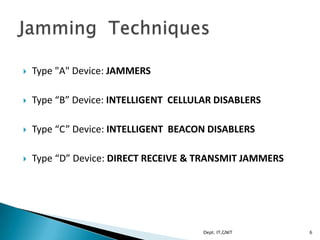
This document discusses mobile phone jammers. It begins with an introduction to what a mobile jammer is and its history of use by law enforcement. It then describes four types of jamming techniques - Type A jammers, Type B intelligent cellular disablers, Type C intelligent beacon disablers, and Type D direct receive and transmit jammers. The document outlines the design and components of jammers, and lists some applications such as use in schools, prisons, hospitals and for security purposes. It concludes by noting both positive and negative aspects of jammer technology.