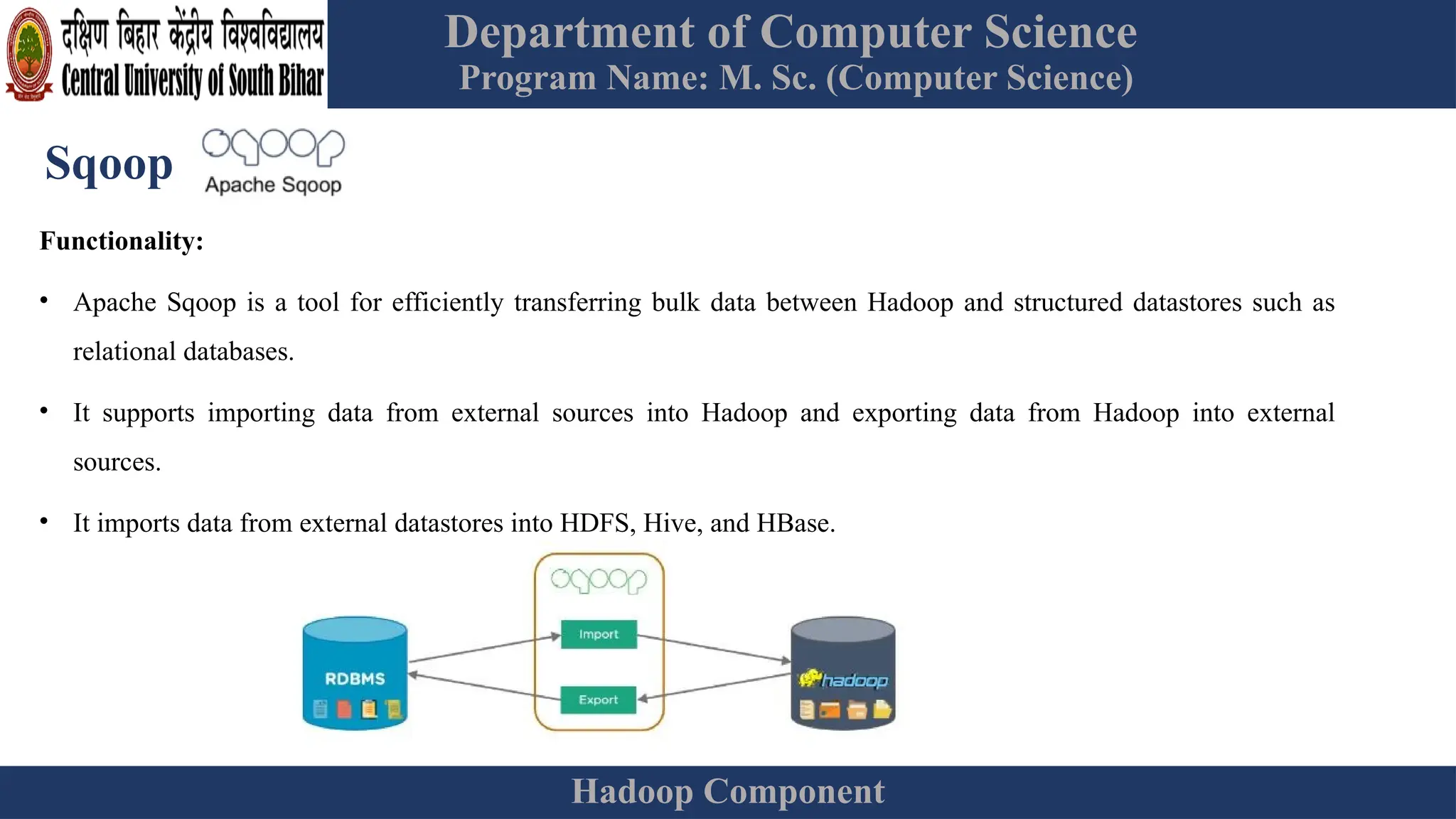
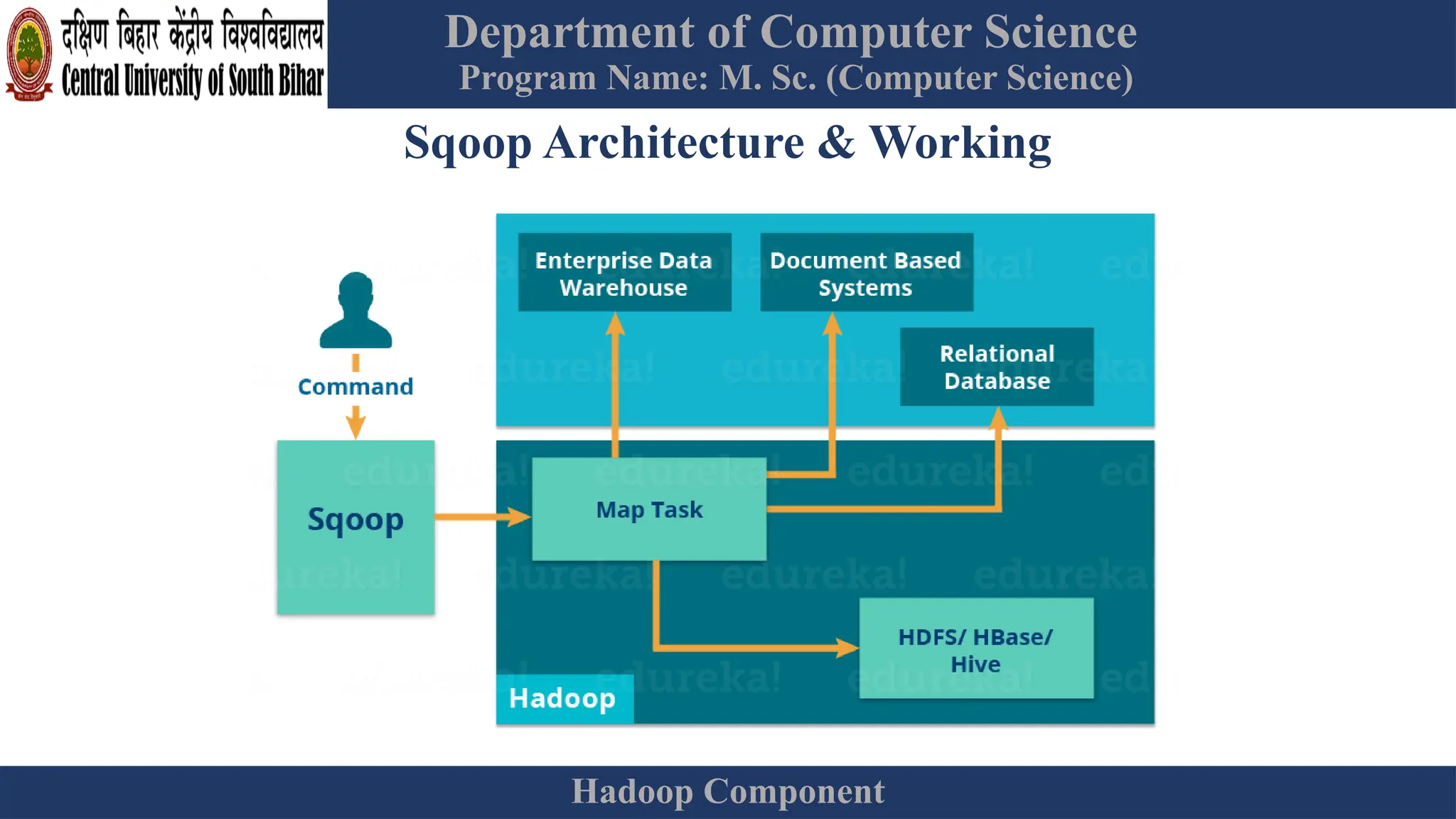
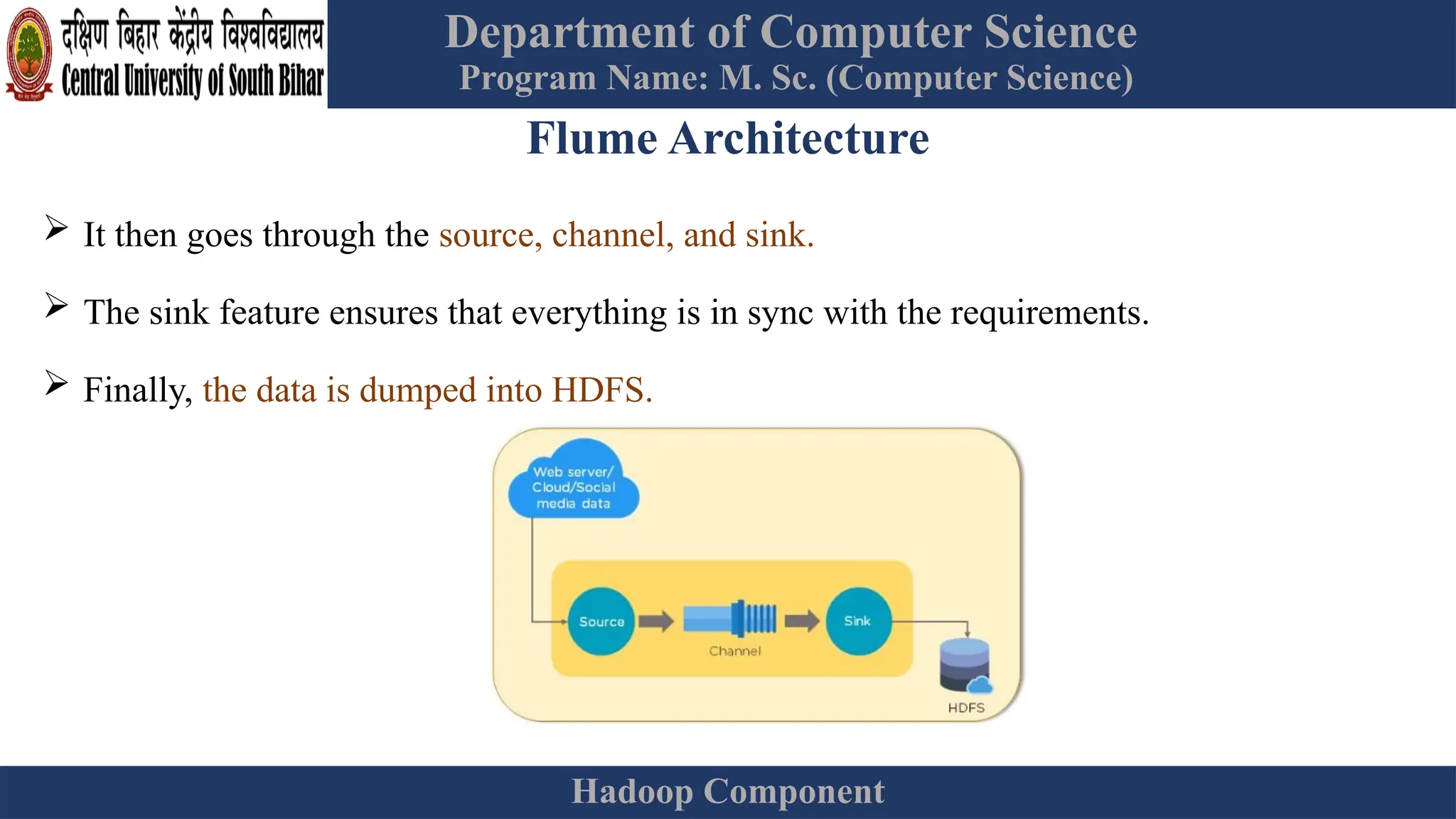
