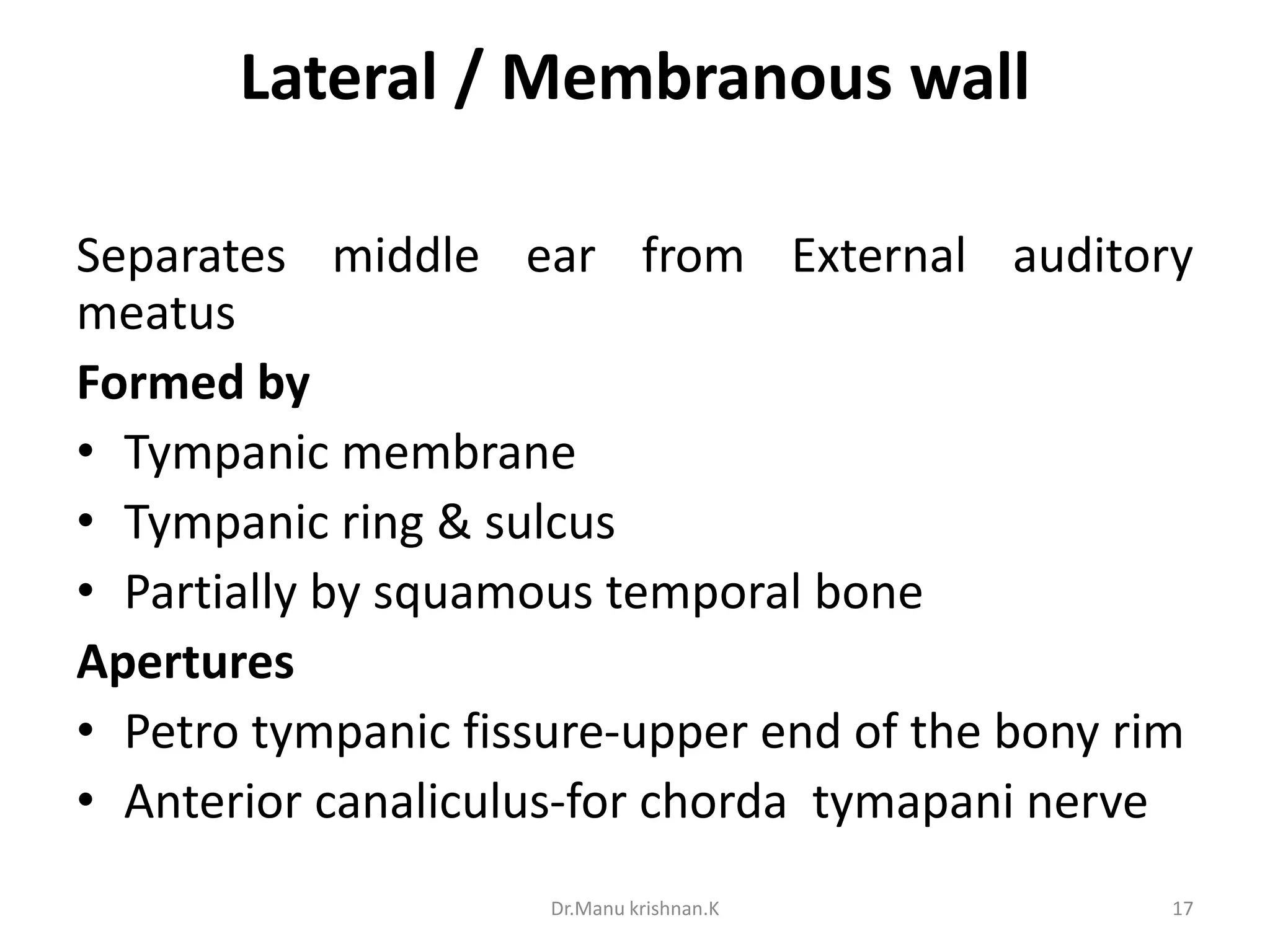
The middle ear is a narrow air-filled cavity located between the external ear and inner ear. It contains the three small ear bones (malleus, incus, stapes) and has six walls. The middle ear is further divided into four portions and communicates with the nasopharynx via the eustachian tube. It contains the ear bones, muscles, blood vessels and nerves that transmit sound from the outer ear to the inner ear.