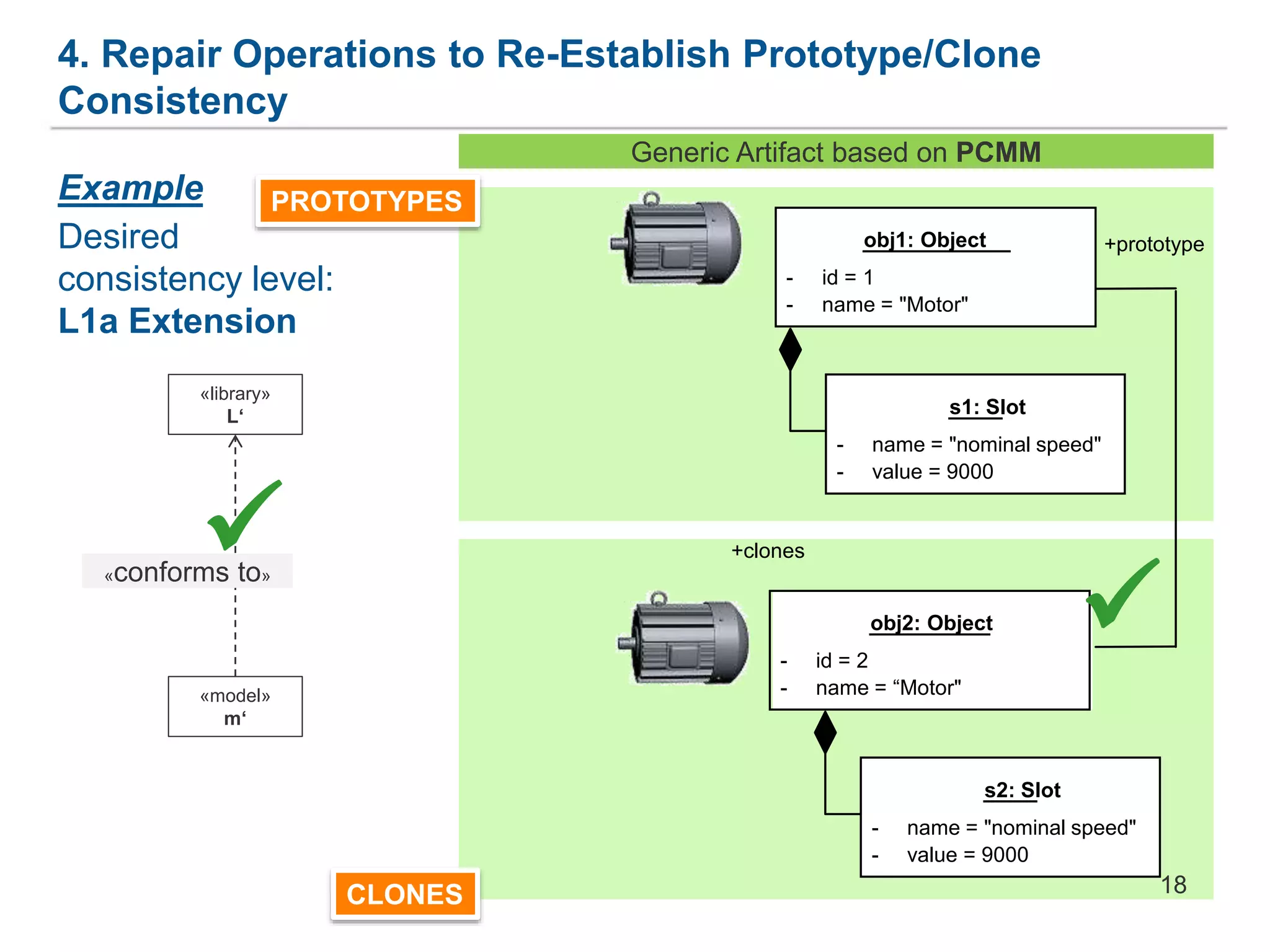
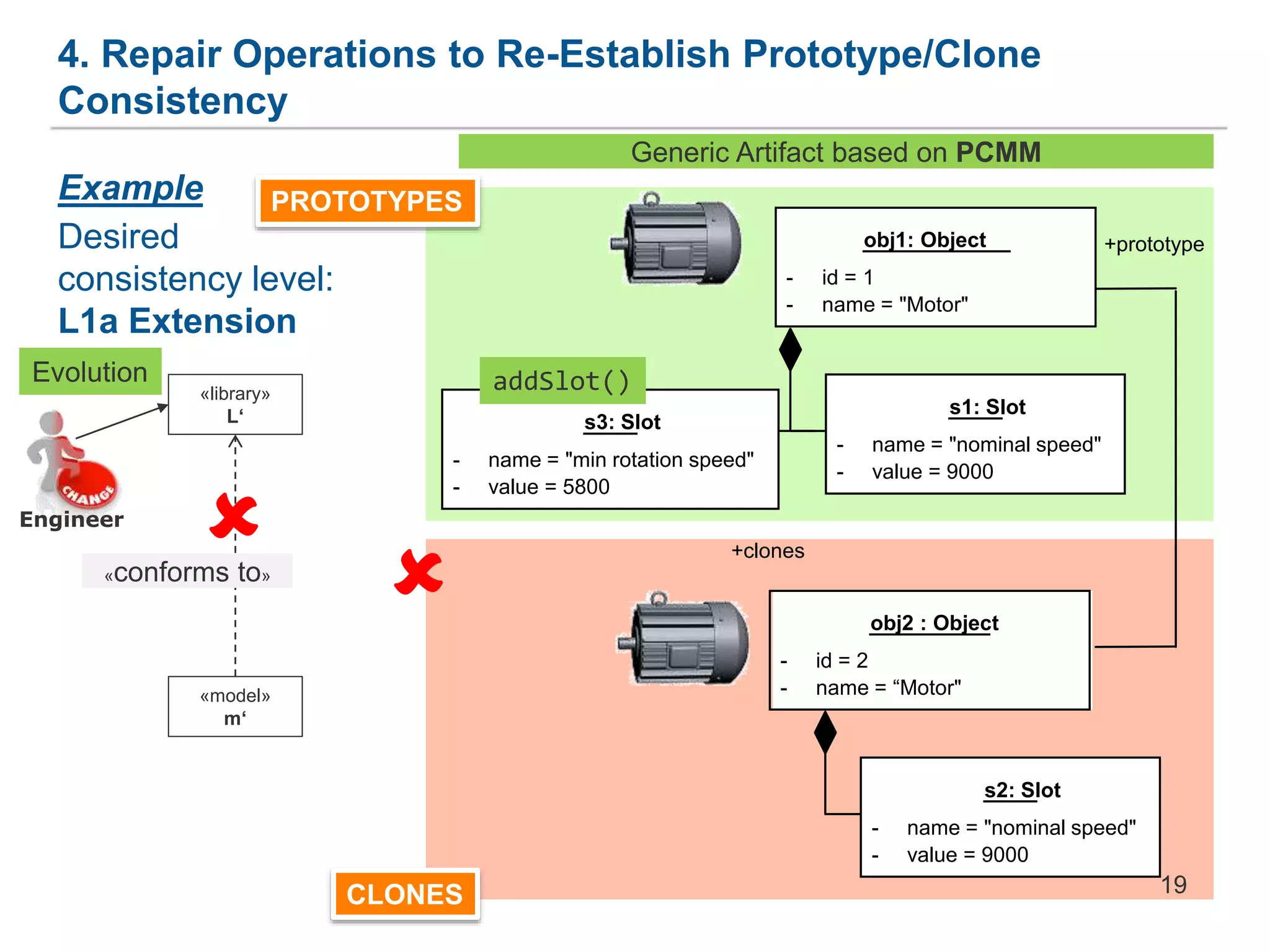
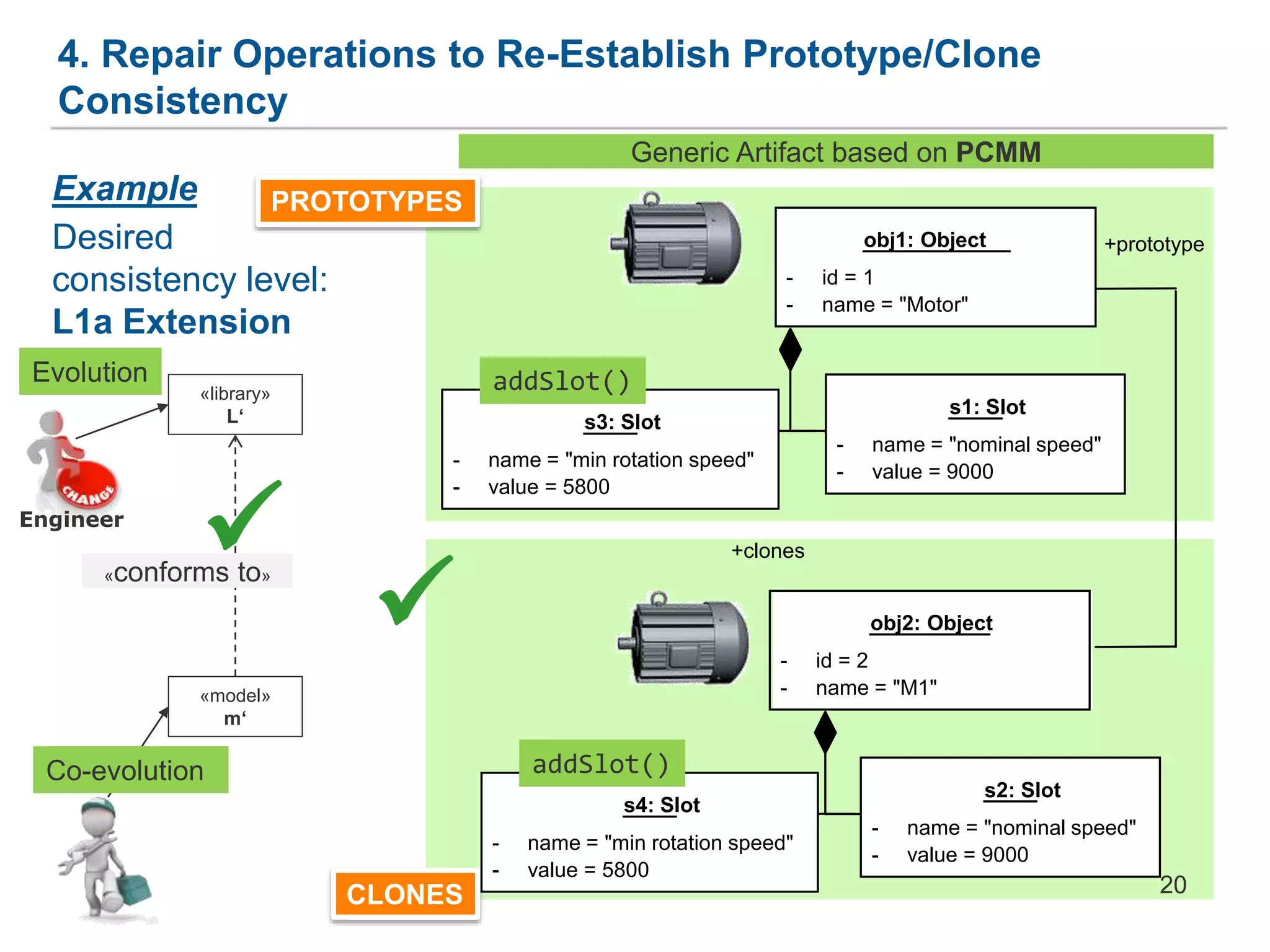
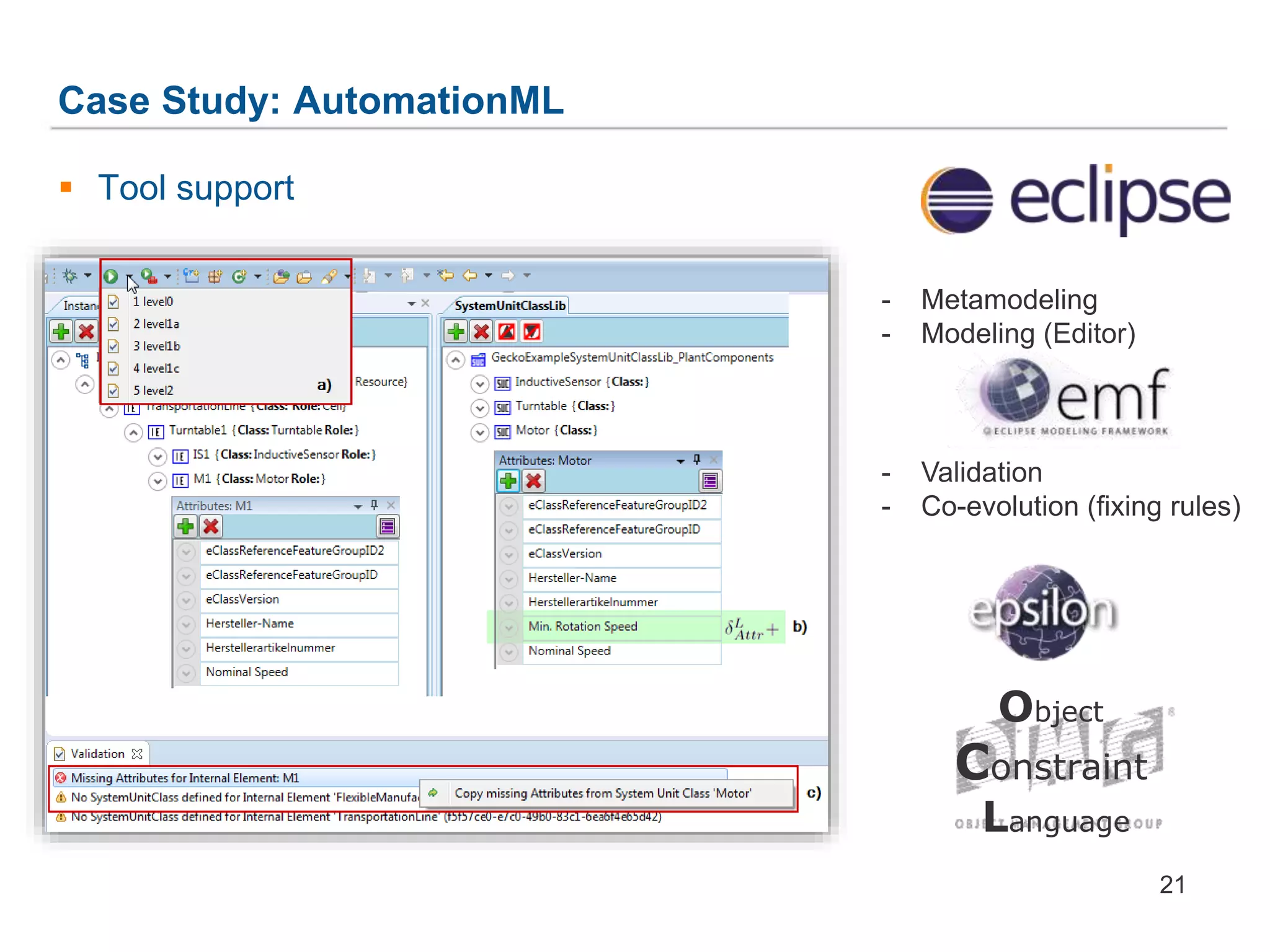
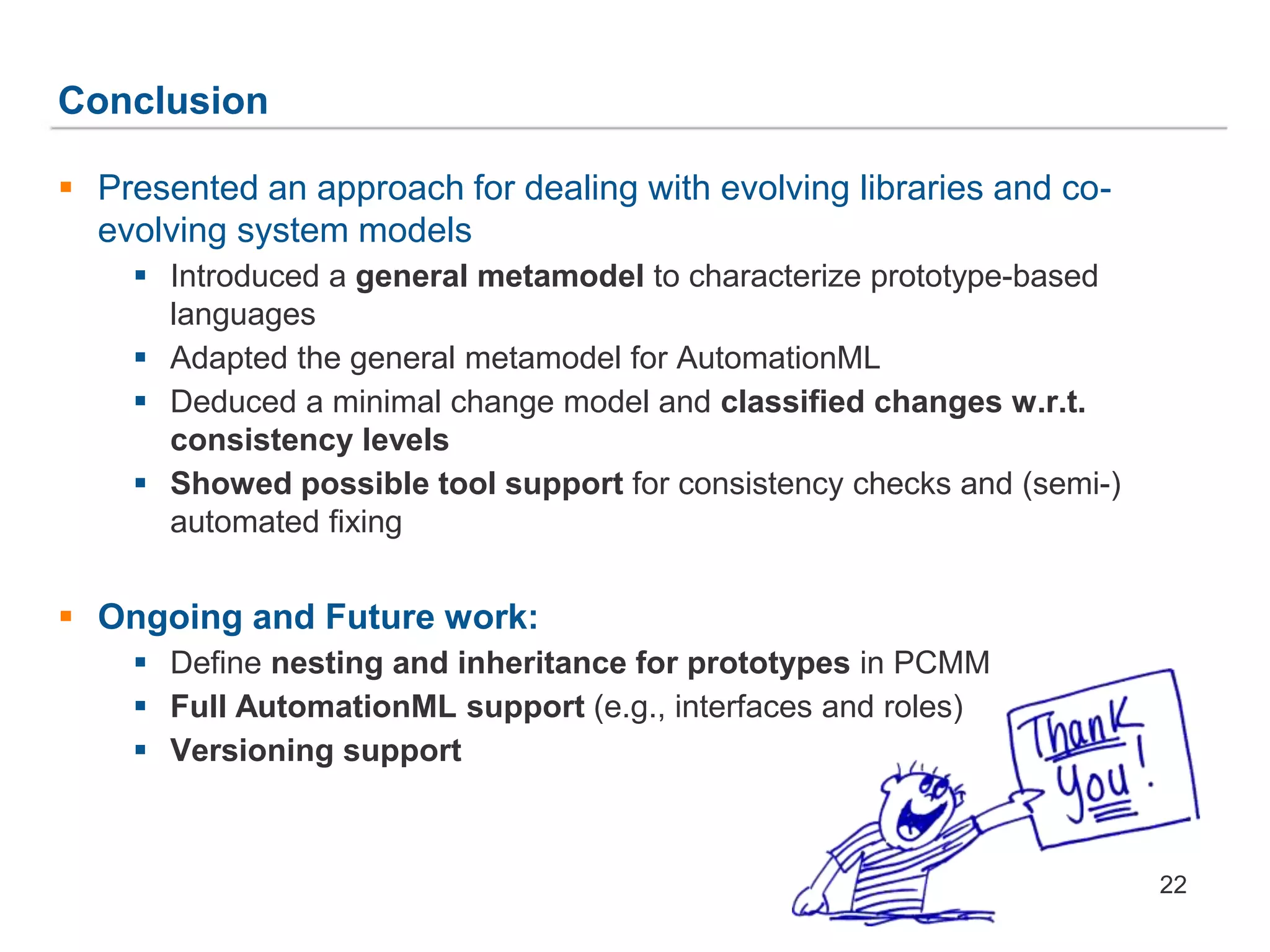