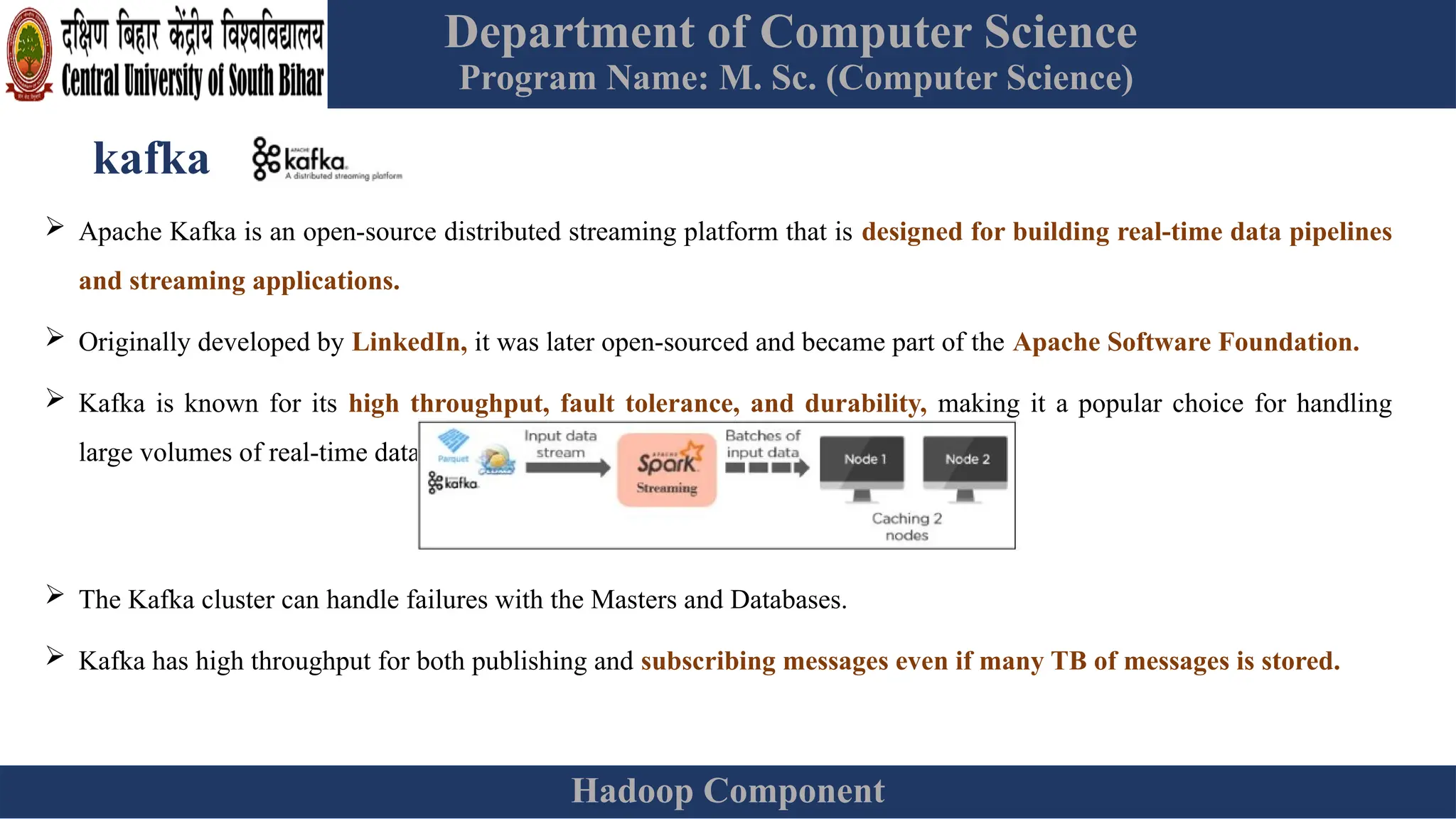
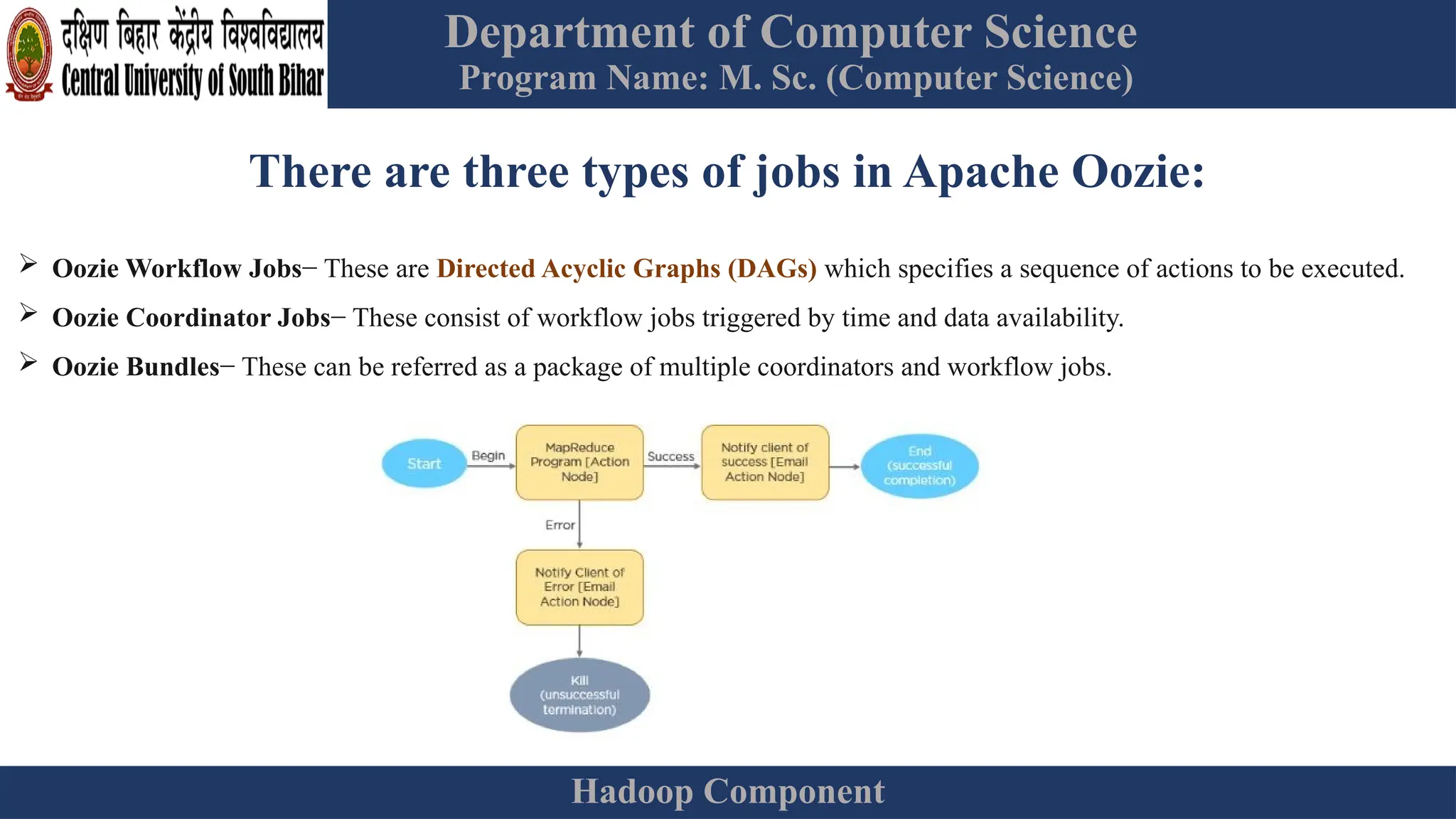
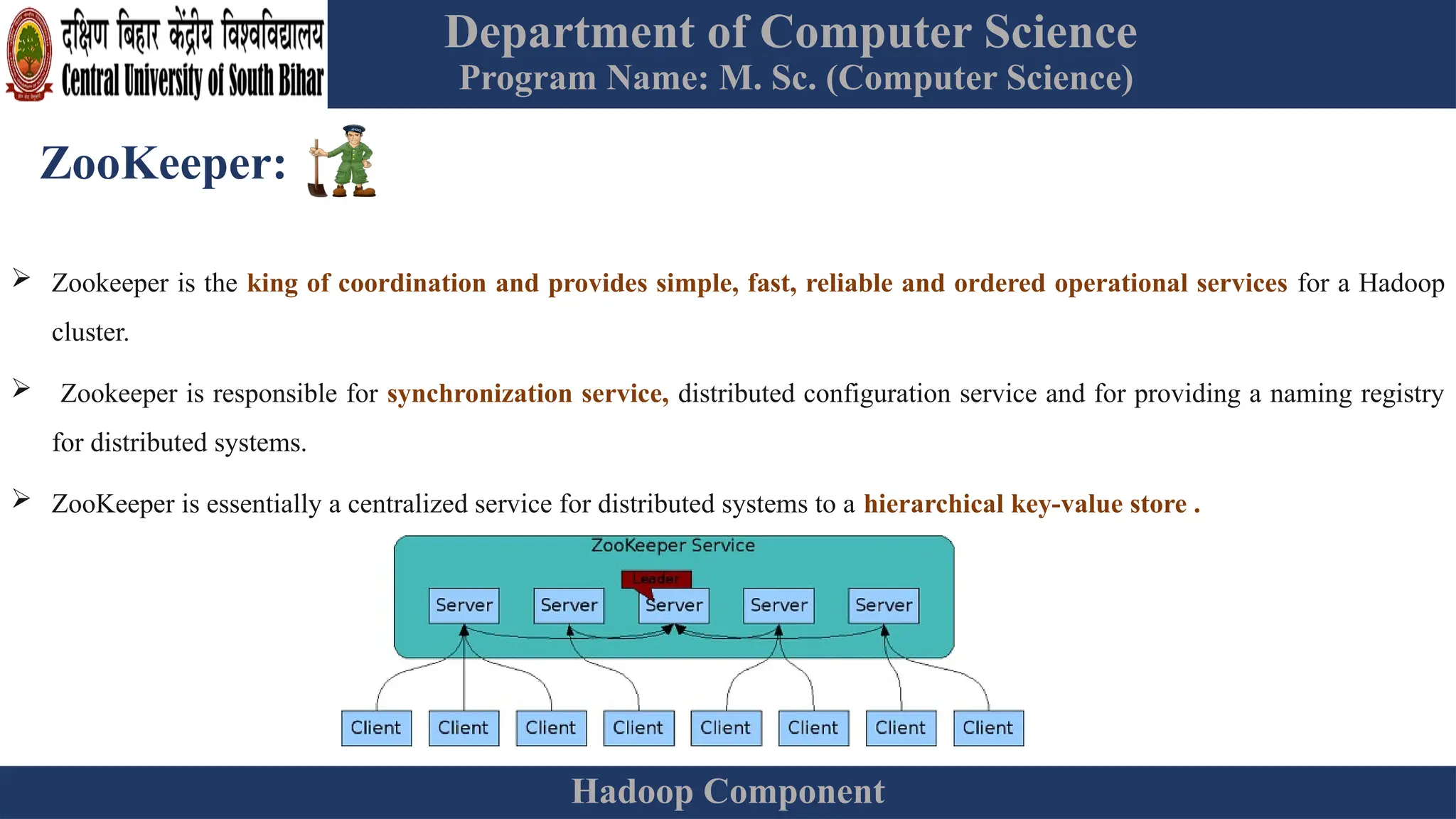
