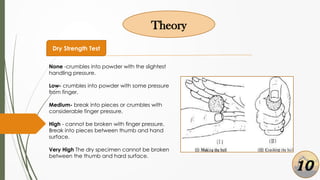
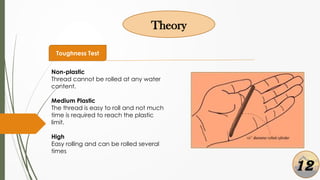
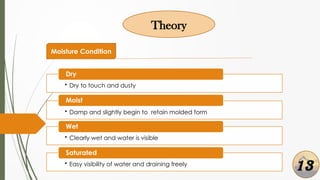
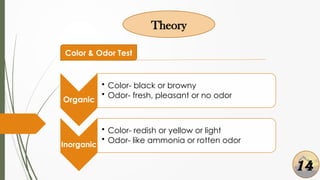
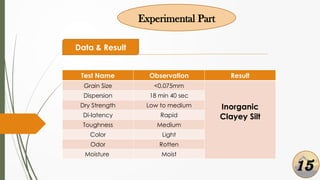
The document presents a presentation on soil identification techniques within the field of geotechnical engineering by students from Mymensingh Engineering College. It covers various tests and classifications for determining soil characteristics essential for construction. The conclusions highlight the importance of practical observation of soil, emphasizing that although it provides initial insights, precise soil testing is crucial for accurate results.