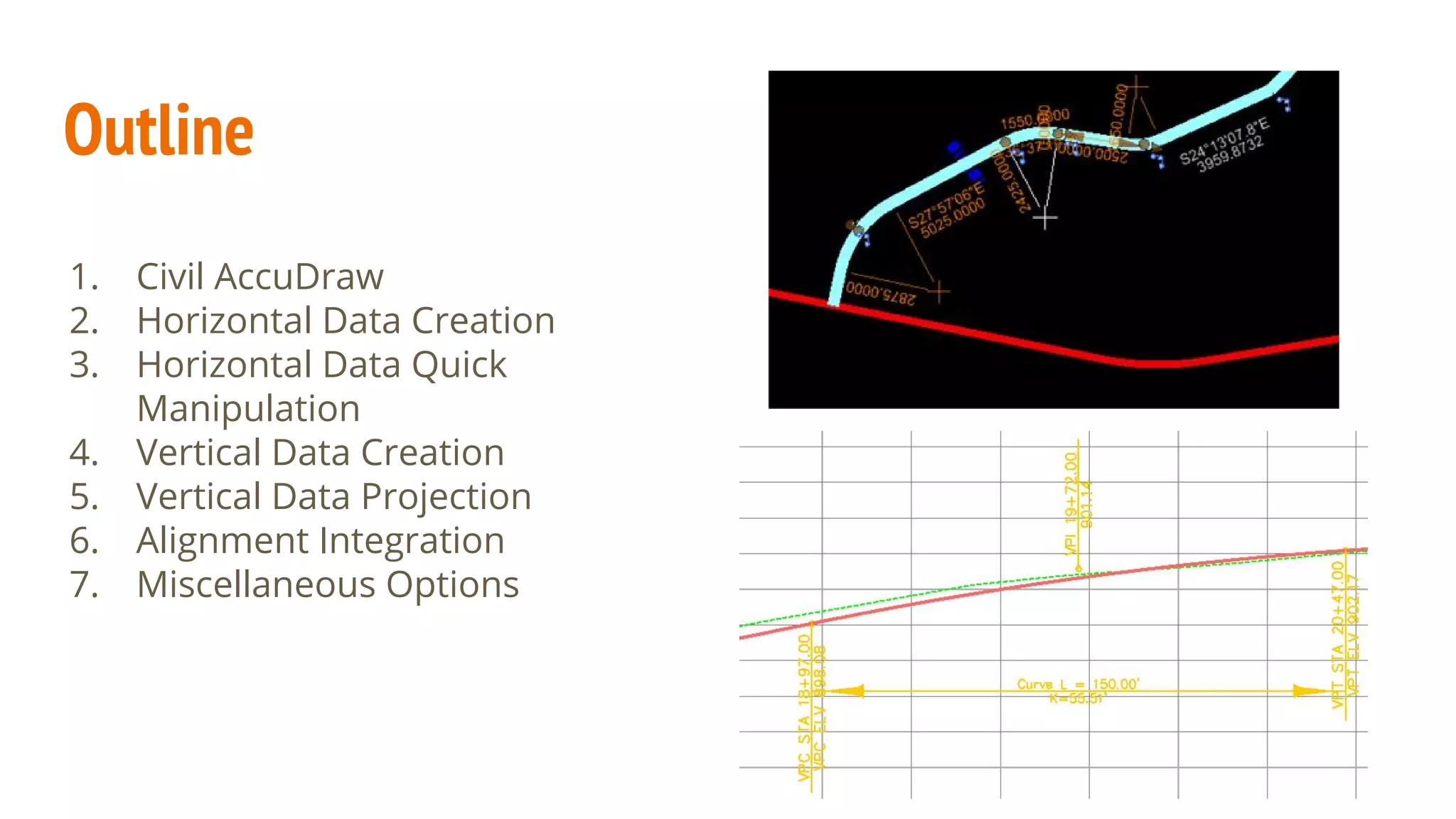
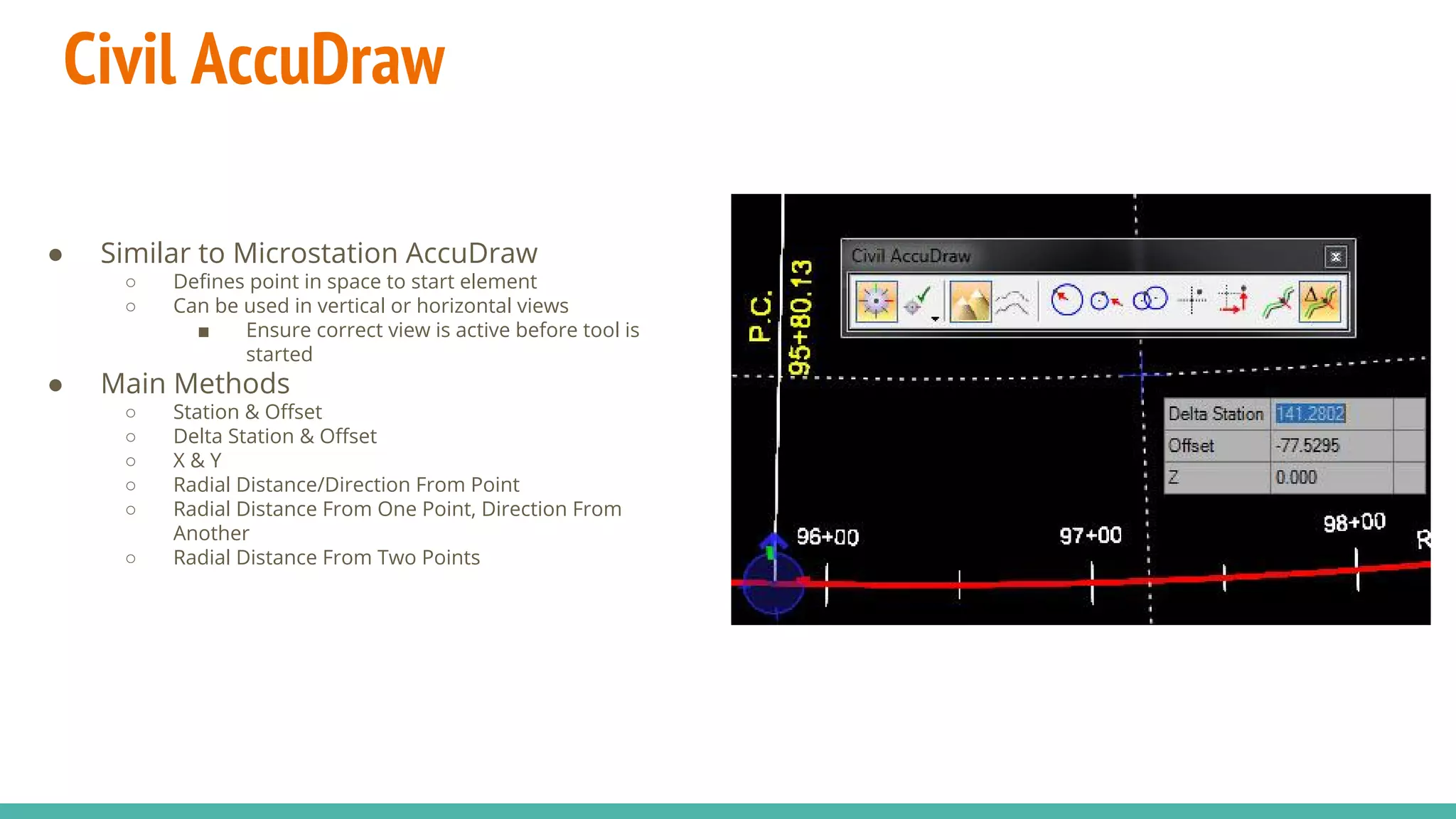
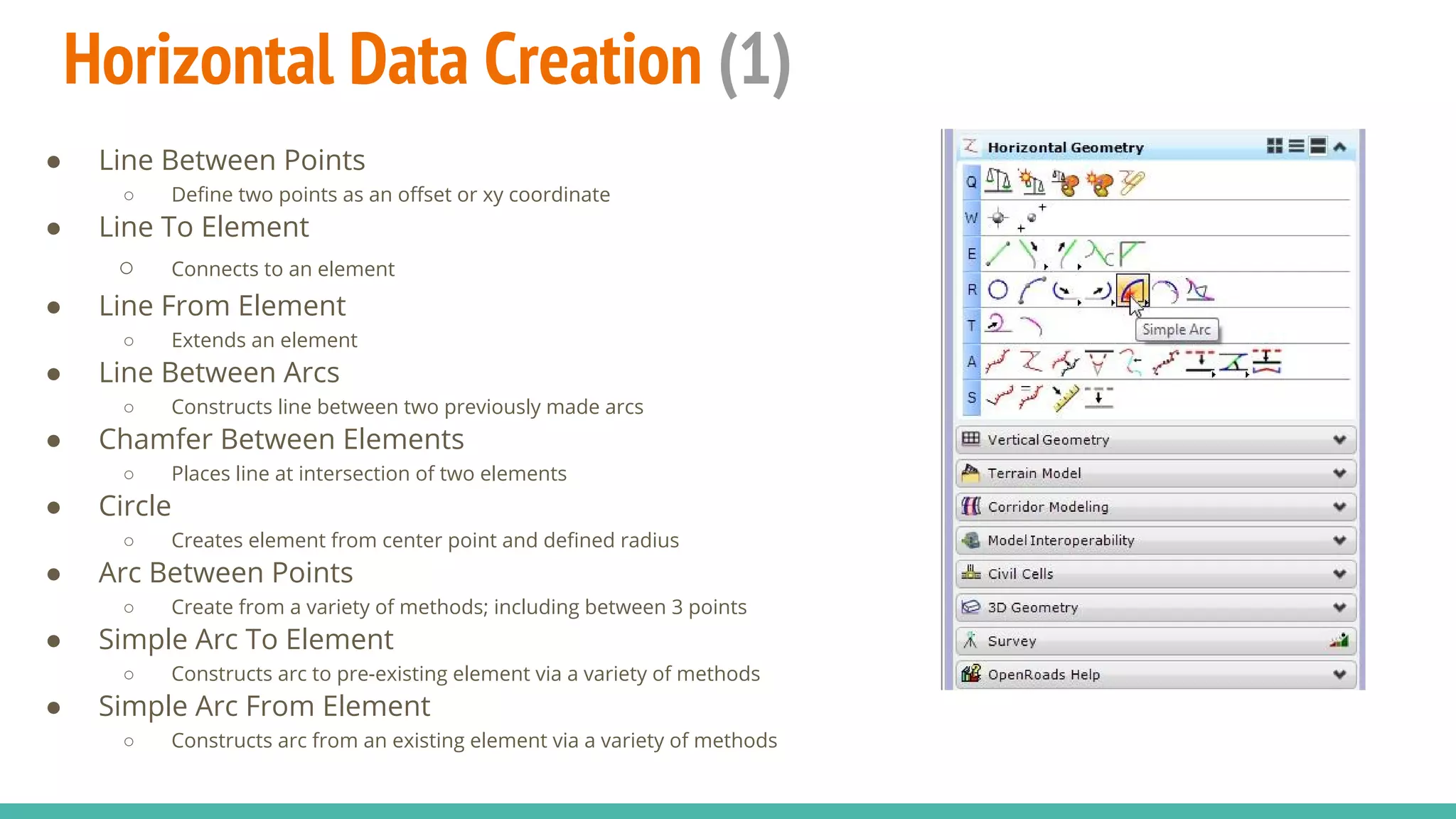
