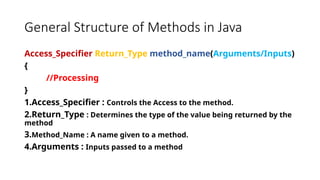
This document explains methods in Java, defining them as blocks of code designed to perform specific tasks and process data. It outlines the general structure of methods, types based on return values and arguments, and how methods can be called from classes or objects. Examples illustrate various method types and the necessary components for calling methods effectively.