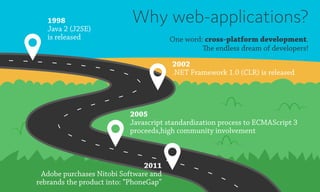
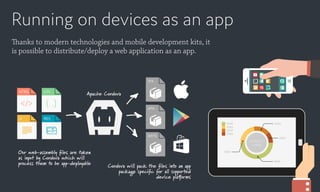
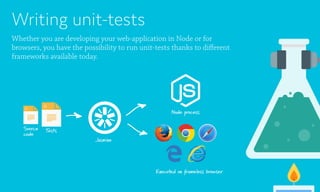
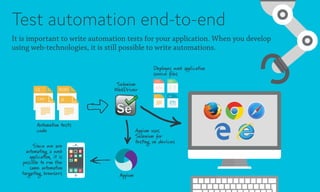
Web applications are software based on web technologies like HTML, JavaScript, and CSS that offer functionality similar to native applications. Languages that compile to JavaScript and CSS can help make codebases more maintainable by adding features like types, object-oriented programming, and variables. Web applications can be distributed both as websites running in browsers and as mobile/desktop apps by using technologies like Node.js and Cordova. Testing and automation of web applications is also possible using frameworks like Jasmine, Selenium, and Appium.