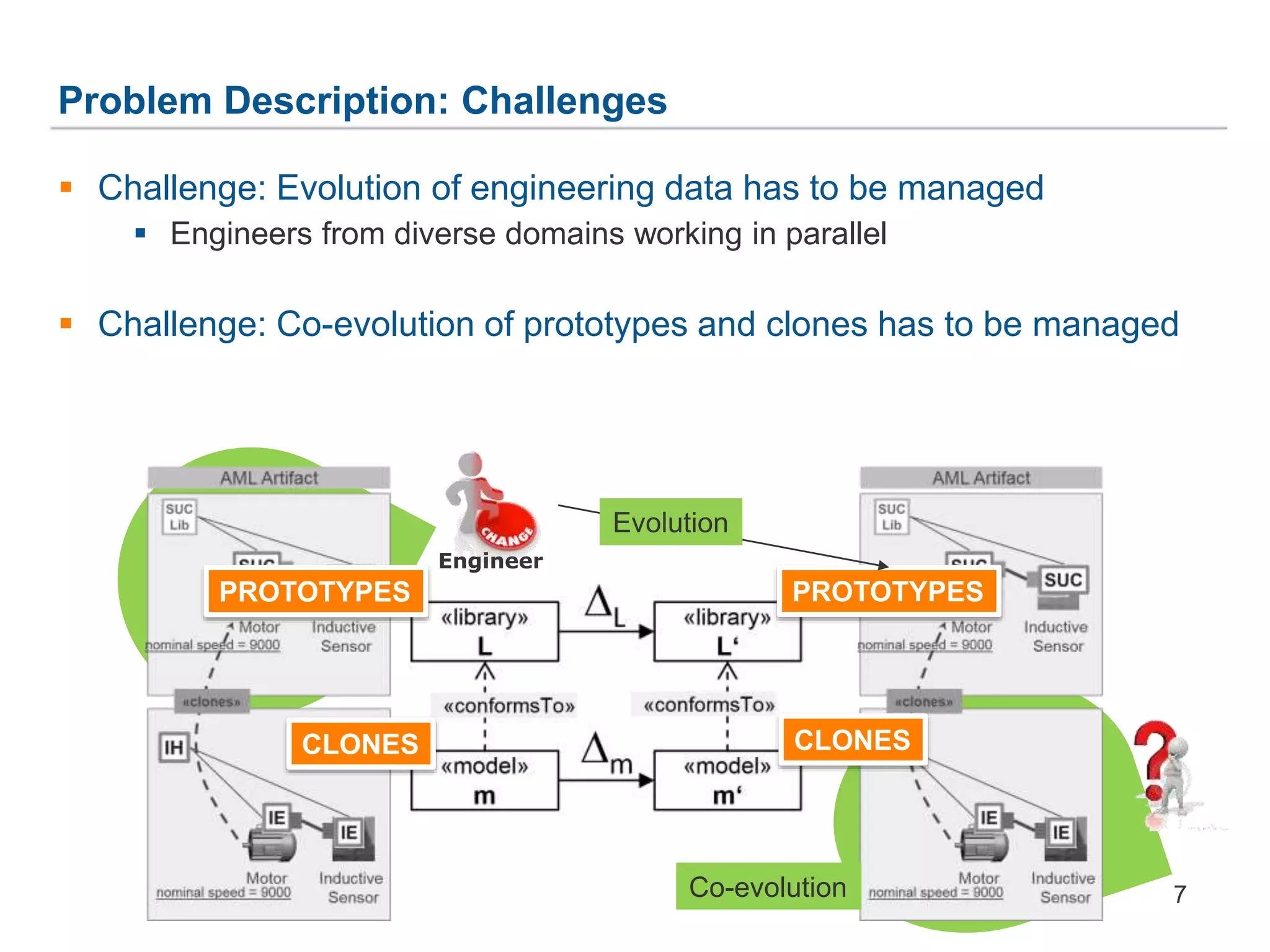
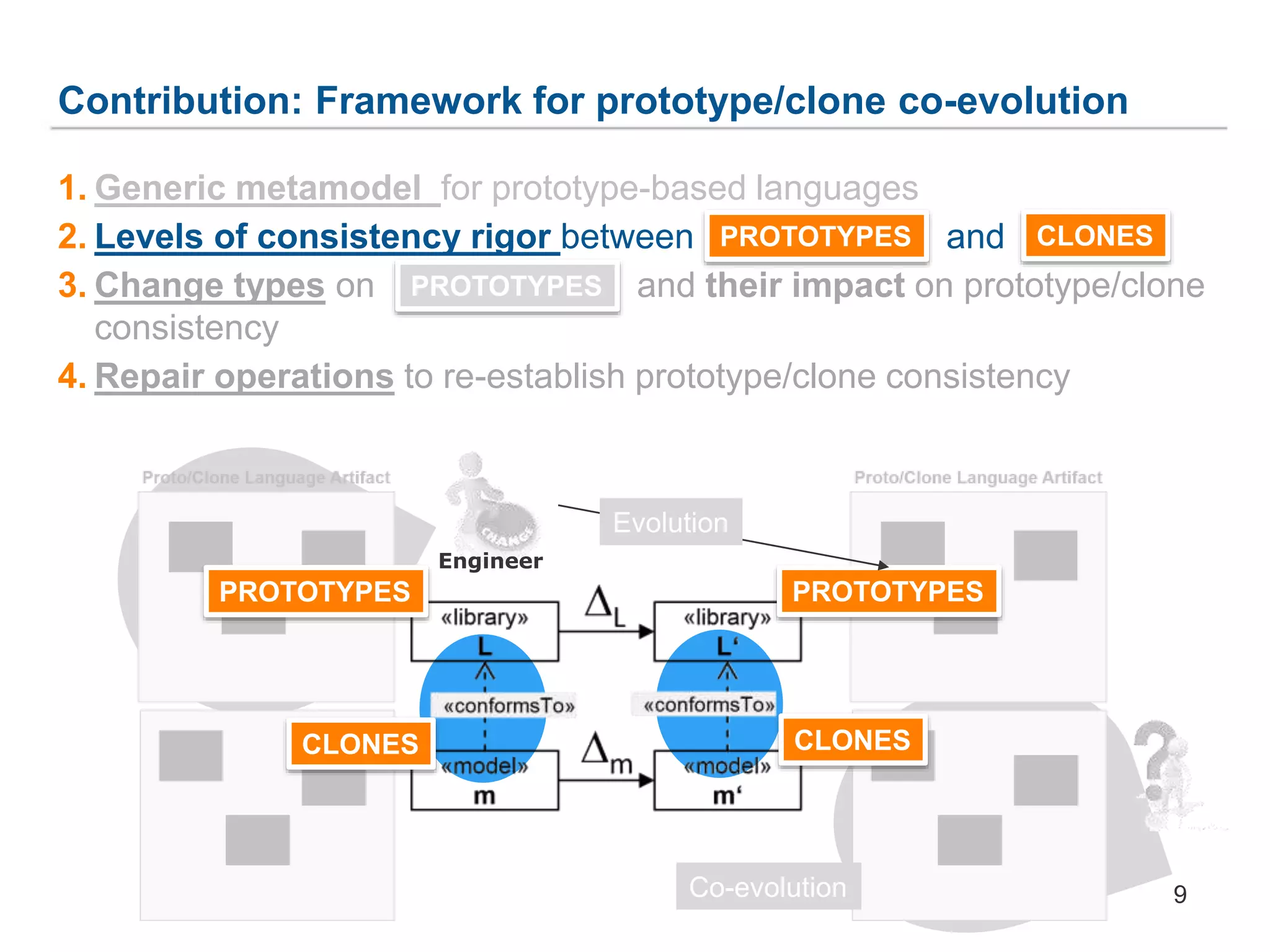
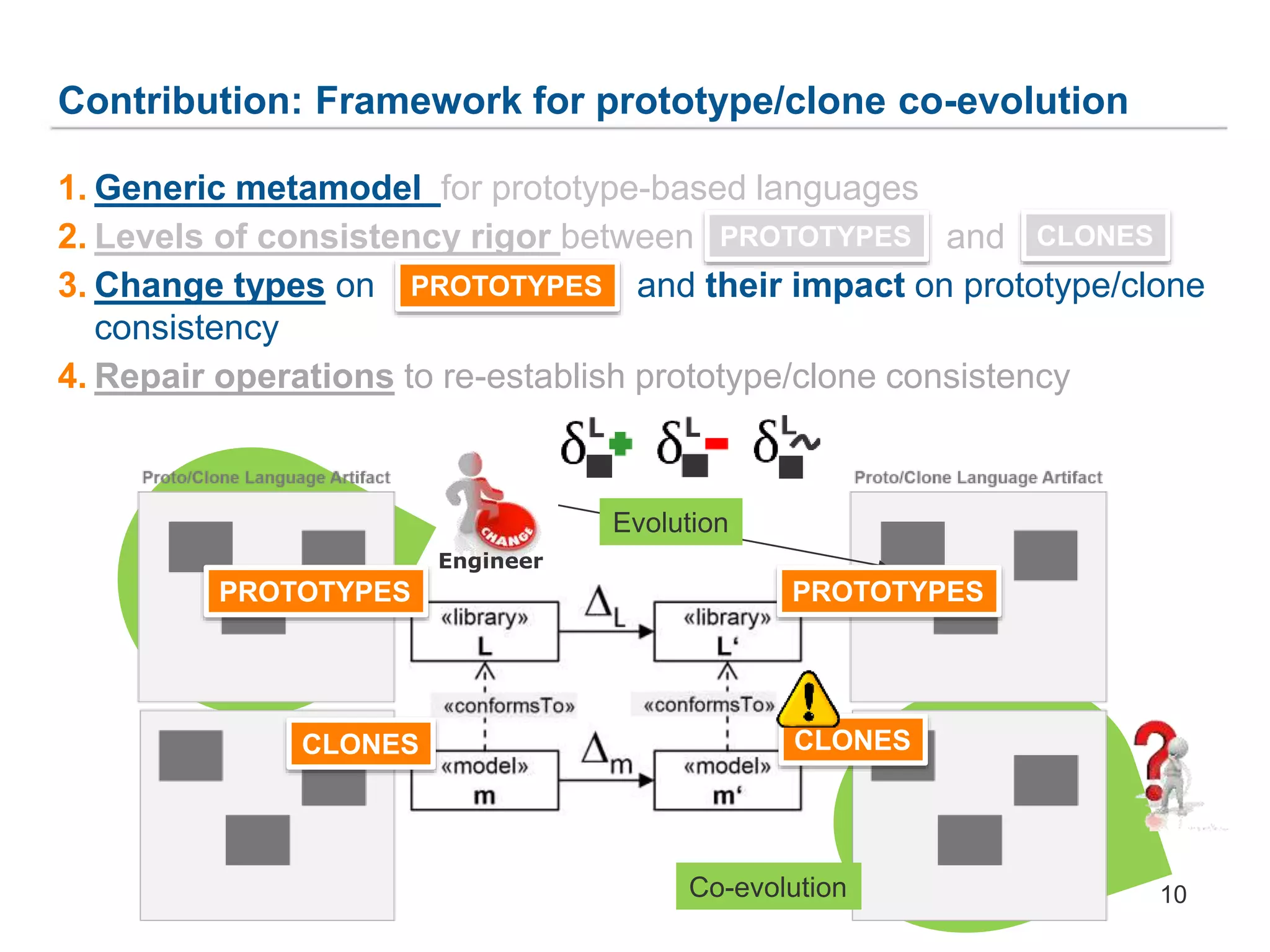
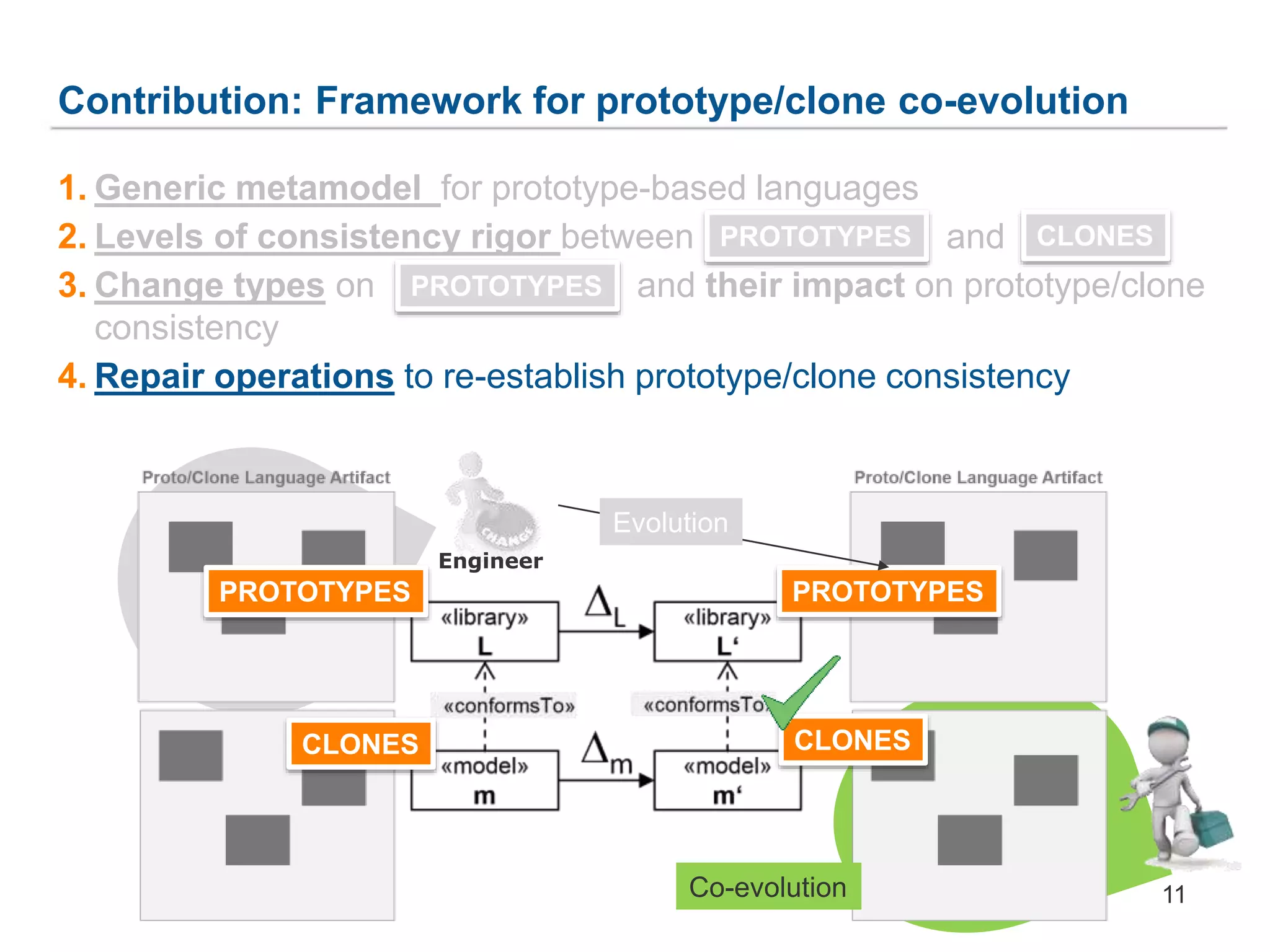
The document discusses a framework