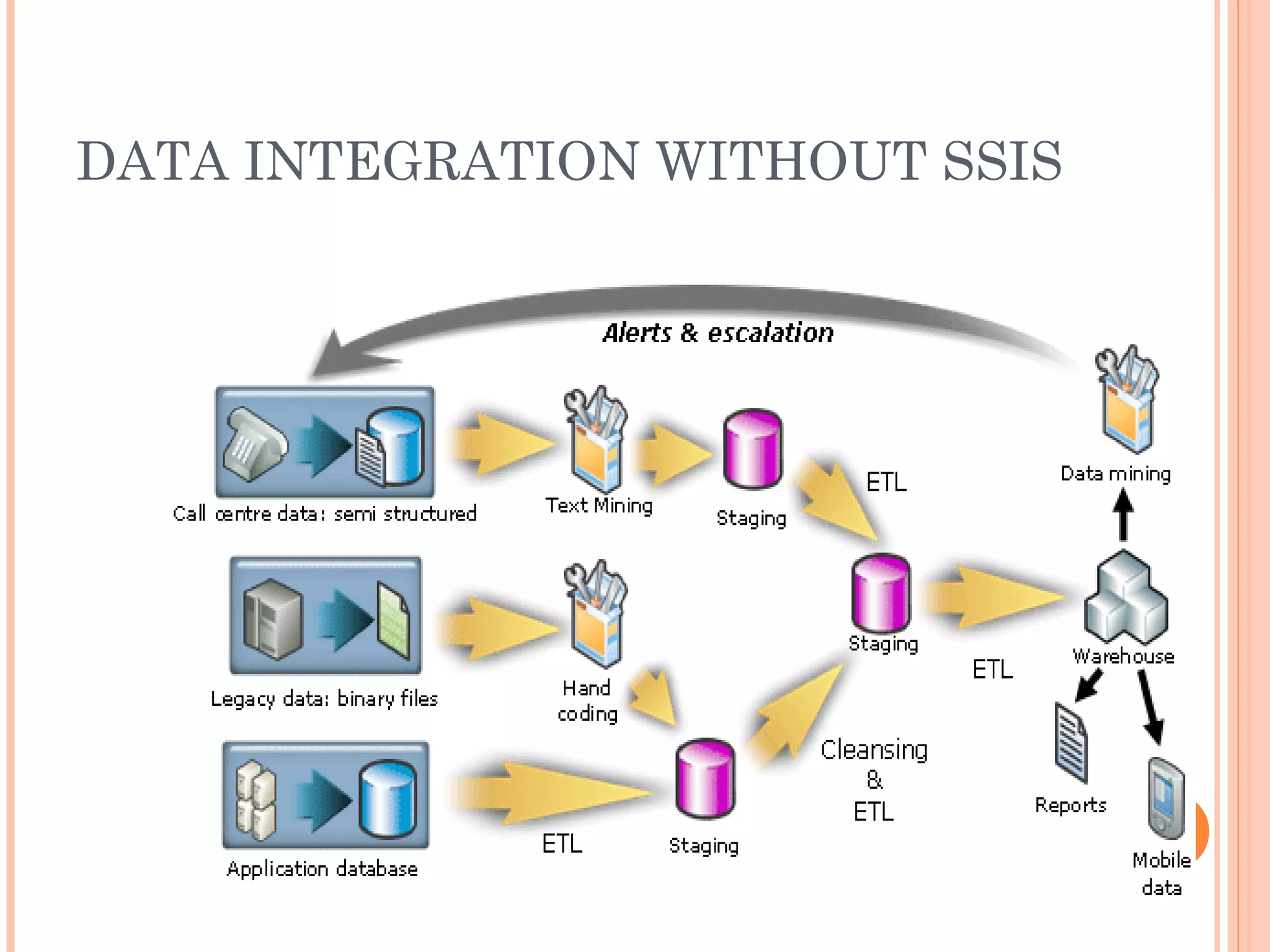
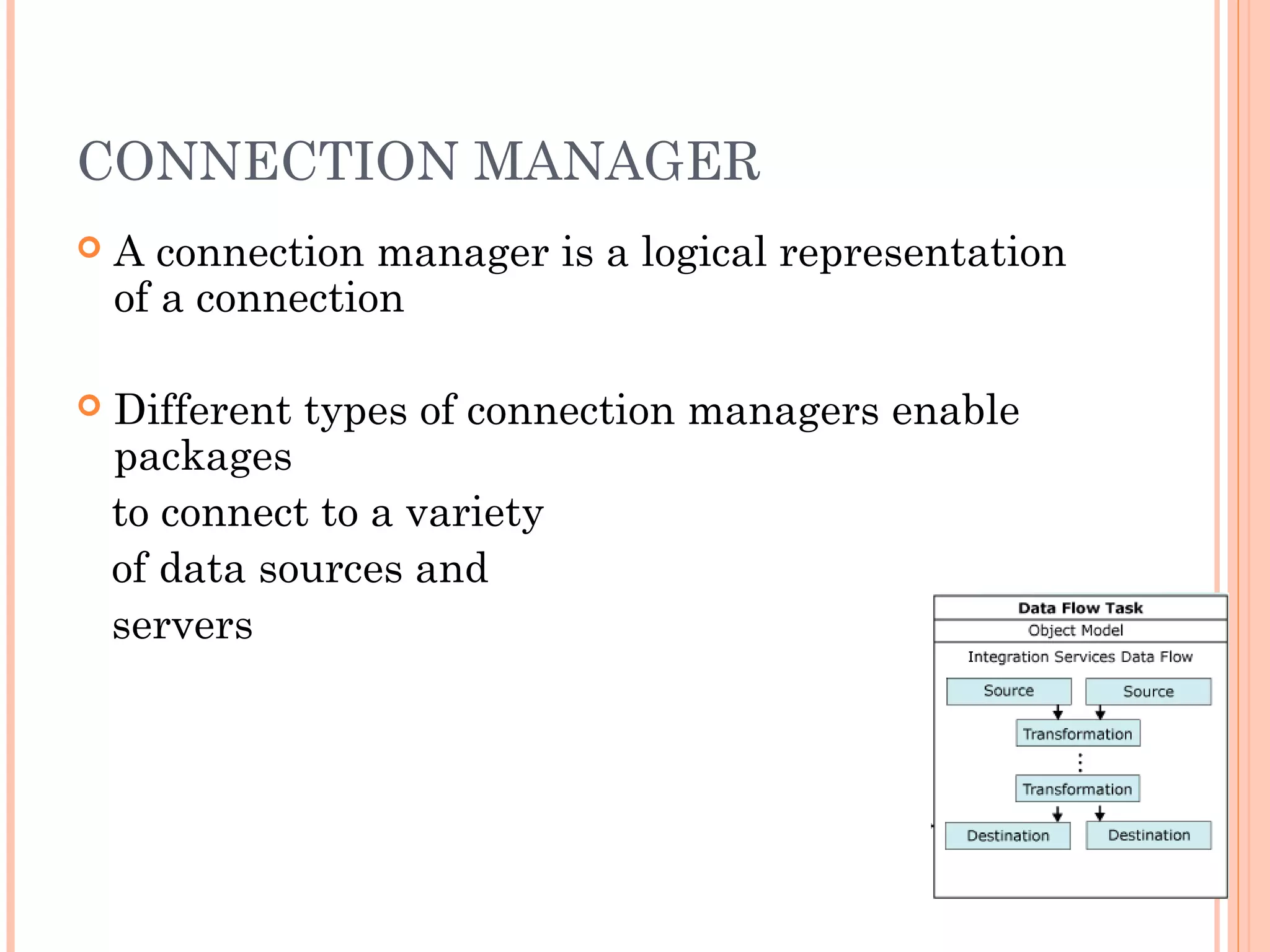
The document provides an overview of Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), emphasizing its role in data integration, transformation, and workflow solutions. It describes SSIS architecture, tools, and components such as data sources, connection managers, and package control flow. Additionally, it outlines development environments, execution methods, debugging features, and security measures related to package management.