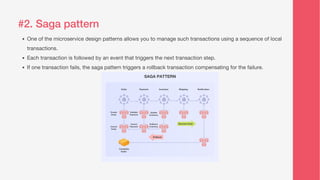
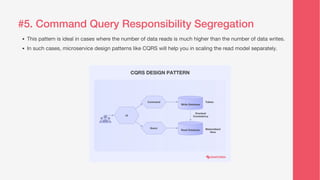
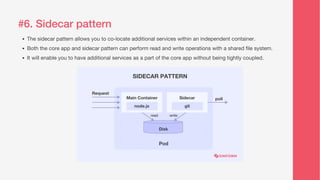
This document discusses various microservice design patterns that can be employed for business applications, including the strangler pattern, saga pattern, aggregator pattern, event sourcing, command query responsibility segregation (CQRS), sidecar pattern, and database per microservice. Each pattern serves a specific function in managing transactions, aggregating services, handling data operations, and improving scalability. The document emphasizes the importance of using independent components and databases to avoid tight coupling and enhance system reliability.