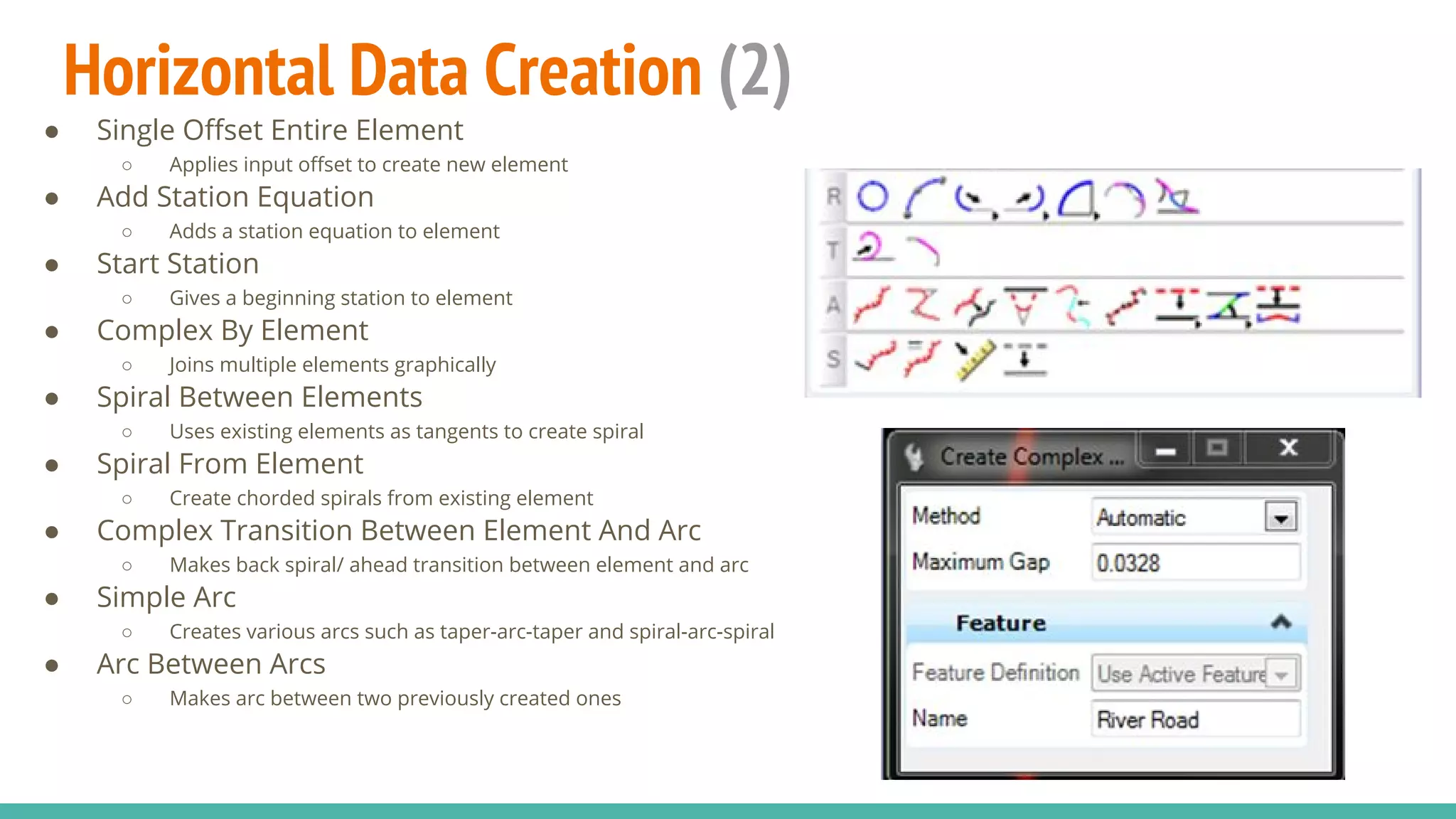
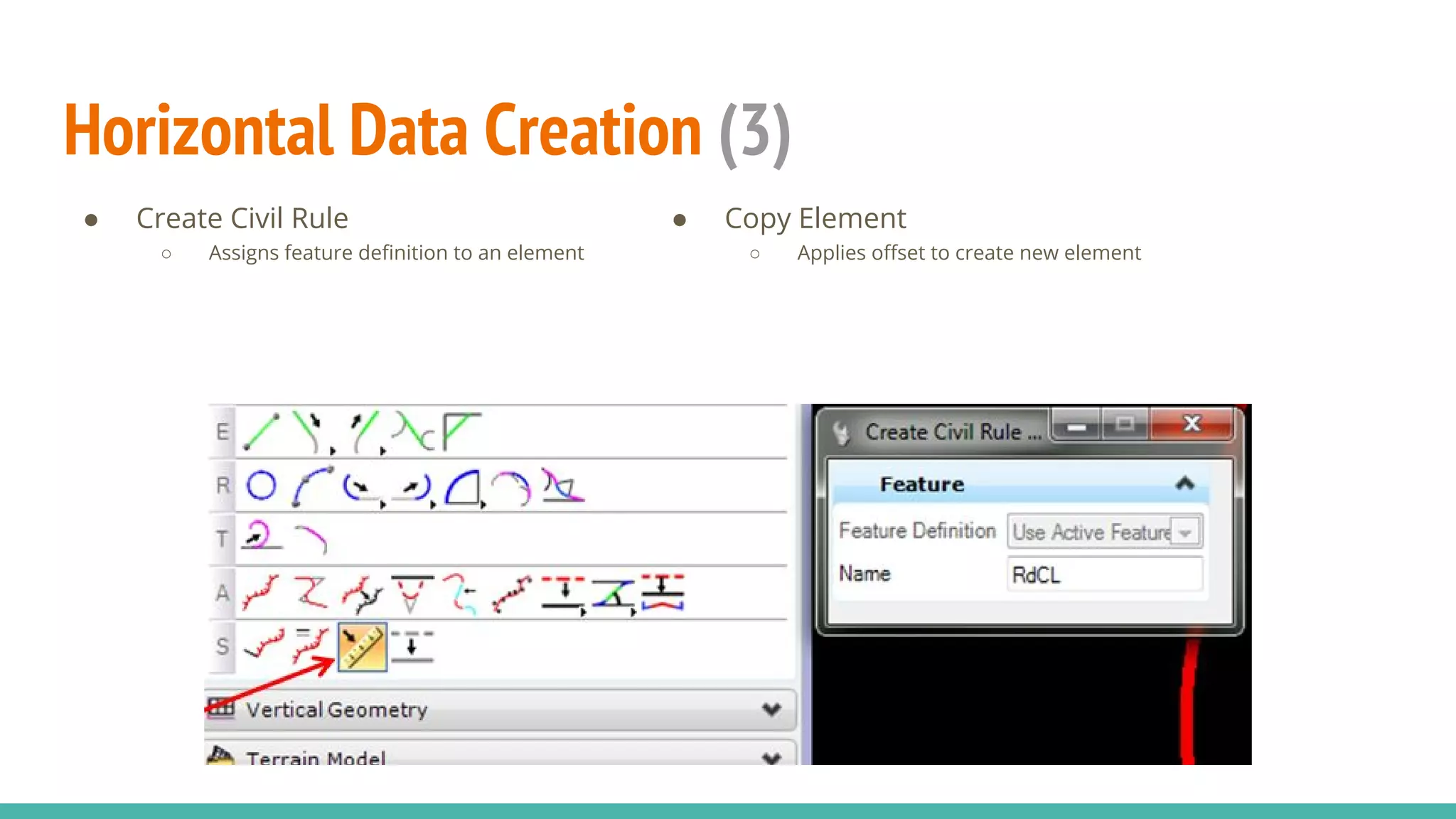
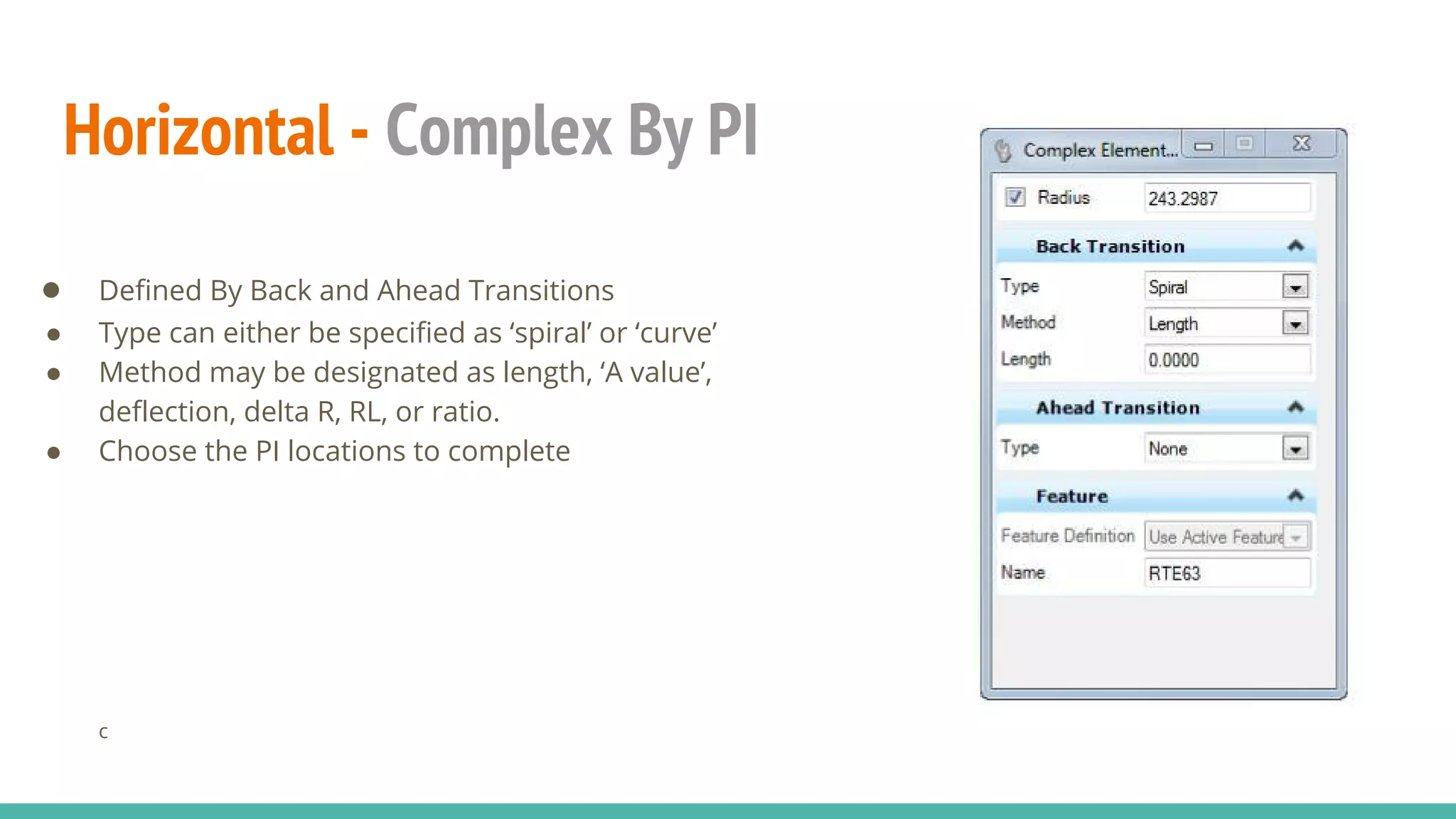
