Embed presentation
Download to read offline



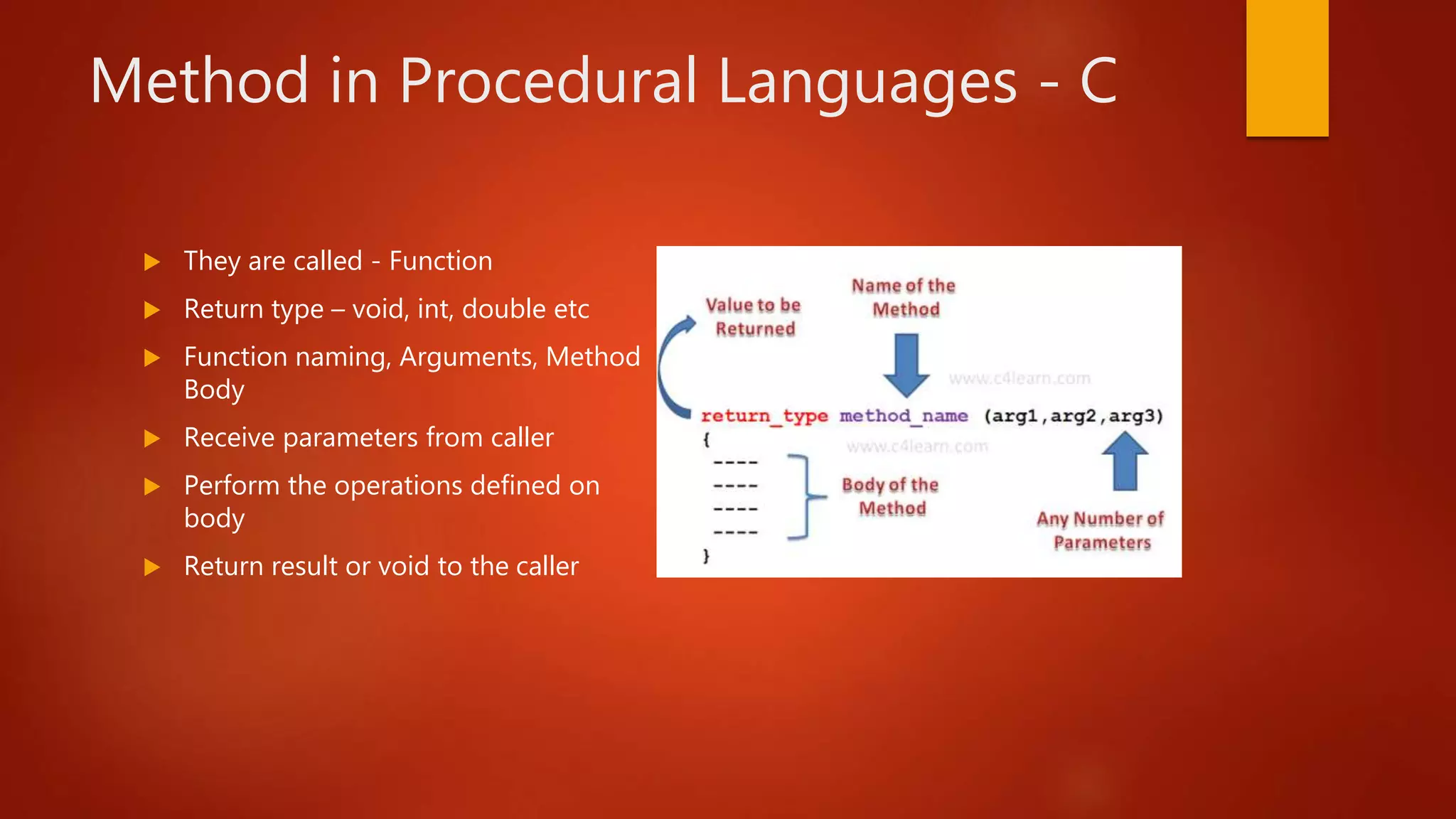



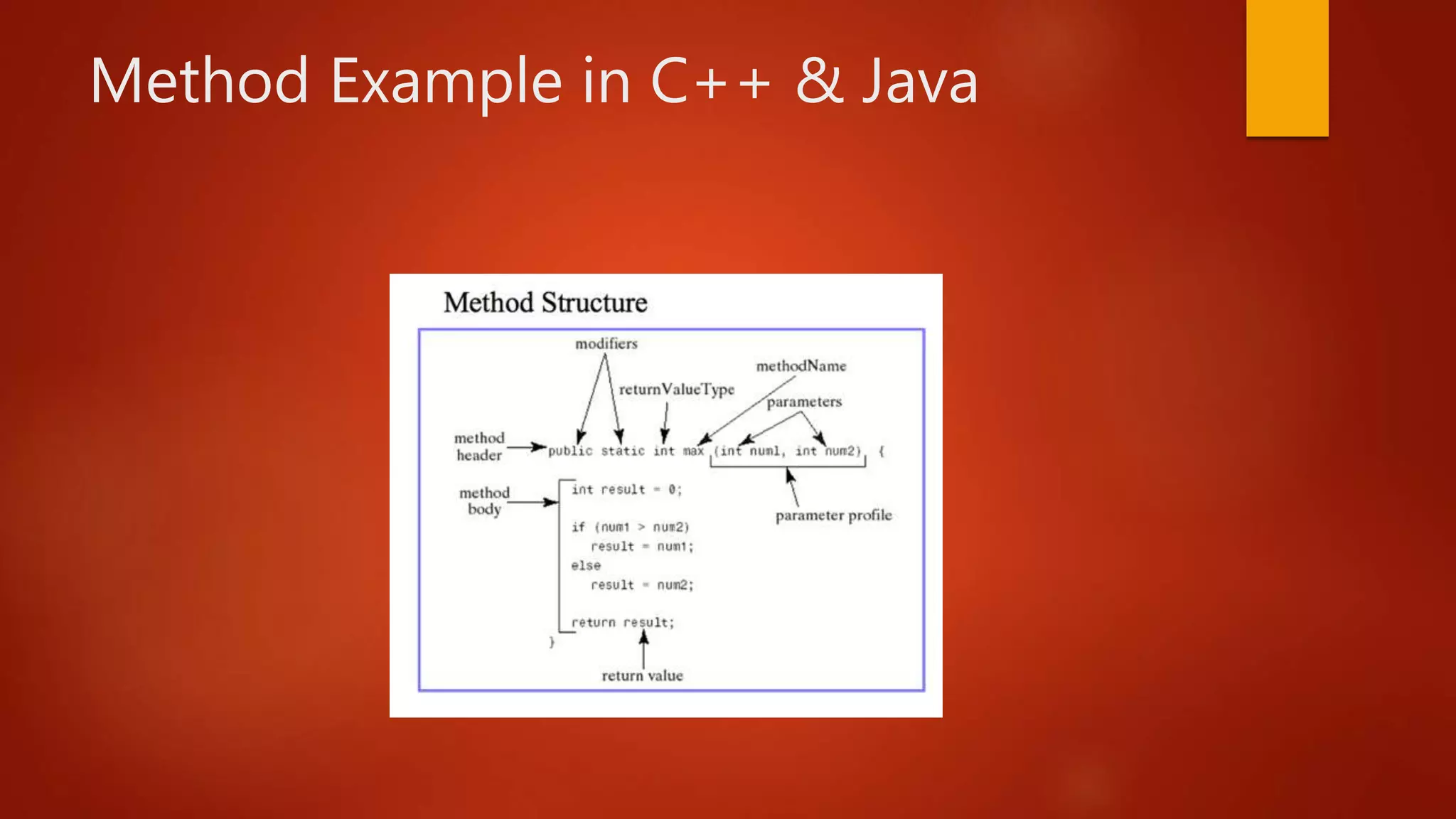

A method is a block of code that defines the behavior of an object or procedure. Methods contain a return type, name, arguments, and body of code. In procedural languages like C, methods are called functions, while in object-oriented languages like C++ and Java, methods define an object's behaviors. Methods allow for code reusability, abstraction, recursion, readability, and simplification. They receive parameters from a caller, perform defined operations, and return a result or void.








