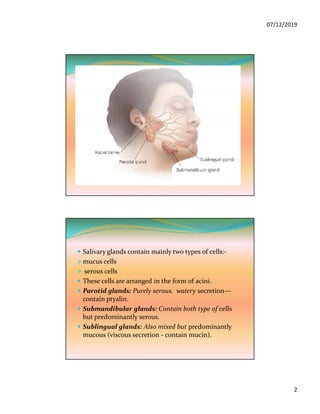
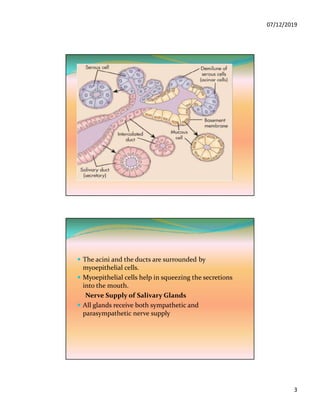
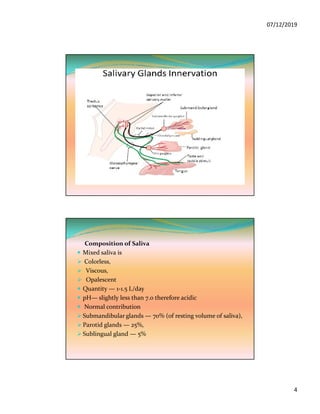
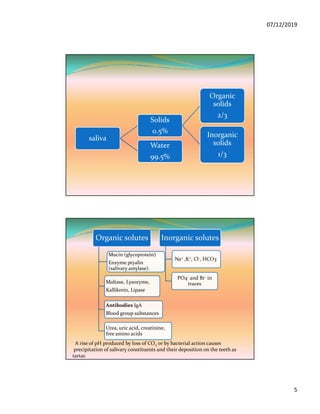
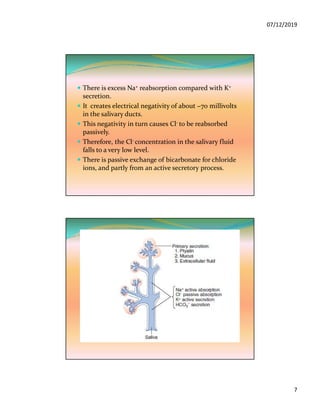
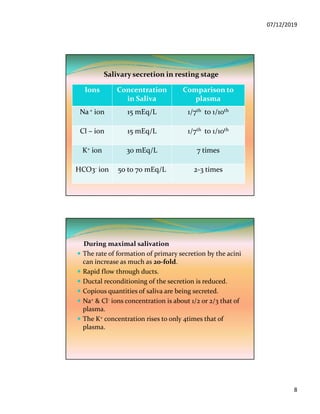
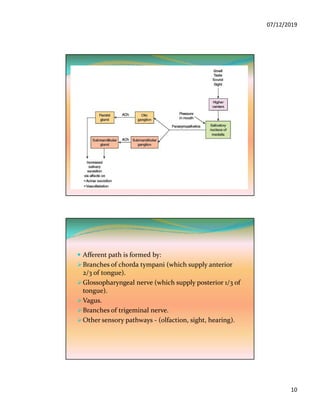
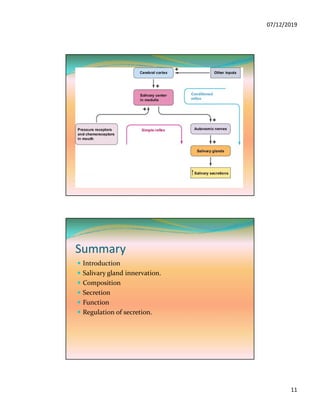
The document discusses the three pairs of major salivary glands, their cell types, secretions, and role in digestion. It describes how saliva is modified as it passes through the ducts via ion transport processes. Finally, it outlines the functions of saliva including lubrication, protection of teeth, and initial digestion of starches through the enzyme ptyalin.