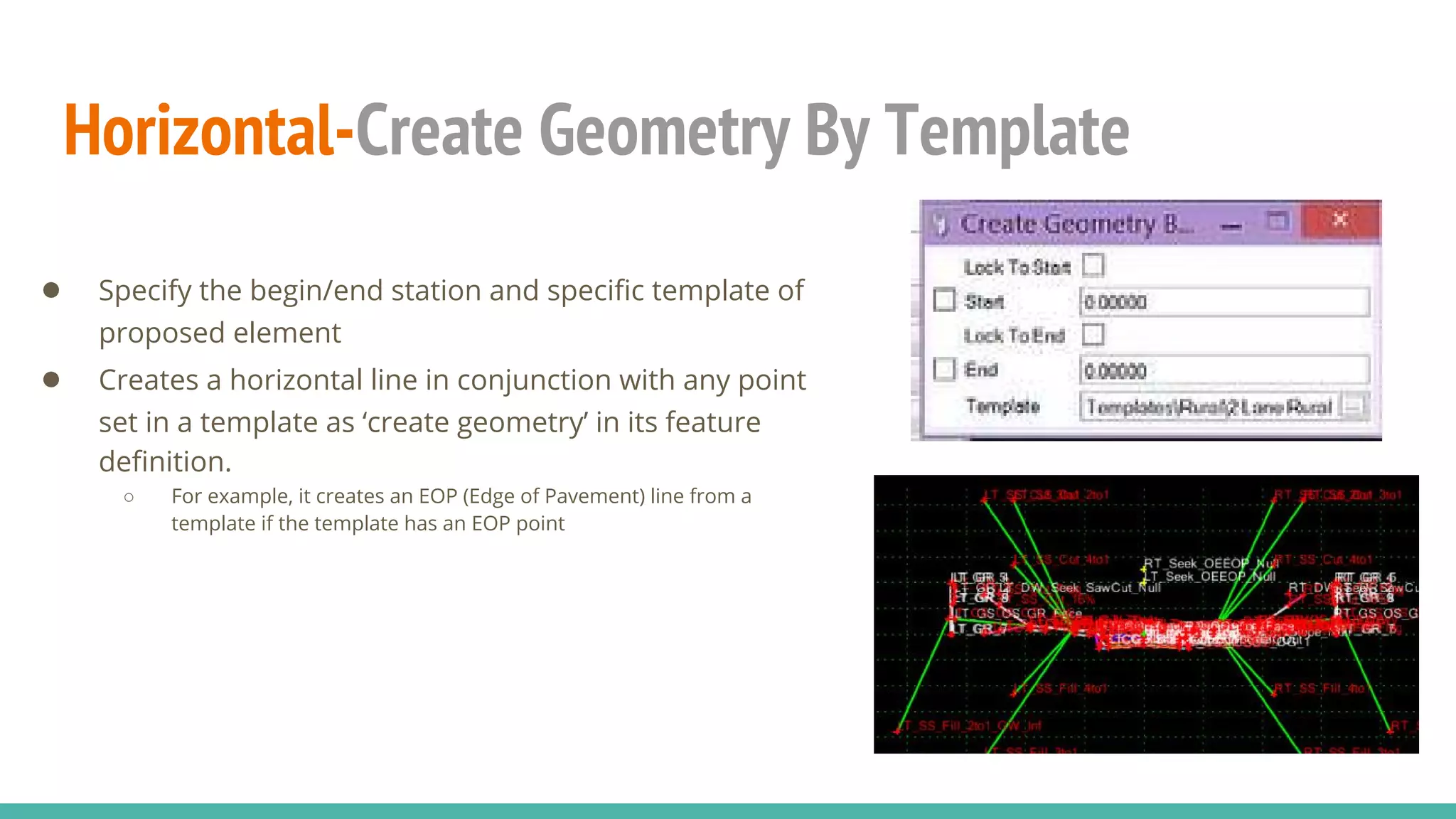
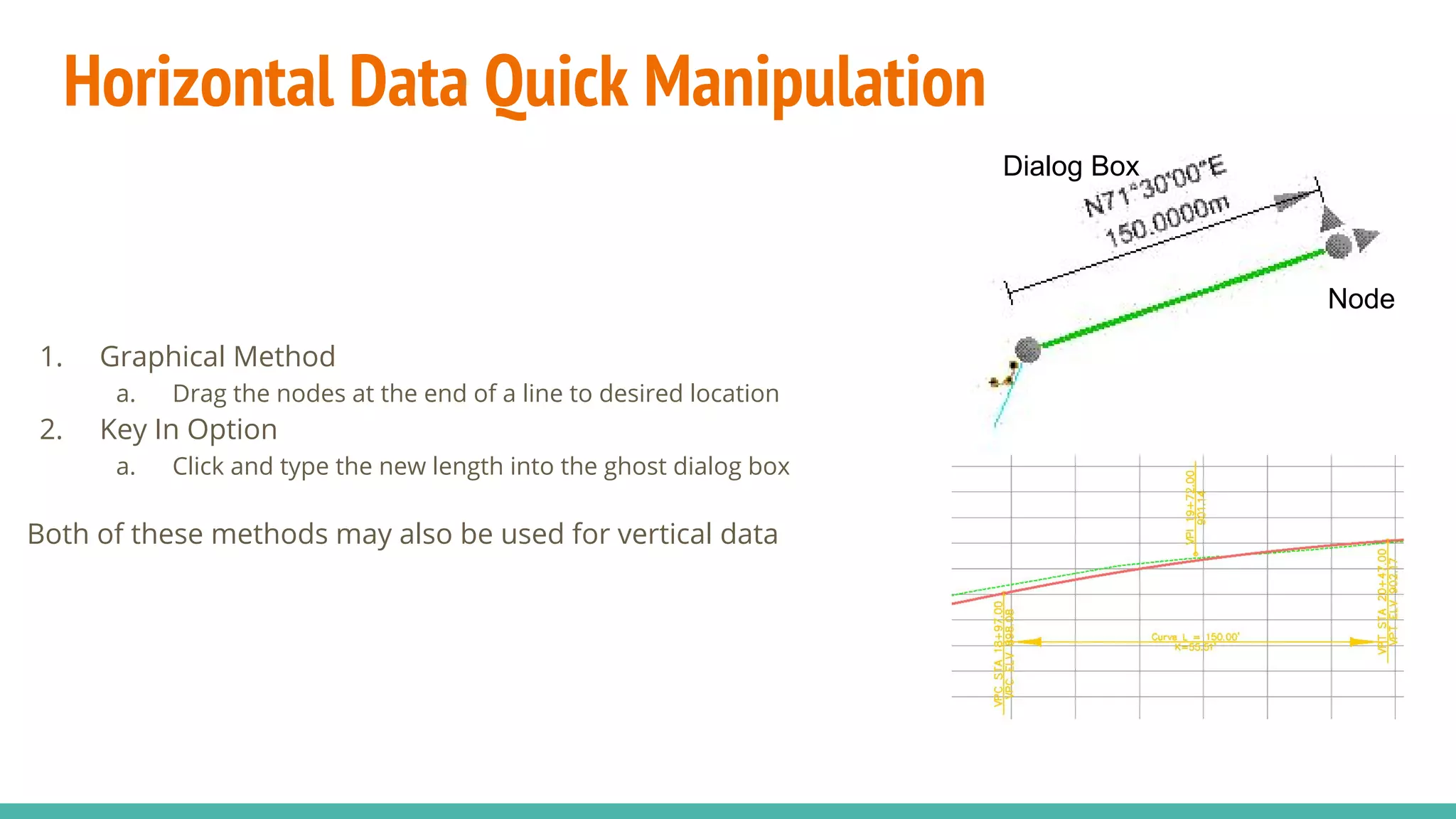
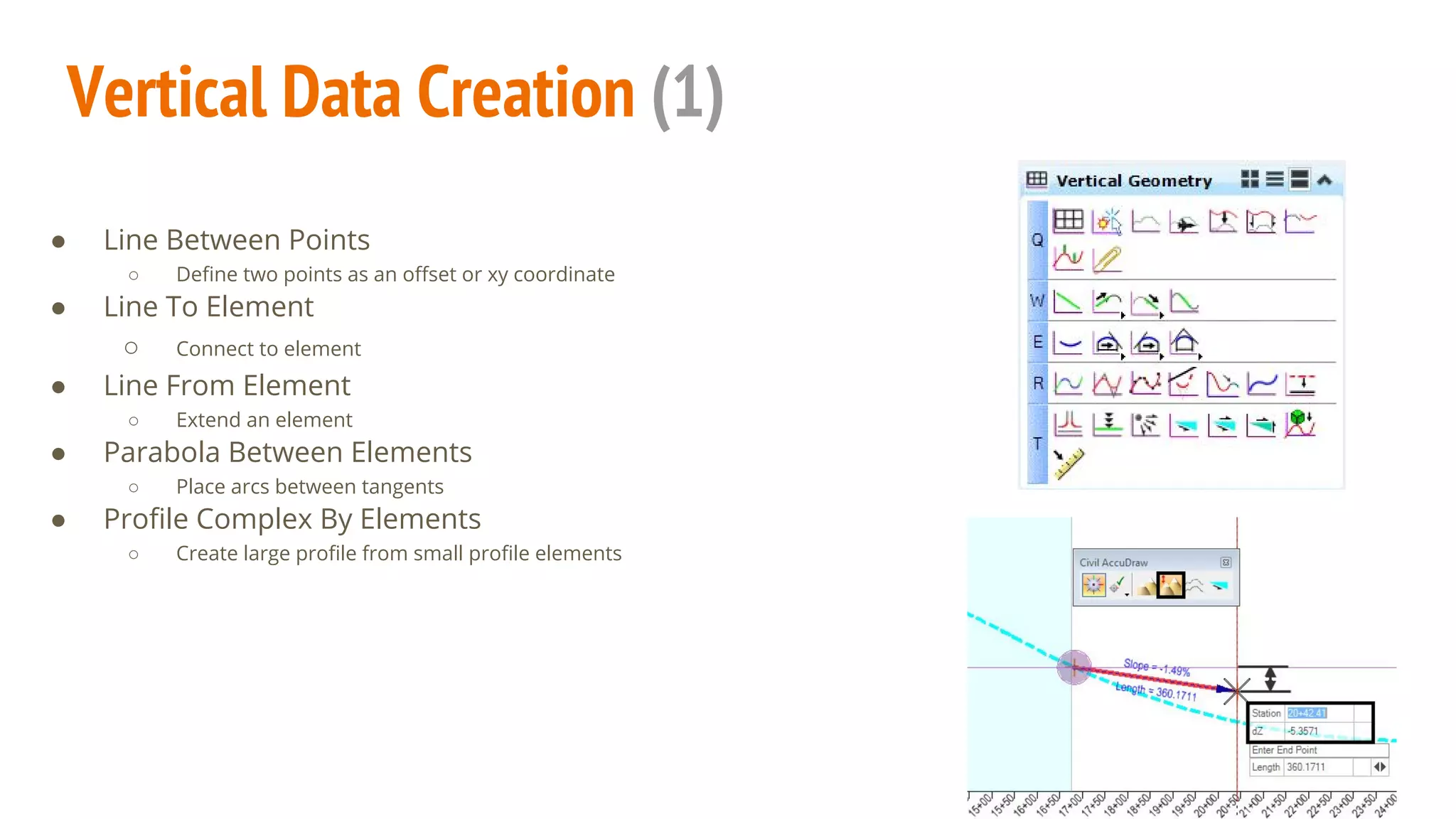
