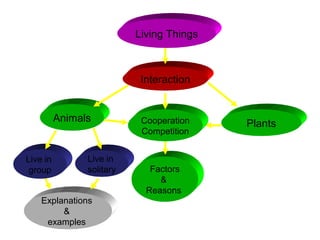
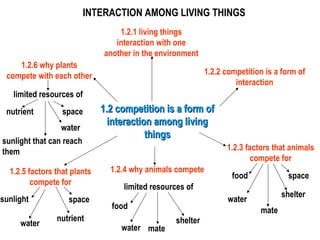
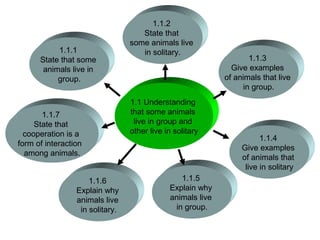
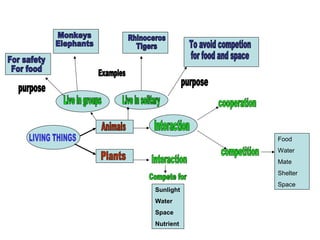
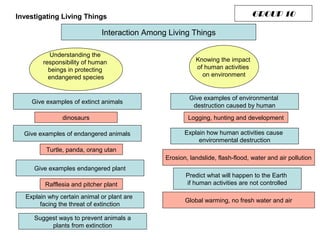
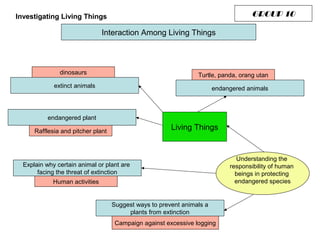
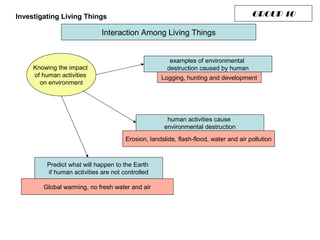
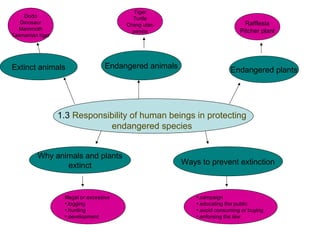
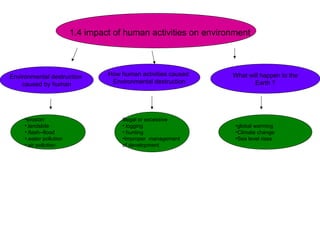
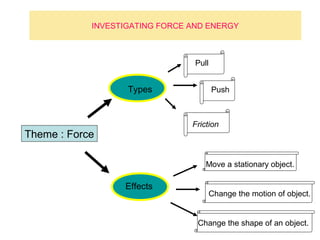
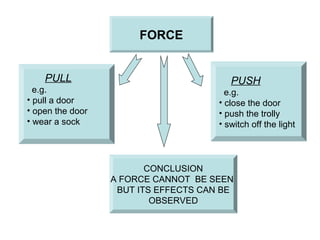
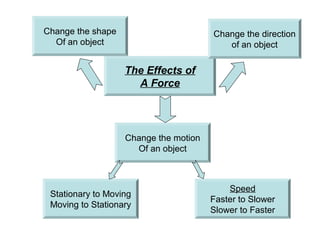
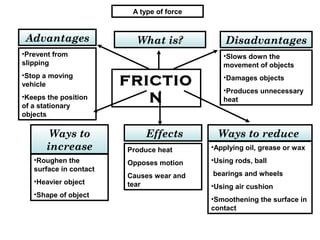
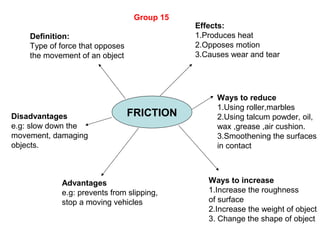
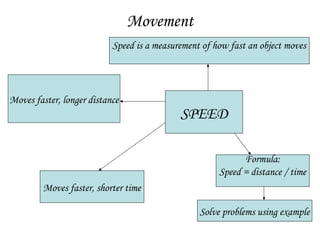
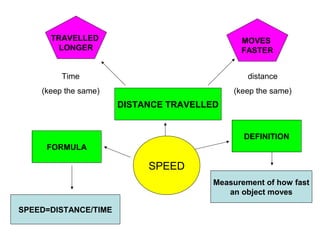
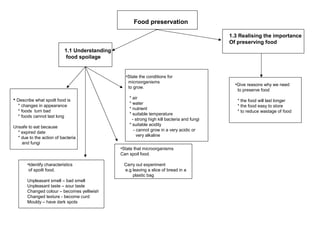
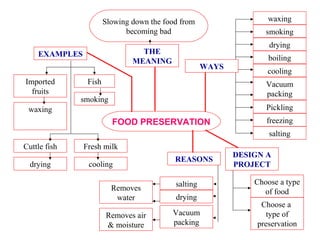
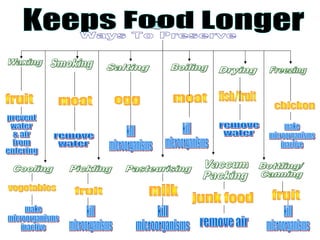
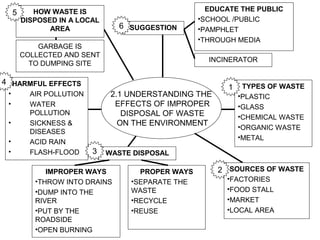
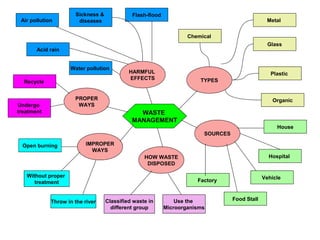
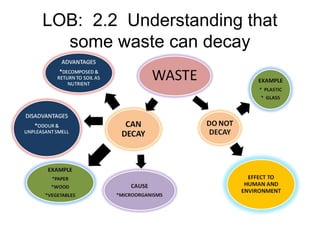
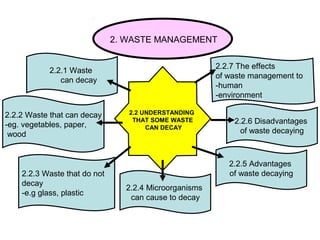
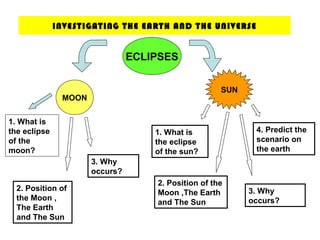
The document discusses interaction among living things, including how some animals live in groups while others live solitary, and how plants and animals compete for limited resources. It also addresses factors like food, water, space, and nutrients that cause competition between living organisms. Various examples are provided to explain competition and cooperation between different types of animals and plants.