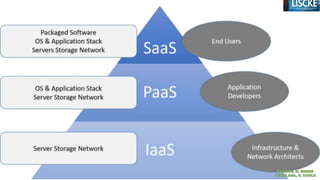
The document discusses mobile cloud computing (MCC) as a merging of mobile and cloud computing technologies, highlighting its importance in accessing resources and applications efficiently from mobile devices. It outlines the benefits MCC brings to libraries, such as improved access to resources, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced user experiences through reduced infrastructure needs and increased data protection. The document also addresses challenges associated with MCC, including network reliability and privacy concerns.