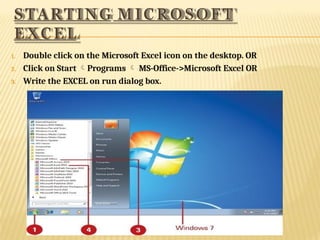
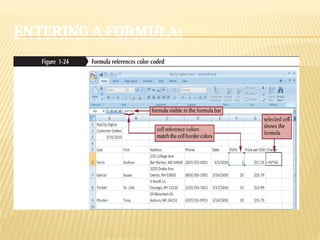
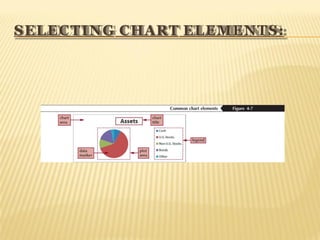
Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool for creating spreadsheets and performing data analysis with features like data entry, formulas, and charts. The program includes a user-friendly interface with a title bar, menu bar, and various toolbars for efficient command access. Users can insert, delete, and modify cells and use functions to perform calculations, alongside options to create and format charts for data visualization.