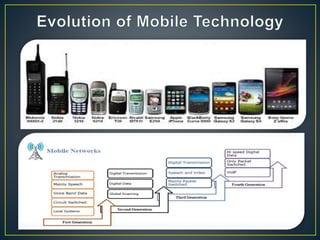
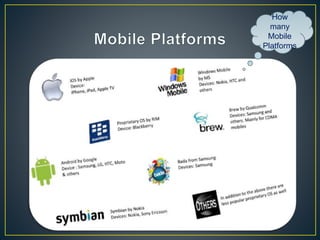
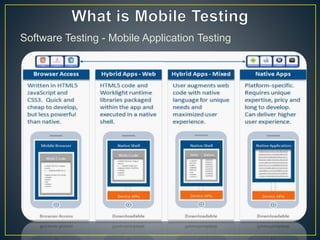
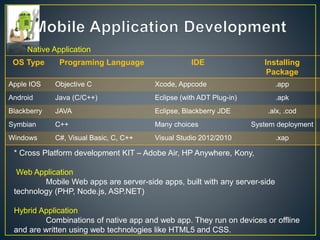
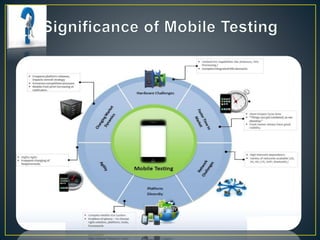
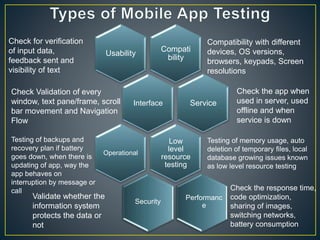
This document discusses mobile platform testing. It lists the major mobile platforms including iOS, Android, Blackberry, Symbian, and Windows. It describes the different types of mobile applications that can be developed - native, web, and hybrid. It also discusses the different aspects of testing mobile applications including compatibility, usability, interfaces, services, security, performance, and more. The document compares emulator/simulator testing to real device testing and lists the pros and cons of each approach. It recommends using emulators for initial development but performing major testing on real devices before commercial release.