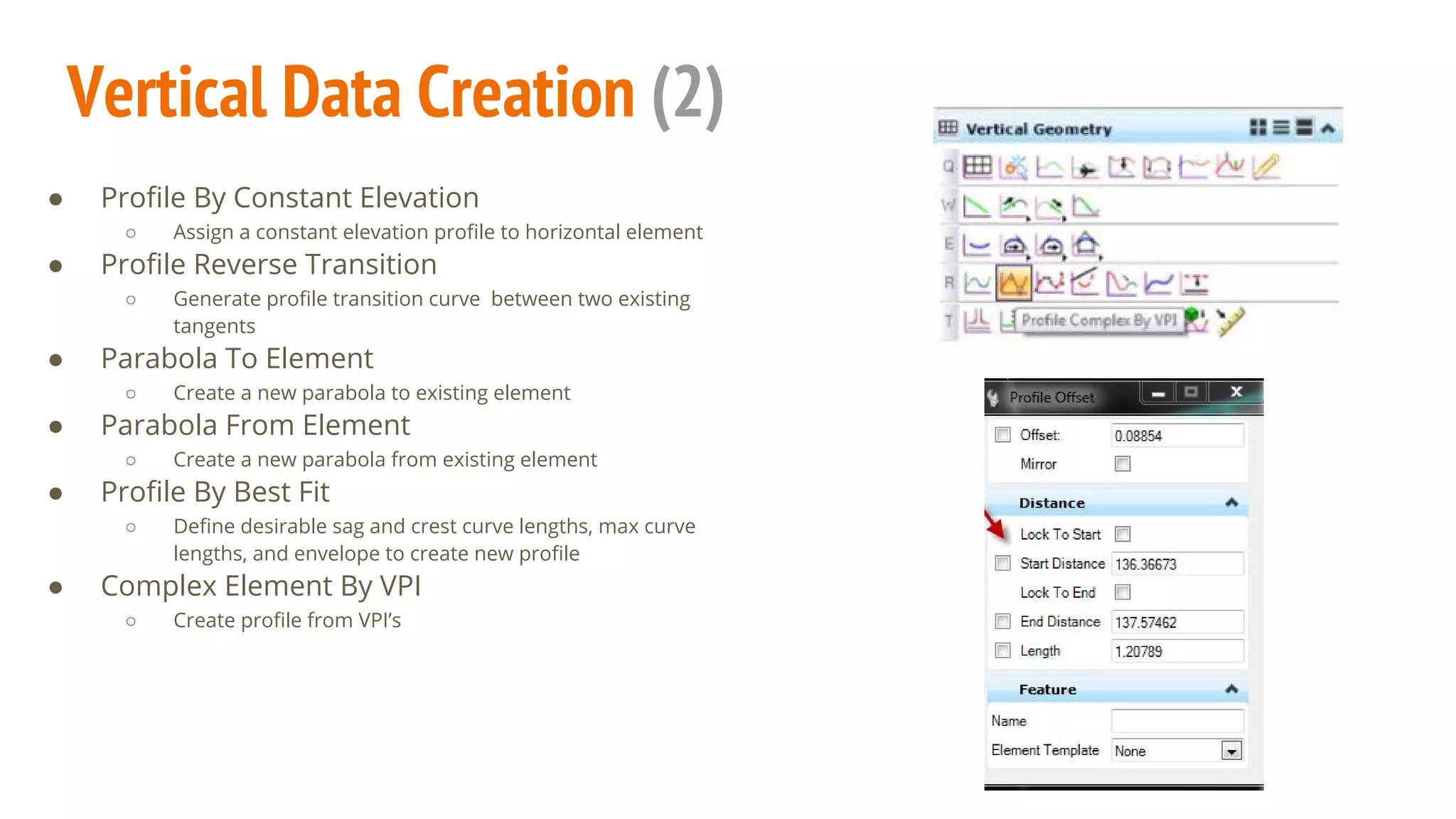
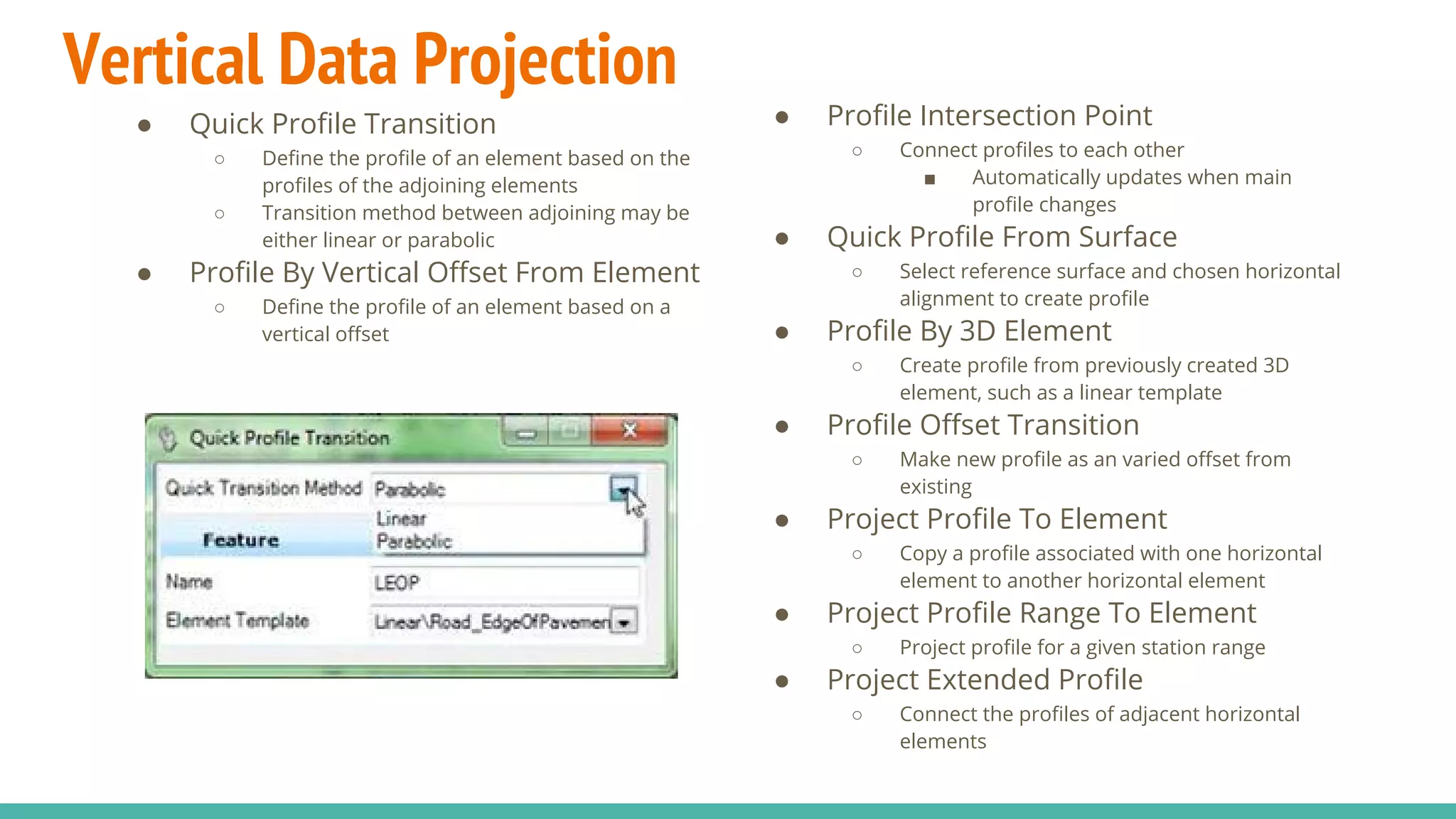
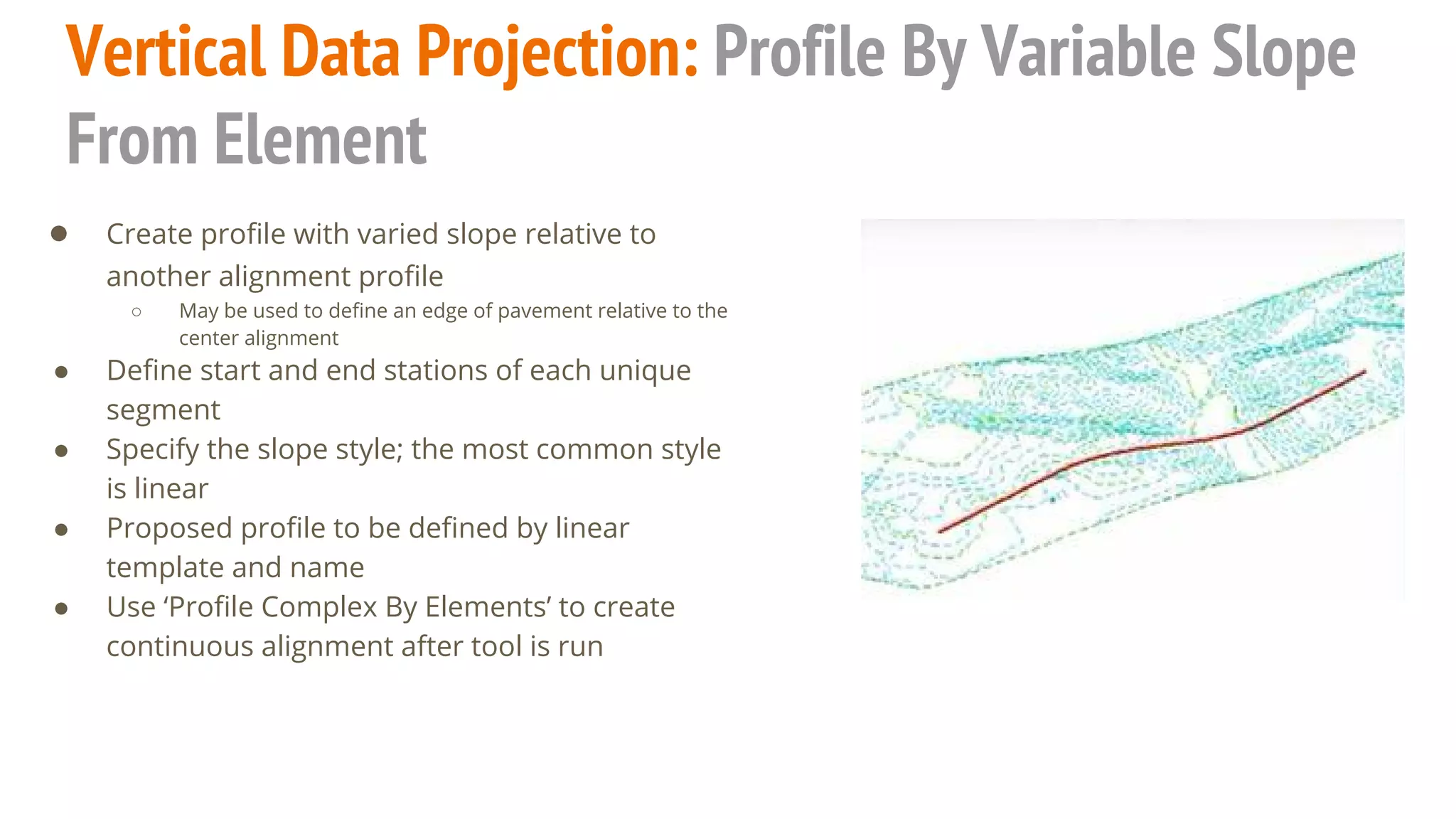