for the co-evolution of prototypes and clones within the context of AutomationML, particularly addressing challenges faced by engineers in diverse domains. It introduces a generic metamodel for prototype-based languages, detailing various levels of consistency and repair operations needed to maintain prototype/clone consistency. The document emphasizes ongoing and future work, including enhanced AutomationML support and versioning.


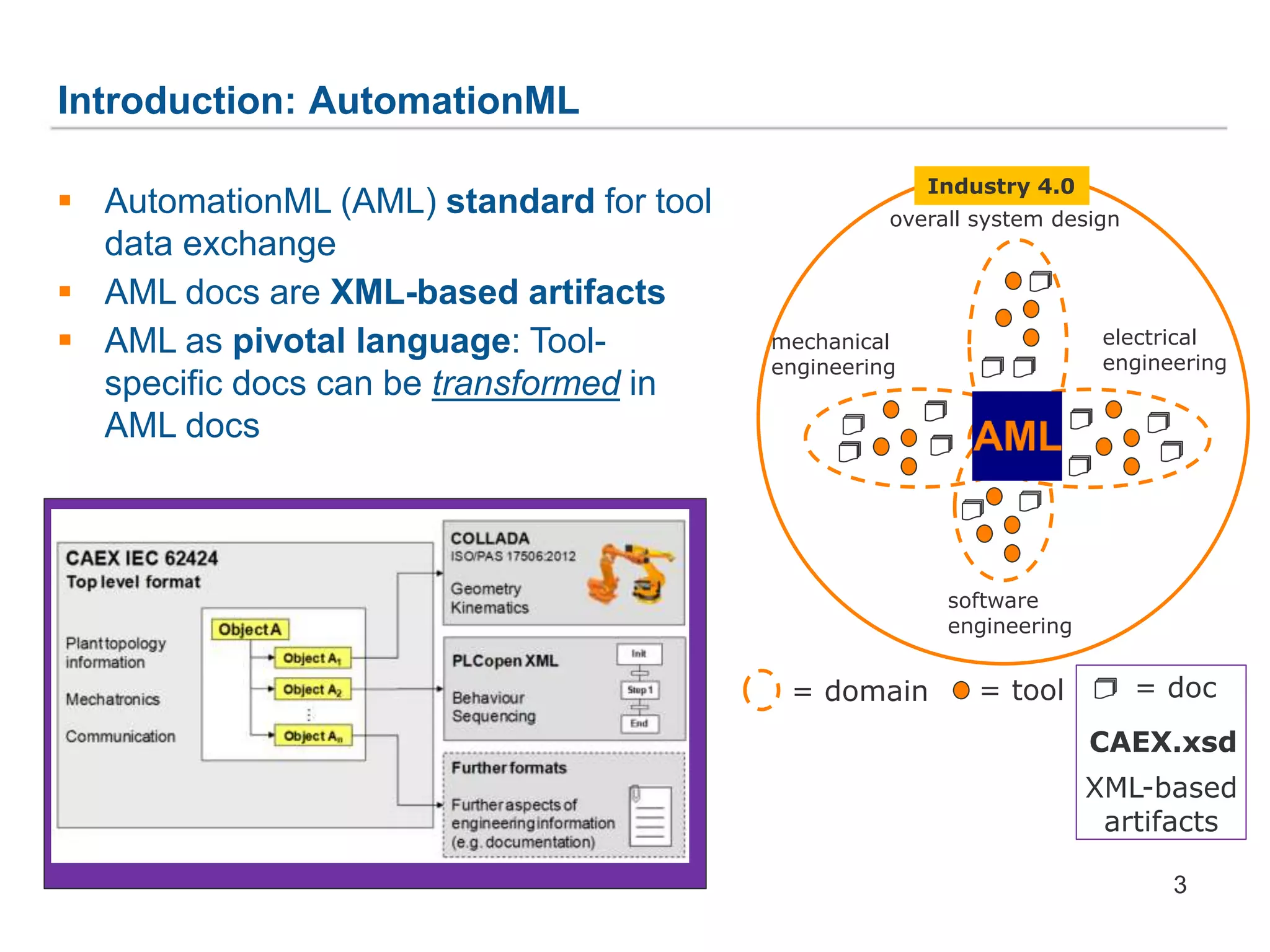
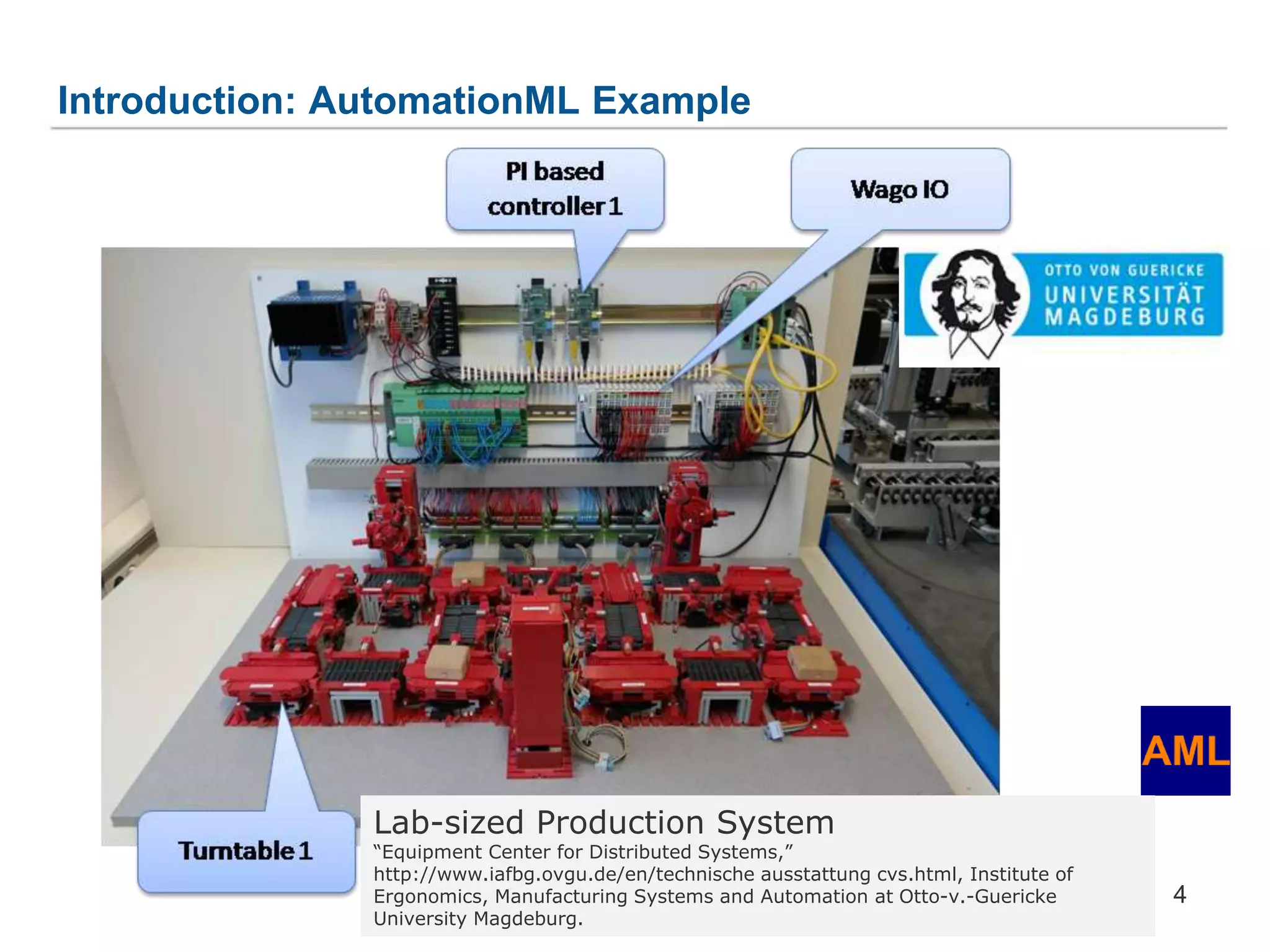
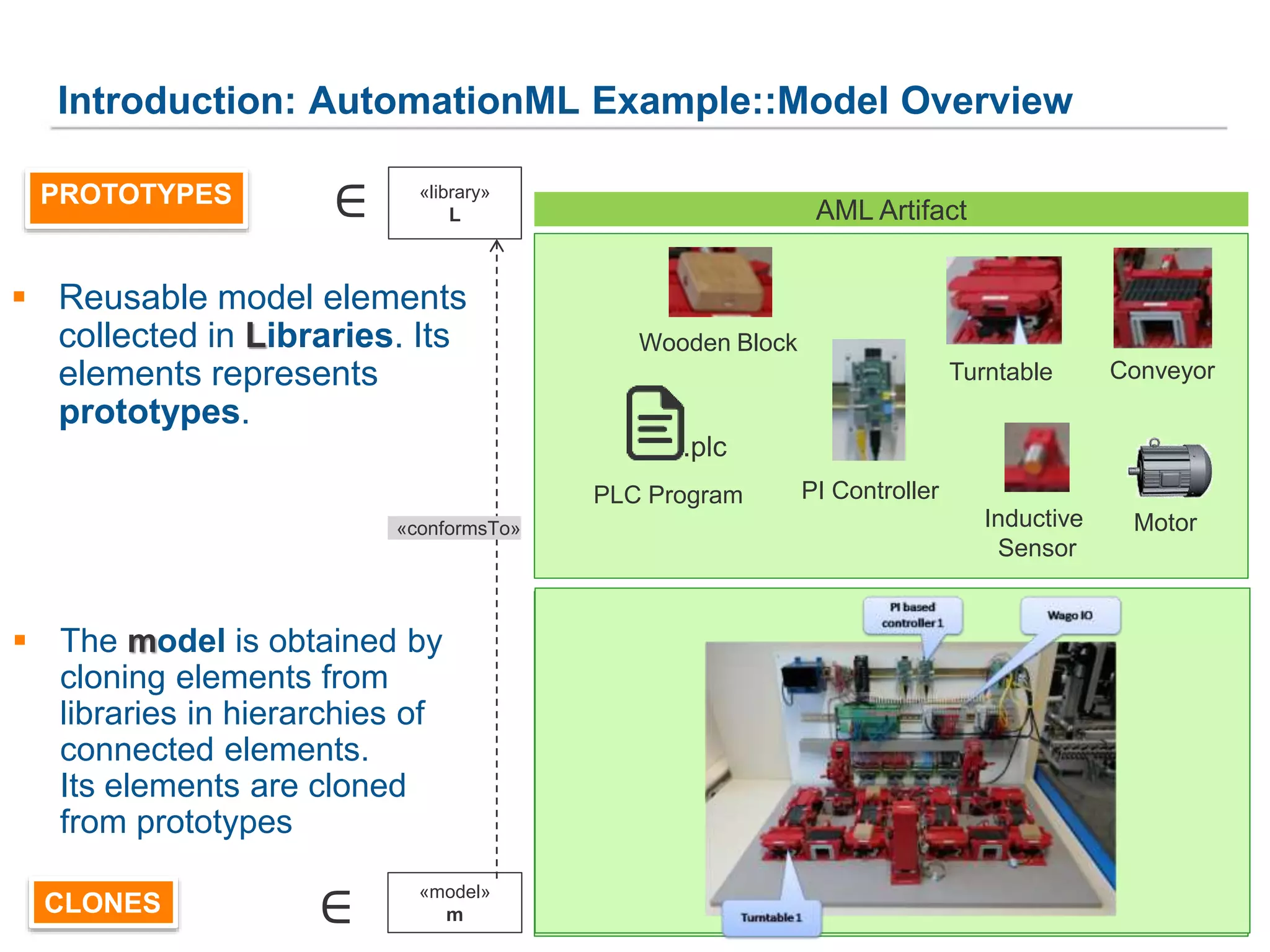
![1. Generic Metamodel for Prototype-Based Languages
