Embed presentation
Download to read offline


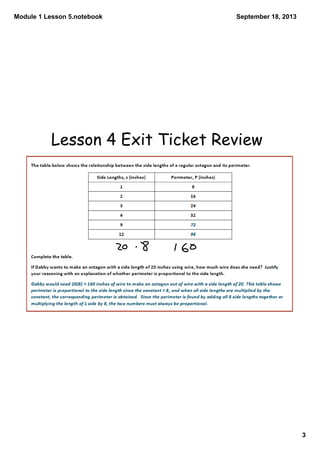

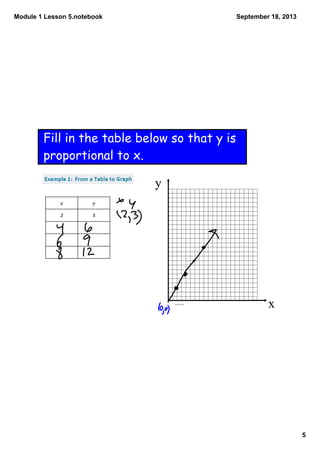
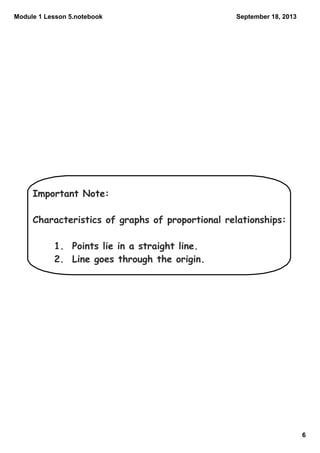
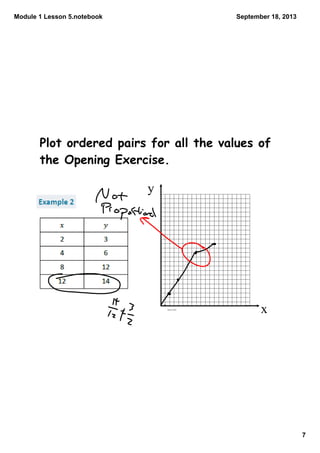
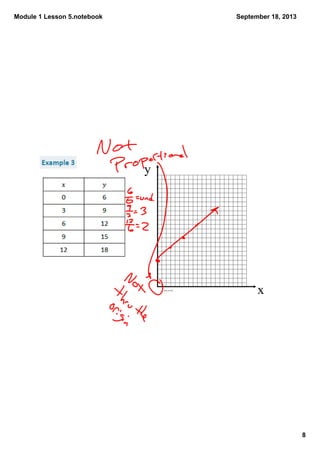
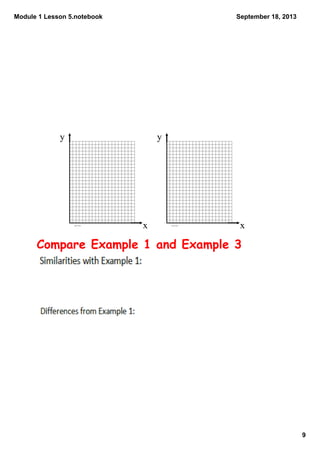

This document contains notes from a math lesson on identifying proportional and non-proportional relationships in graphs. It includes examples of filling in tables with proportional values and plotting those points on a graph. It emphasizes that for quantities to be proportional, their graph must be a straight line passing through the origin. The closing questions review that proportional relationships are represented by graphs with points on a line through the origin, and that a common mistake is thinking quantities are proportional if their graph is a straight line but does not pass through the origin.










