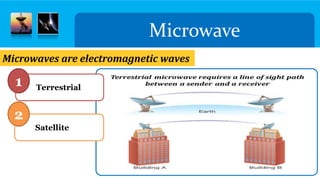
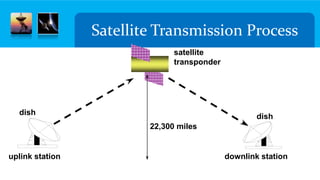
The document discusses microwave transmission, detailing two main types: terrestrial and satellite. Terrestrial microwave communication involves line-of-sight signals between ground stations using high-frequency waves, while satellite microwave communication relays signals between ground stations via satellites in geostationary orbit. Advantages include no cables and multiple channels, but disadvantages consist of line-of-sight requirements and potential interference.