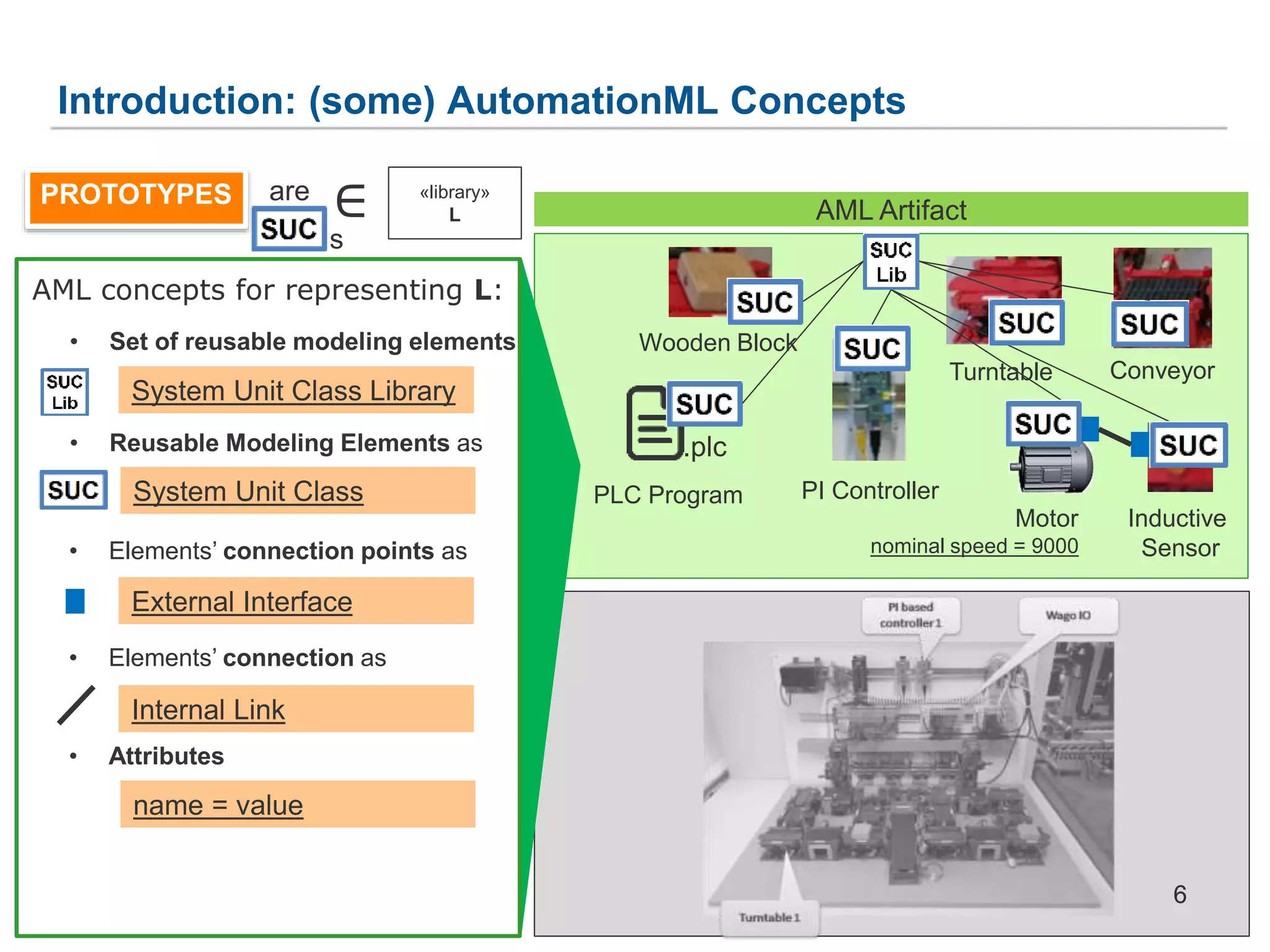
A general metamodel for prototypes
and clones (prototype clone metamodel,
PCMM) whose concepts can be
adopted for several modeling languages.
