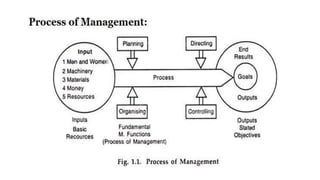
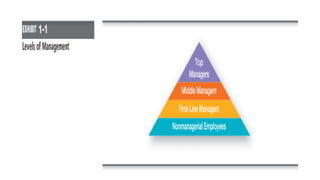
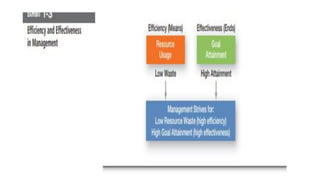
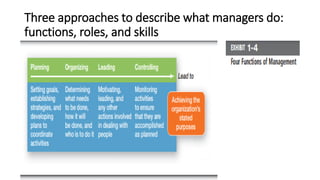
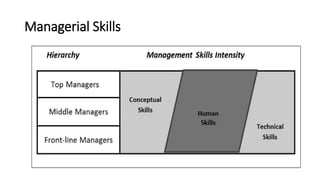
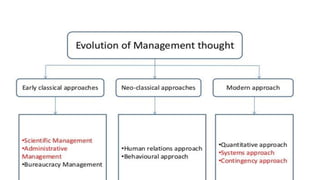
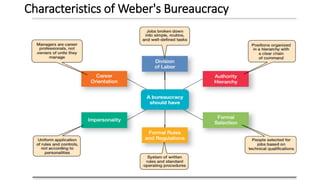
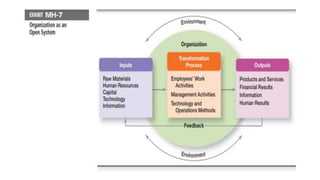
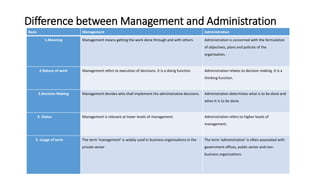
This document provides an overview of classical management theories including scientific management, bureaucracy, and general administrative theory. It discusses the key contributors and principles of each approach. Scientific management, developed by Frederick Taylor, emphasized increasing efficiency through dividing work into tasks, implementing incentive pay, and adopting a scientific approach. Max Weber's bureaucracy theory described an ideal type of organization with division of labor, hierarchy, rules, and impersonal relationships. Henri Fayol's general administrative theory identified functions of management as planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating and controlling. While providing a foundation for modern management, the classical theories took a narrow view of organizations and overemphasized economic rewards and rules. However, some of their techniques related to work analysis and productivity improvements