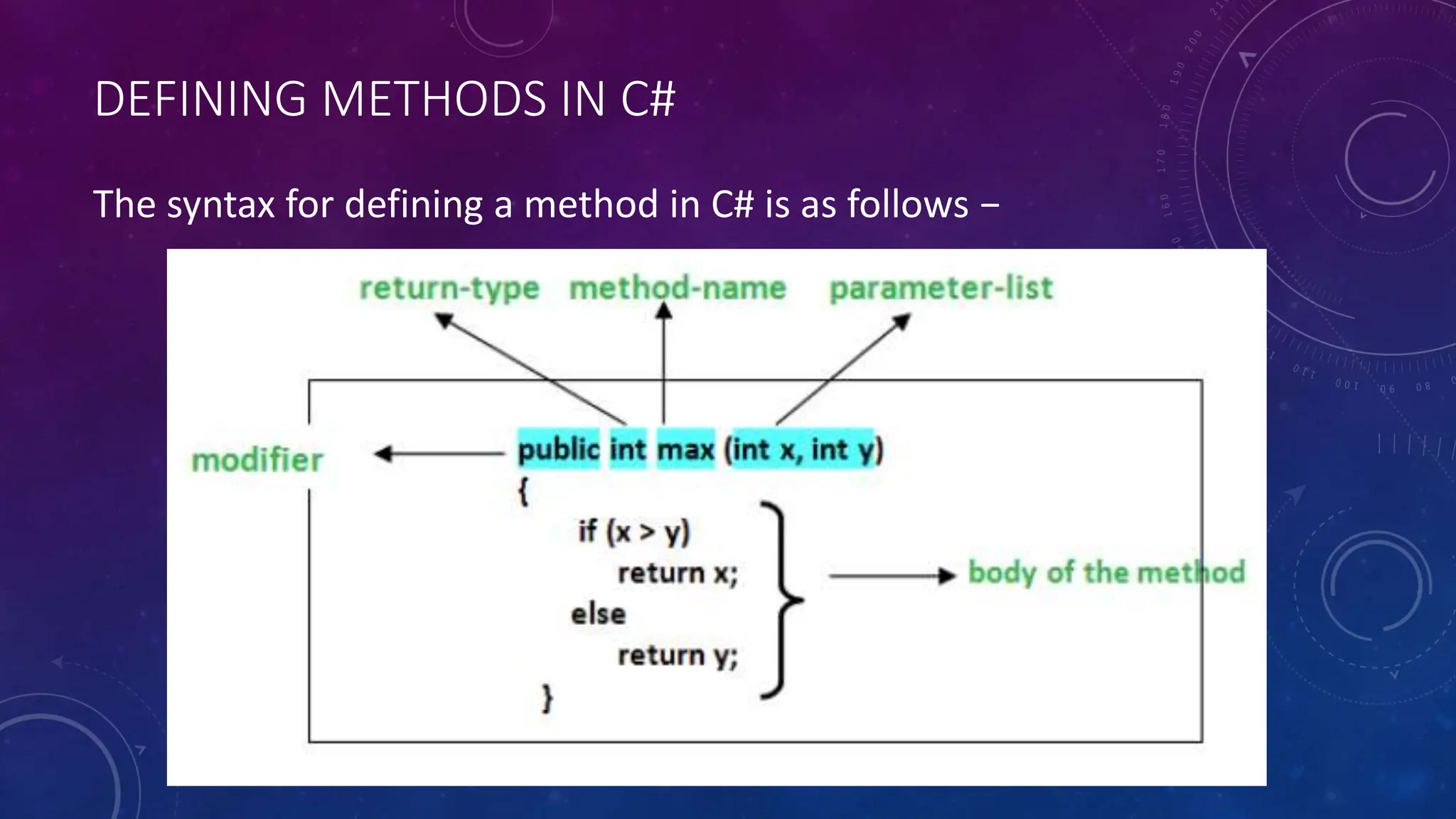
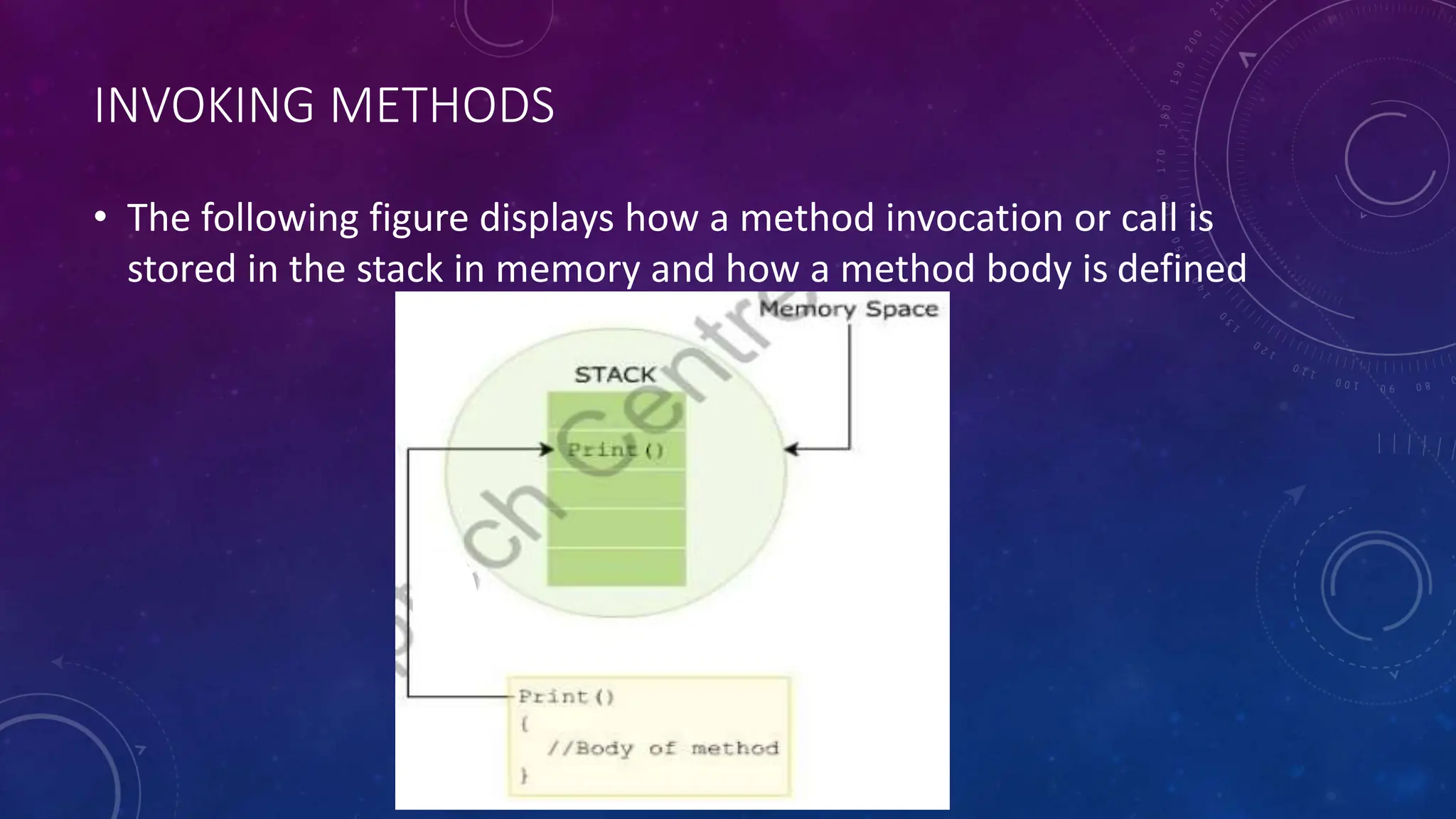
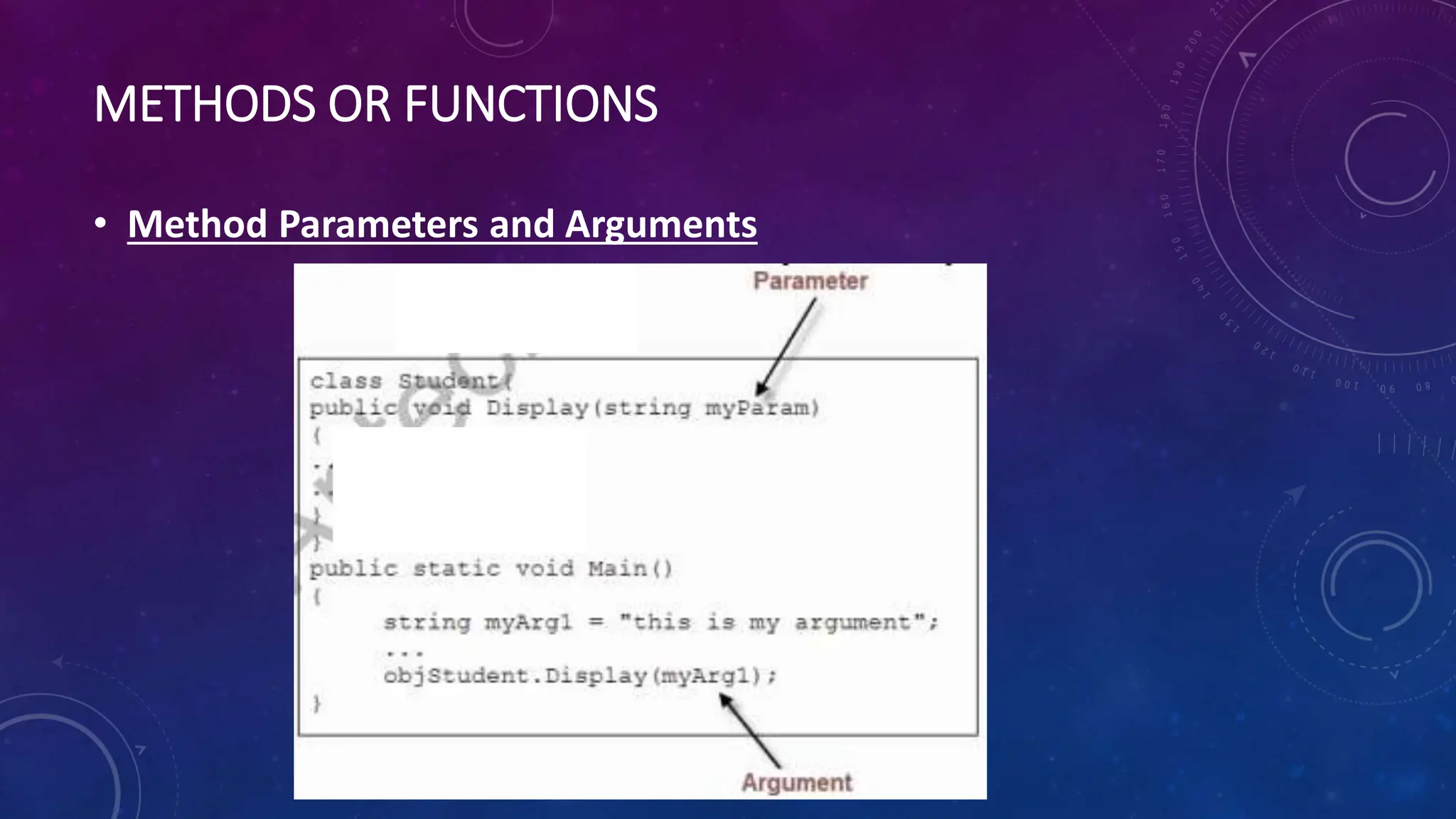
Methods in C# are blocks of code that perform specific tasks. They can take parameters and may or may not return values. The syntax for defining a method includes access modifiers, return types, names, and parameter lists. Methods are invoked by calling the method name from another method. Parameters pass data into methods while arguments are the actual values passed during a method call. Methods make programs more reusable, readable, and optimized.