PROTOTYPES CLONES and as roles
A Object can play different roles,
depending on its current relationships
ObjectStore
+ createObject() :Object
+ deleteObject() :void
Slot
- name :String
- Value :Object[*]
+objects
+slots
Object
- id :int
- name :String
+ createClone():Object
+ addSlot() :Slot
+ deleteSlot() :void
+ modifySlot() :void
+prototype 0..1+clones *
*
*
12
PCMM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finaletfa2015slideshare-150924074326-lva1-app6892/75/Model-Based-Co-Evolution-of-Production-Systems-and-their-Libraries-with-AutomationML-13-2048.jpg)
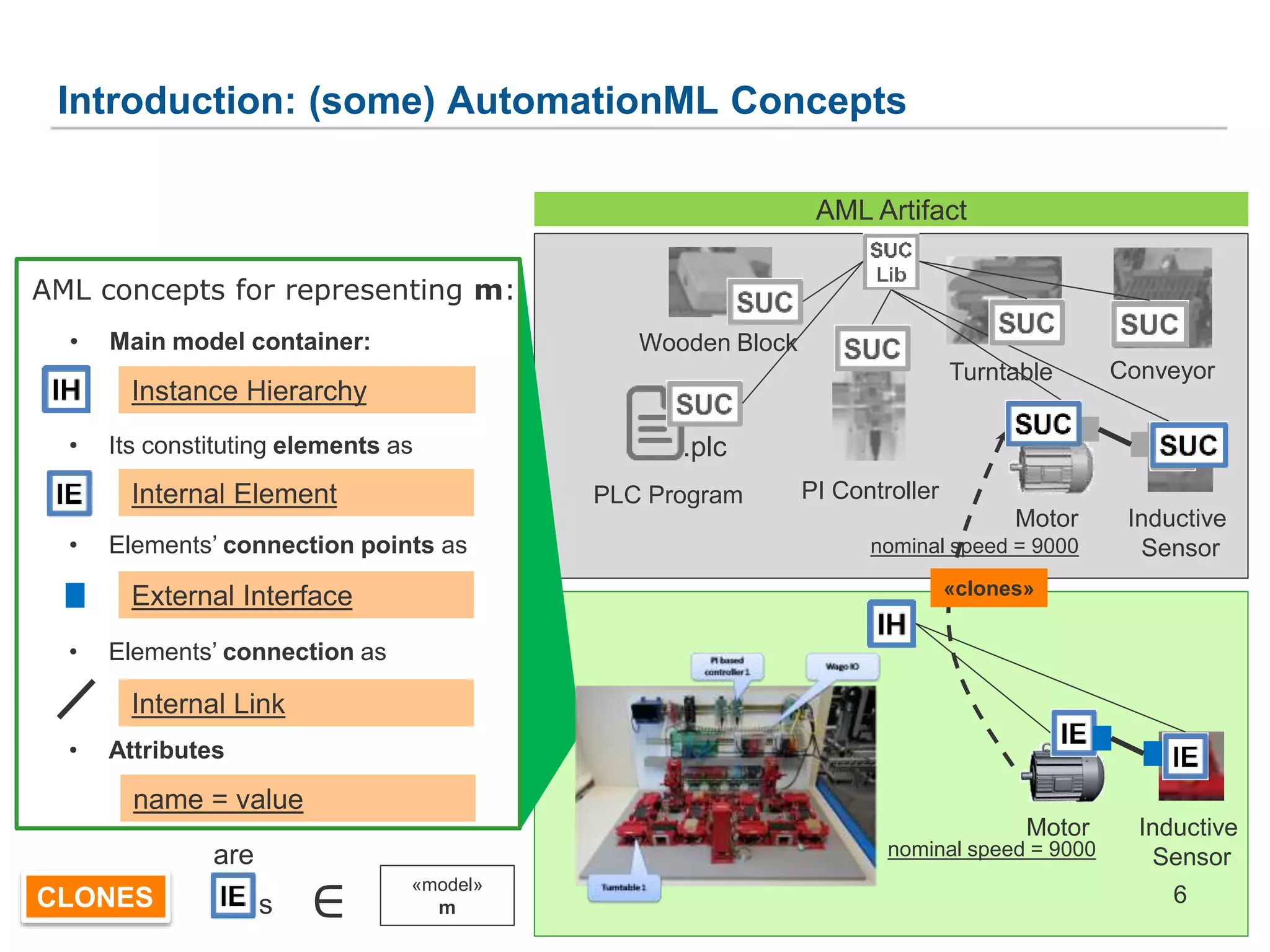
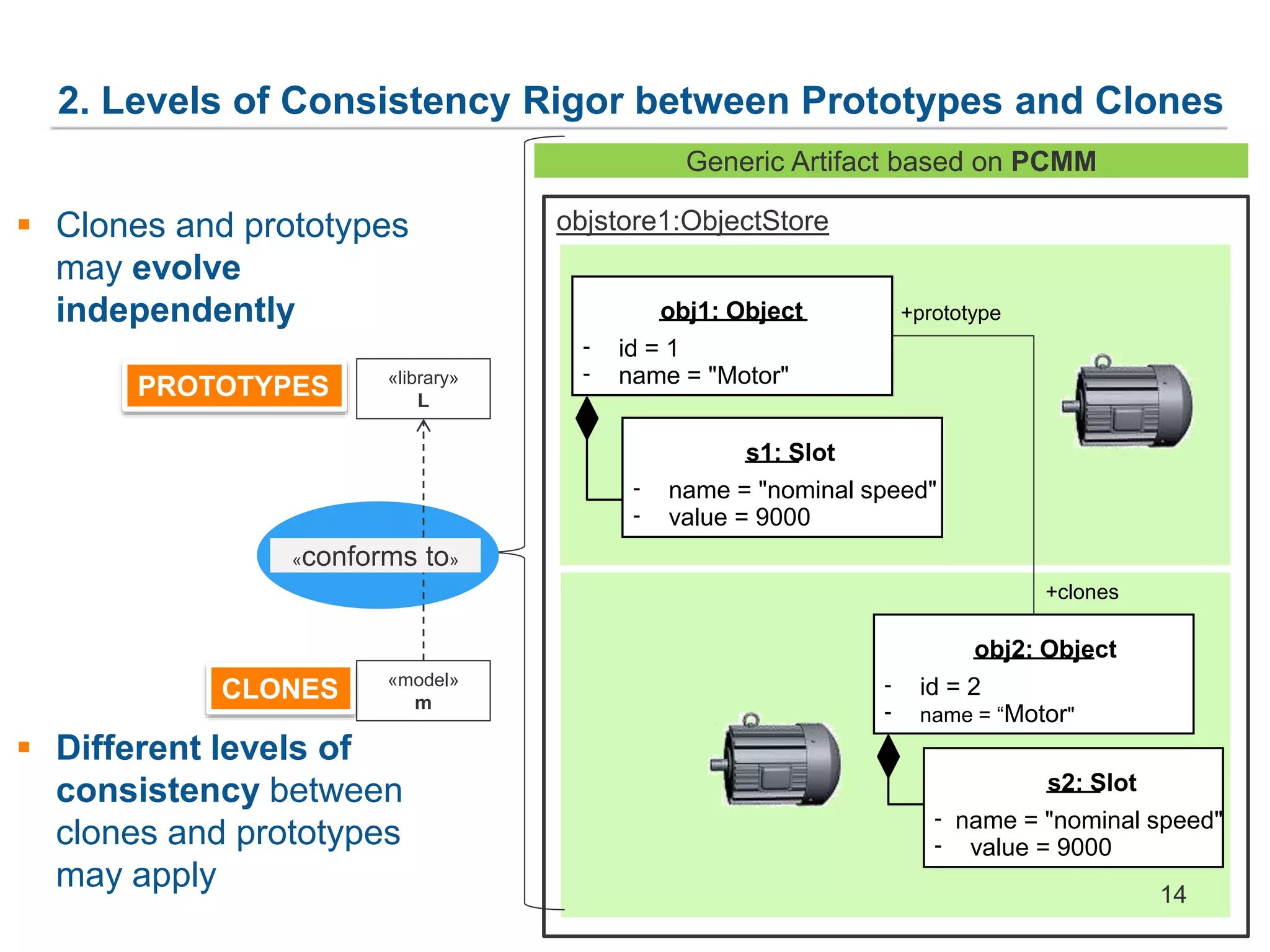
![1. Generic Metamodel for Prototype-Based Languages
ObjectStore
+ createObject() :Object
+ deleteObject() :void
Slot
- name :String
- Value :Object[*]
+objects
+slots
Object
- id :int
- name :String
+ createClone():Object
+ addSlot() :Slot
+ deleteSlot() :void
+ modifySlot() :void
+prototype 0..1+clones *
*
*
Generic Artifact based on PCMM
objstore1:ObjectStore
obj1: Object
- id = 1
- name = "Motor"
s1: Slot
- name = "nominal speed"
- value = 9000
obj2: Object
- id = 2
- name = “Motor"
s2: Slot
- name = "nominal speed"
