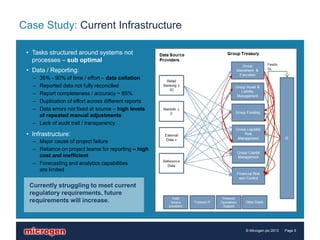
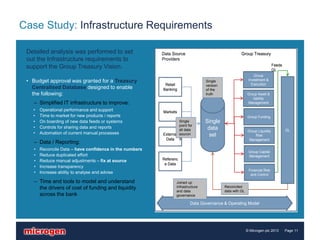
This document discusses the challenges that Basel III regulations present for liquidity management and reporting. It outlines the goals of more stringent liquidity requirements in Basel III, and why early and granular analysis of balance sheet, funding sources, collateral and more will be needed. It also discusses how to turn liquidity reporting into a valuable business asset that supports both regulatory compliance and day-to-day decision making. A case study further illustrates these points by showing how one organization addressed their liquidity reporting challenges through a new centralized database infrastructure.