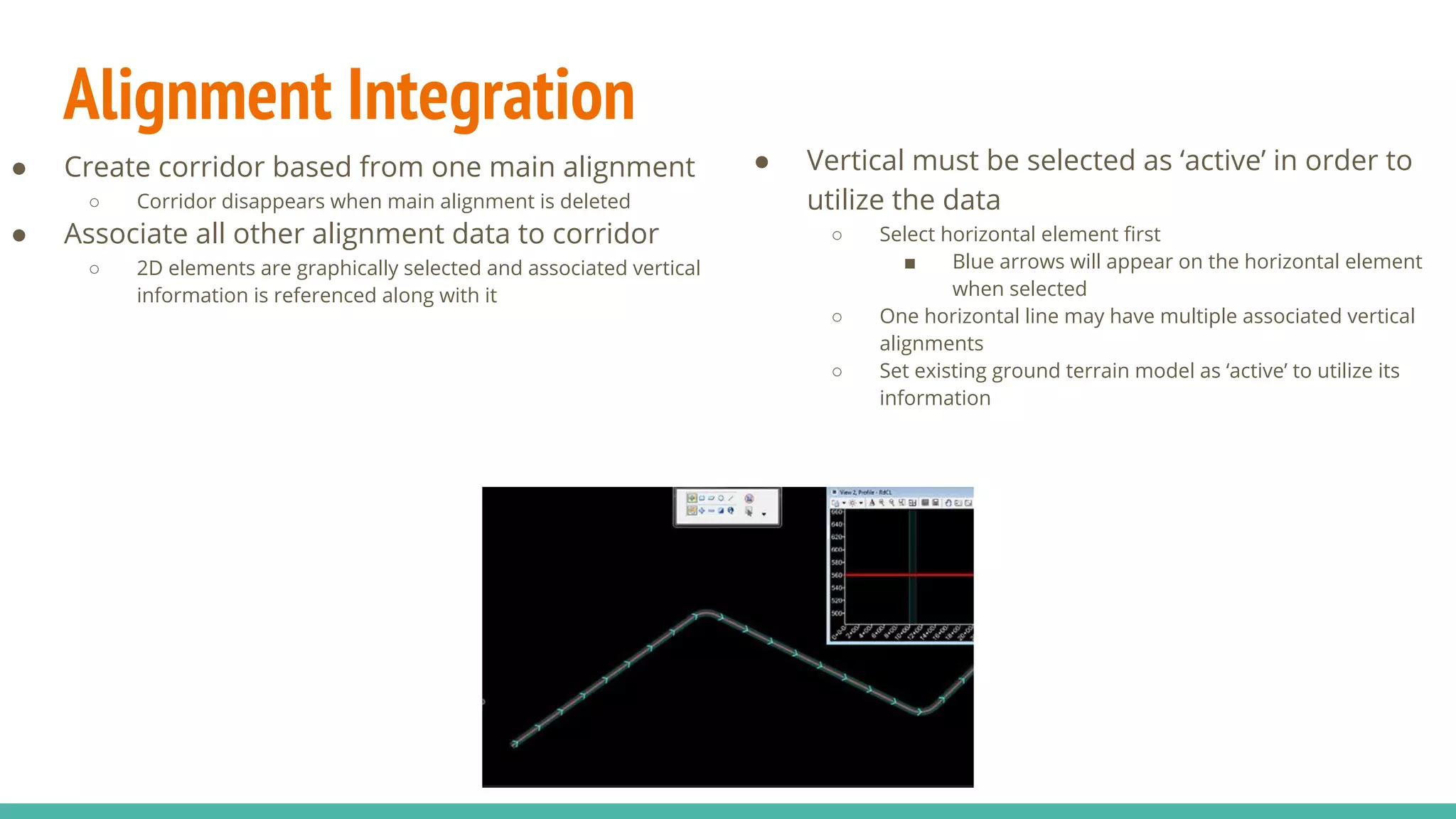
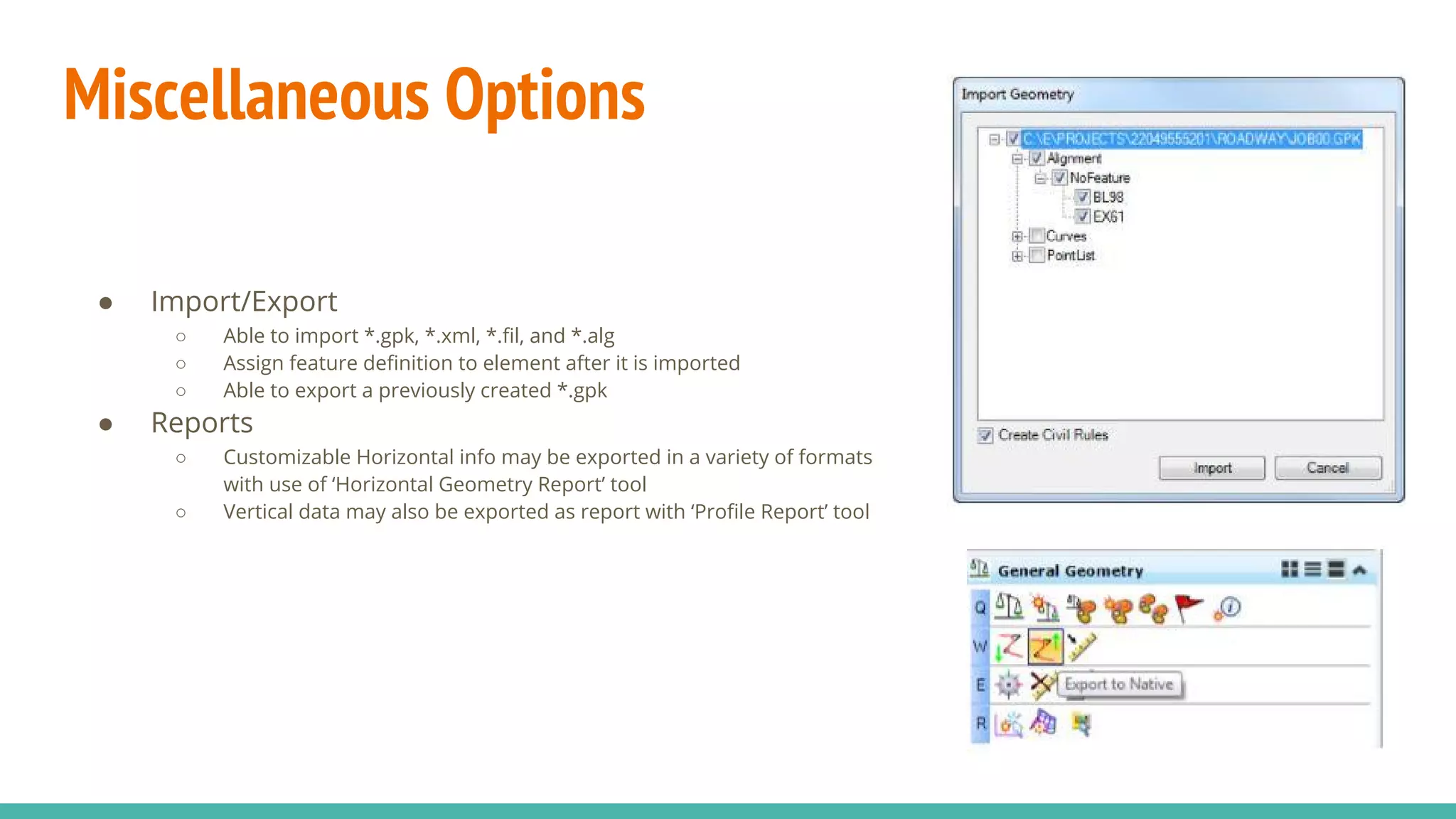
The document serves as a guide to the MicroStation SS4 Corridor Modeler, detailing various components involved in alignment data handling. It outlines features such as data creation, manipulation, and integration for horizontal and vertical alignments, along with methods for importing/exporting data and generating reports. The guide emphasizes the use of Civil AccuDraw for effective alignment design and manipulation.