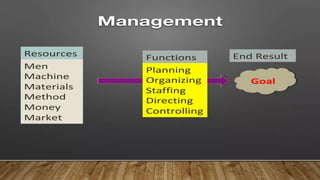
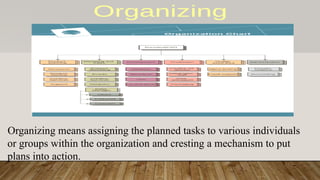
Management has its roots in human civilization and focuses on directing and coordinating individual activities to achieve organizational objectives using various resources. It involves different levels—top, middle, and lower management—each playing a crucial role in planning, organizing, and implementing strategies. Henri Fayol's 14 principles of management emphasize efficiency in handling these organizational activities across all levels and departments.