1) The document discusses leveraging Modelica and FMI standards in Scilab open-source engineering software.
2) Key topics covered include Scilab use cases, integrating Modelica models into Scilab/Xcos, and using FMI for co-simulation and model exchange.
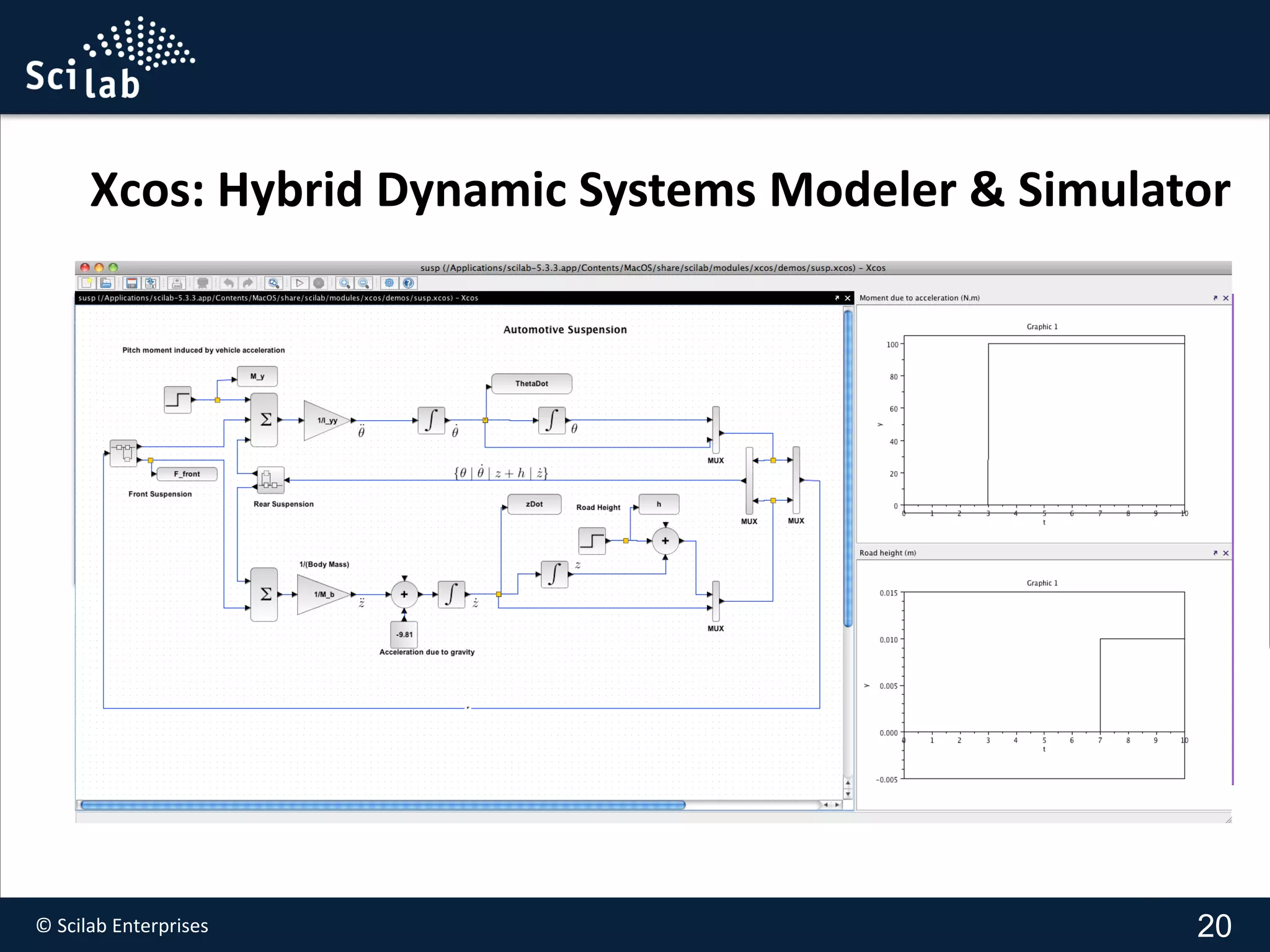
3) Demonstrations show automotive suspension modeling with Scilab/Xcos/Modelica, parameter identification in Xcos, and using FMI in Xcos for co-simulation.




























![Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) in Scilab
function yp=quarter_car_ode(t, y)
v = 4; // Speed [m/s]
m = 50;
c_F = 10000; // [N/m]
c_D = 400; // [Ns/m]
x = v*t ;
yp = [y(2);
1/m*(c_D*(v*zp-y(2))+c_F*(z-y(1)))];
endfunction
t = linspace(t0,t1);
y= ode("rkf",[0;0],t0,t,quarter_car_ode);
© Scilab Enterprises 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scilabmodelica20150921-150924140501-lva1-app6892/75/Scilab-Modelica-conference-20150921-30-2048.jpg)