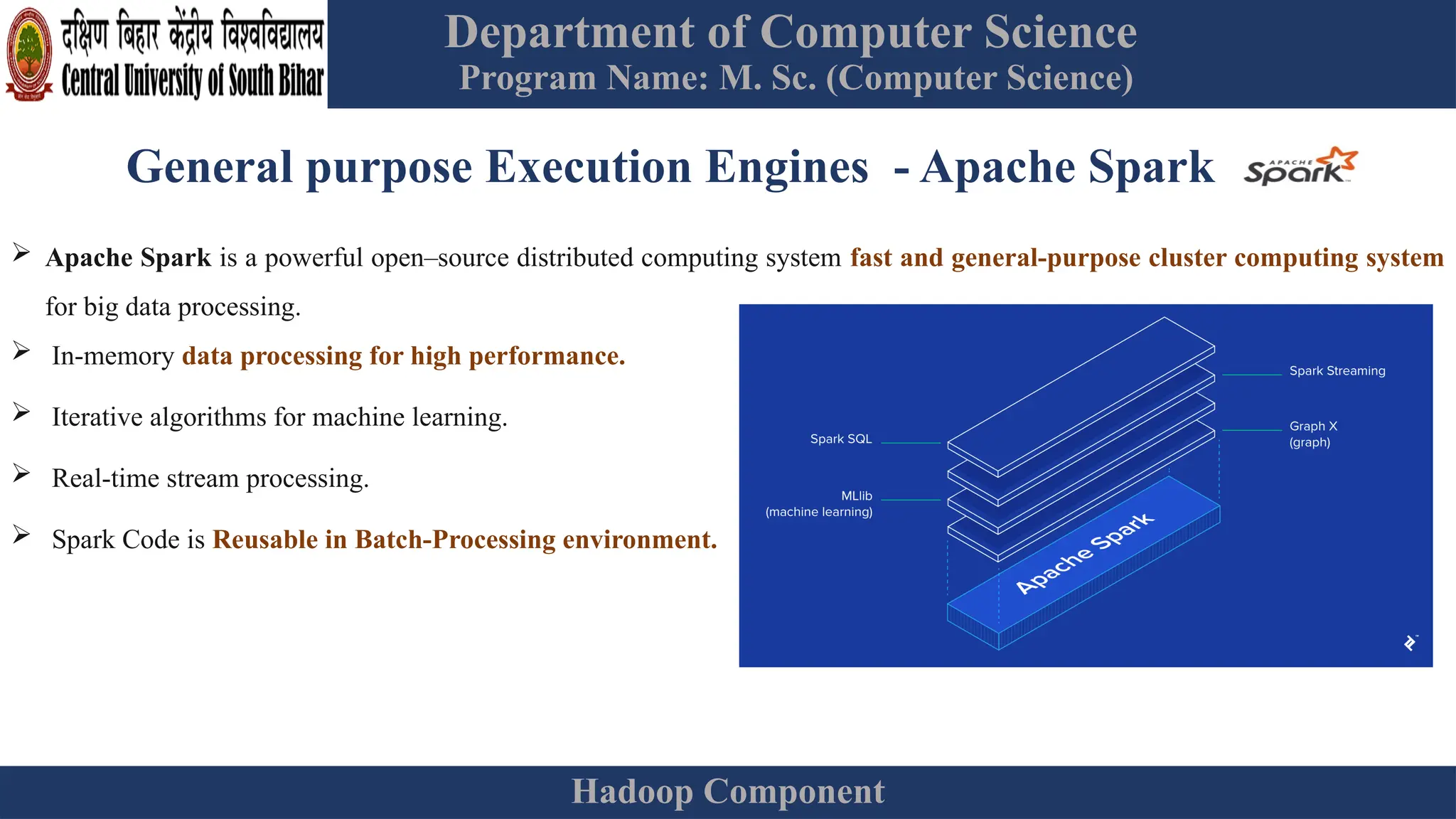
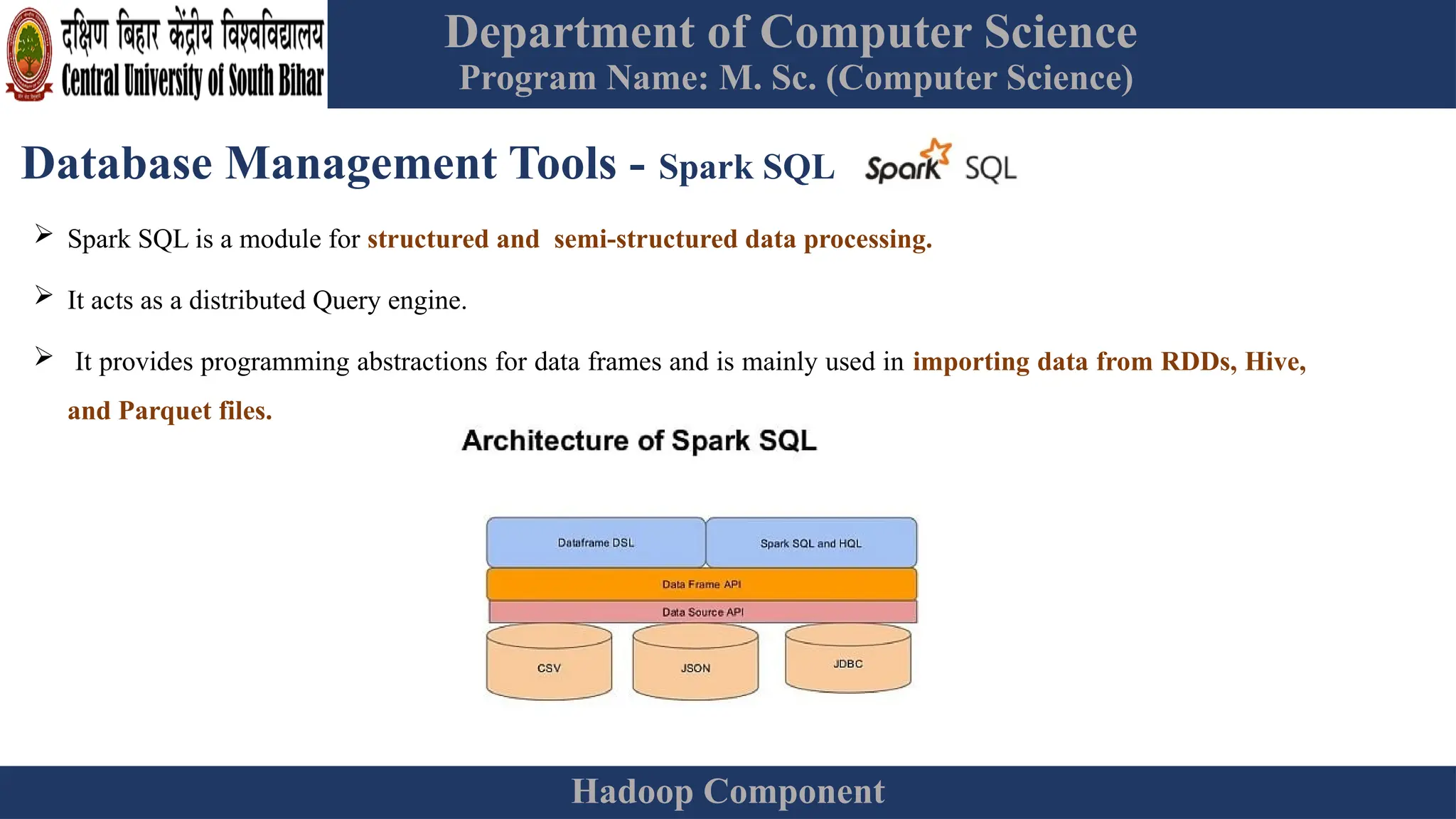
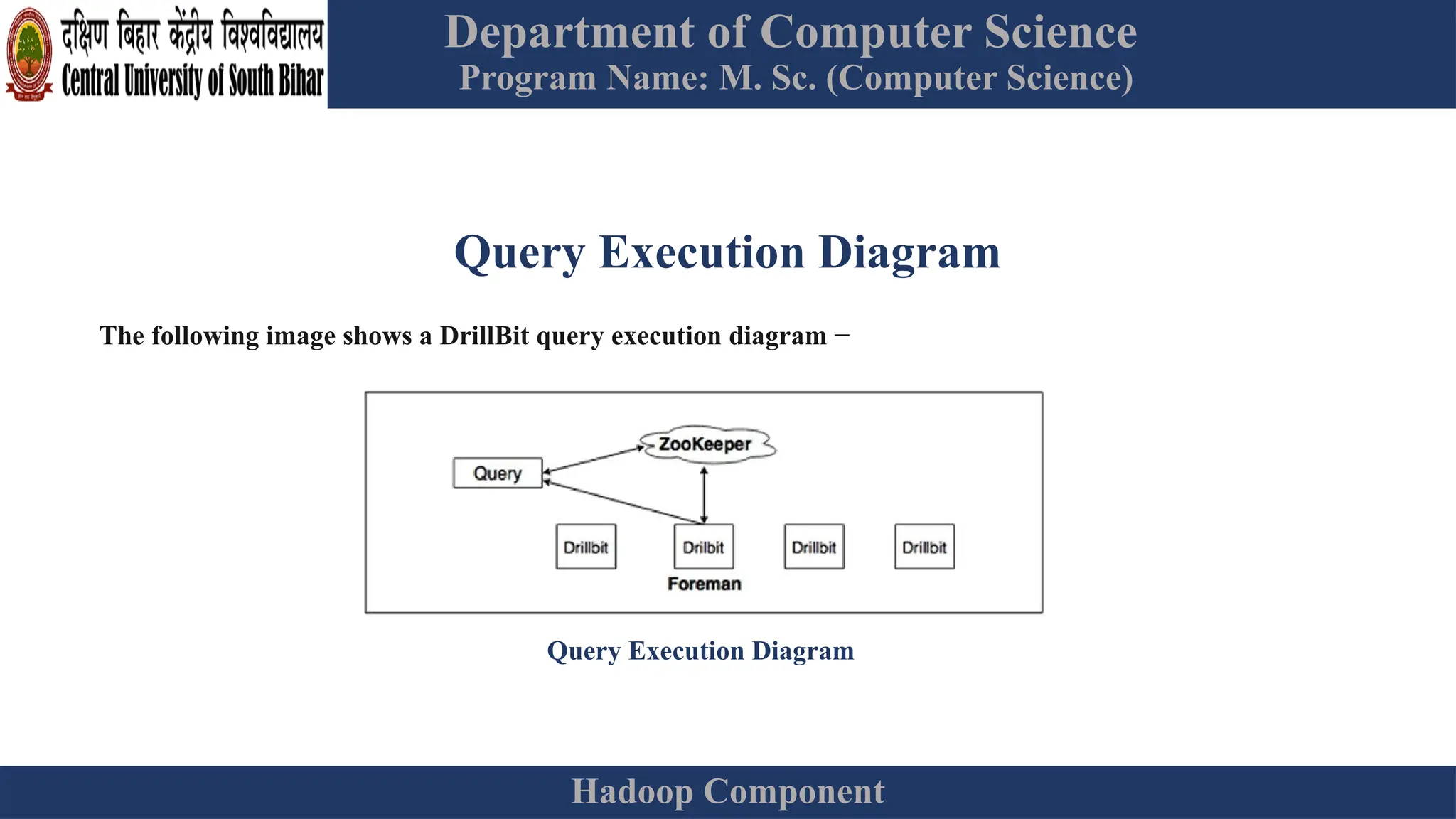
The document provides an overview of Hadoop 3.3.6, detailing its components, including HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN, along with their architectures and functionalities. It highlights the workflow of data processing in Hadoop, the advantages and disadvantages of HDFS, and describes essential tools like Apache Hive, Pig, Sqoop, Flume, and Kafka that enhance data management and processing capabilities. Furthermore, it elaborates on the significance of YARN in managing resources and the importance of fault tolerance and scalability within the Hadoop ecosystem.