- value = 9000
+prototype
+clones
PROTOTYPES
CLONES
Attr
Attr
13
PCMM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finaletfa2015slideshare-150924074326-lva1-app6892/75/Model-Based-Co-Evolution-of-Production-Systems-and-their-Libraries-with-AutomationML-14-2048.jpg)
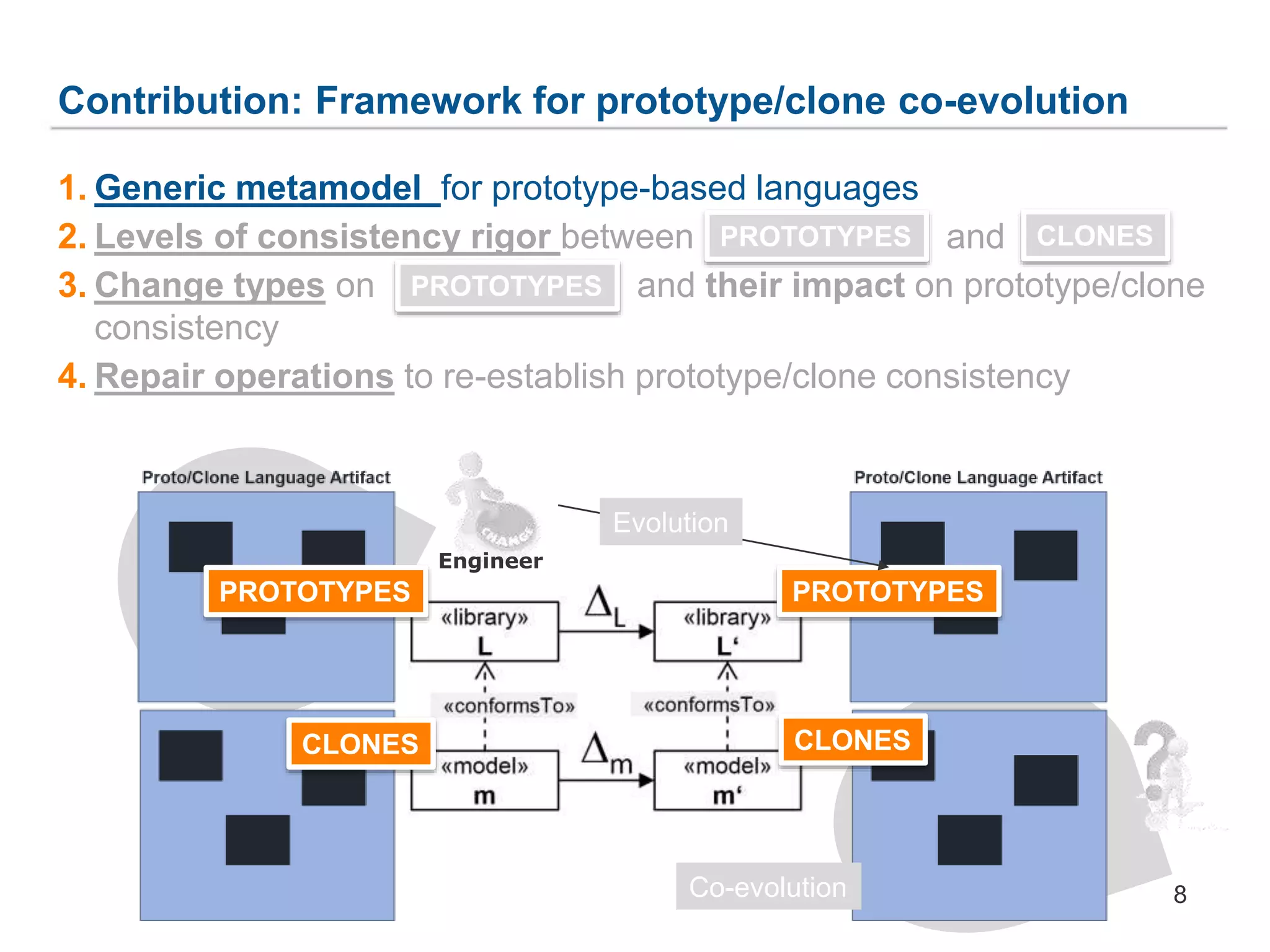
![3. Change Types on Prototypes and their Impact on
Prototype/Clone Consistency
17
Operation L0 L1a L1b L1c L2
ObjectStore::createObject ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
ObjectStore::deleteObject ≠ ≠ ≠ ≠ ≠
Object::addSlot ↑ ≠ ↑ ≠ ≠
Object::deleteSlot ↑ ↑ ≠ ≠ ≠
Object::modifySlot ↑ ≠ ≠ ↑ ≠
ObjectStore
+ createObject() :Object
+ deleteObject() :void
Slot
- name :String
- Value :Object[*]
+objects
+slots
Object
- id :int
- name :String
+ createClone():Object
+ addSlot() :Slot
+ deleteSlot() :void
+ modifySlot() :void
+prototype 0..1+clones *
*
*
PROTOTYPES
«conforms to»
«library»
L‘
«model»
m‘
CLONES
Engineer
↑ = non-breaking
≠ =breaking
are
s
are
s
PCMM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finaletfa2015slideshare-150924074326-lva1-app6892/75/Model-Based-Co-Evolution-of-Production-Systems-and-their-Libraries-with-AutomationML-17-2048.jpg)