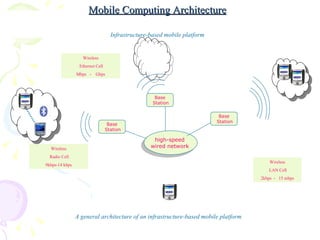
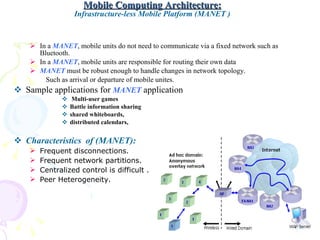
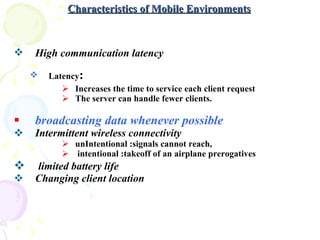
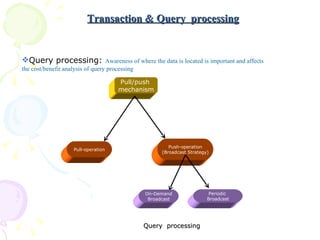
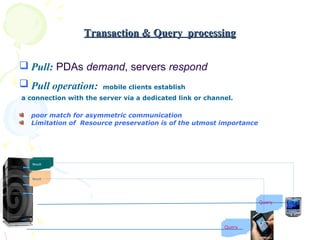
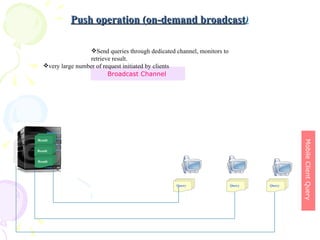
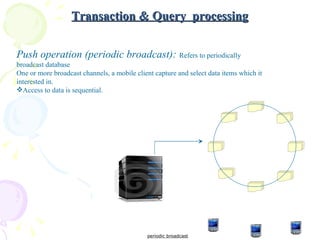
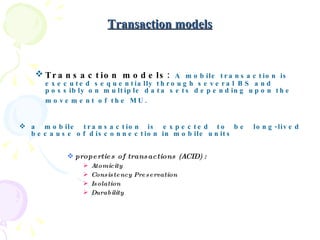
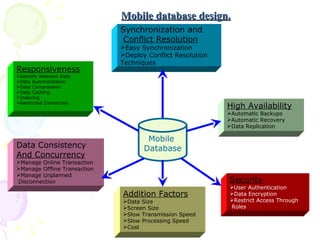
The document discusses characteristics of mobile environments and computing architectures, including intermittent connectivity, location changes, and limited battery life. It also covers various approaches to managing data and processing queries and transactions in mobile databases, such as push and pull mechanisms, broadcasting, and transaction models that account for disconnections. Security, recovery from failures, and design considerations for mobile databases are additional topics covered in the document.