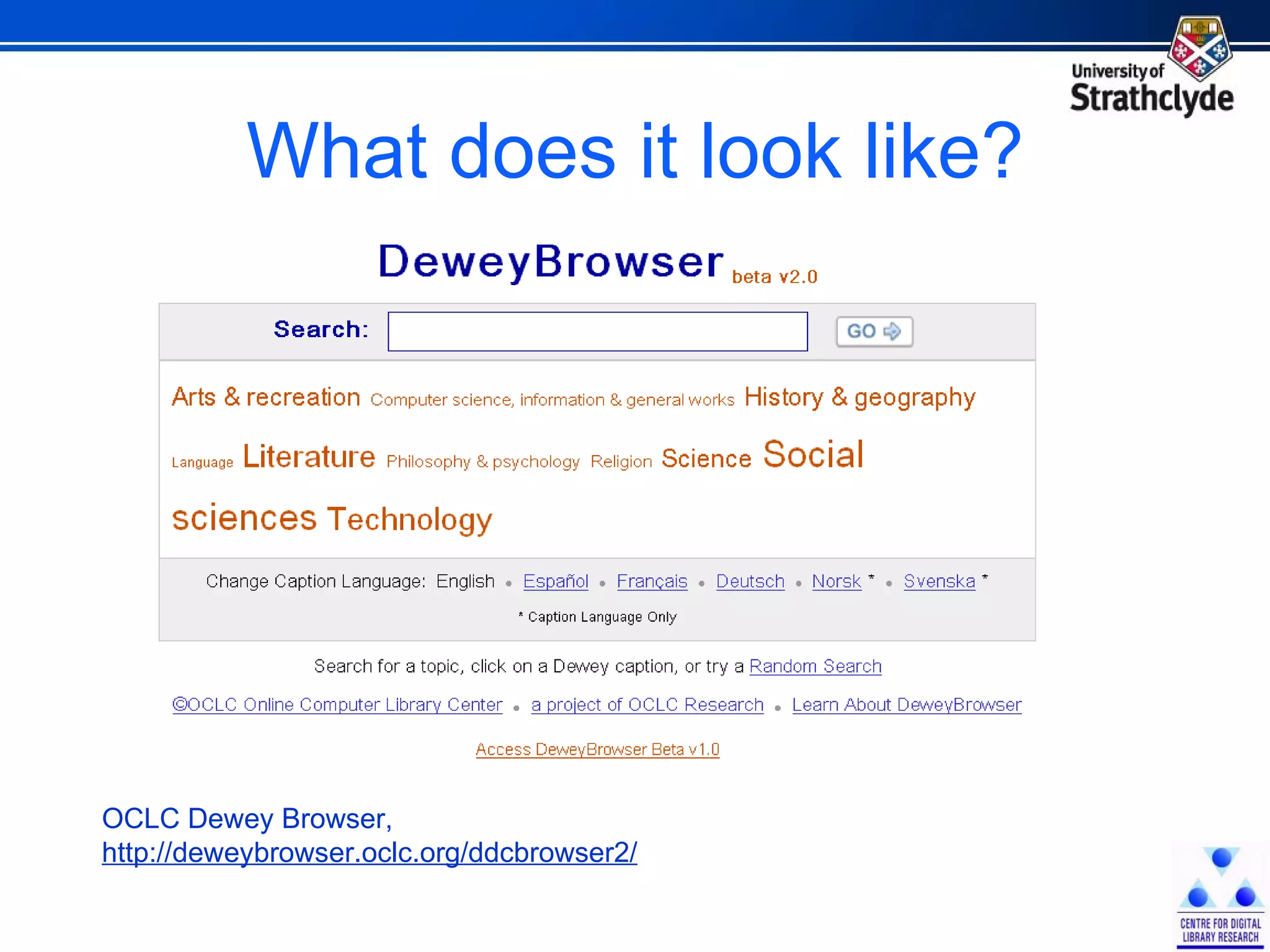
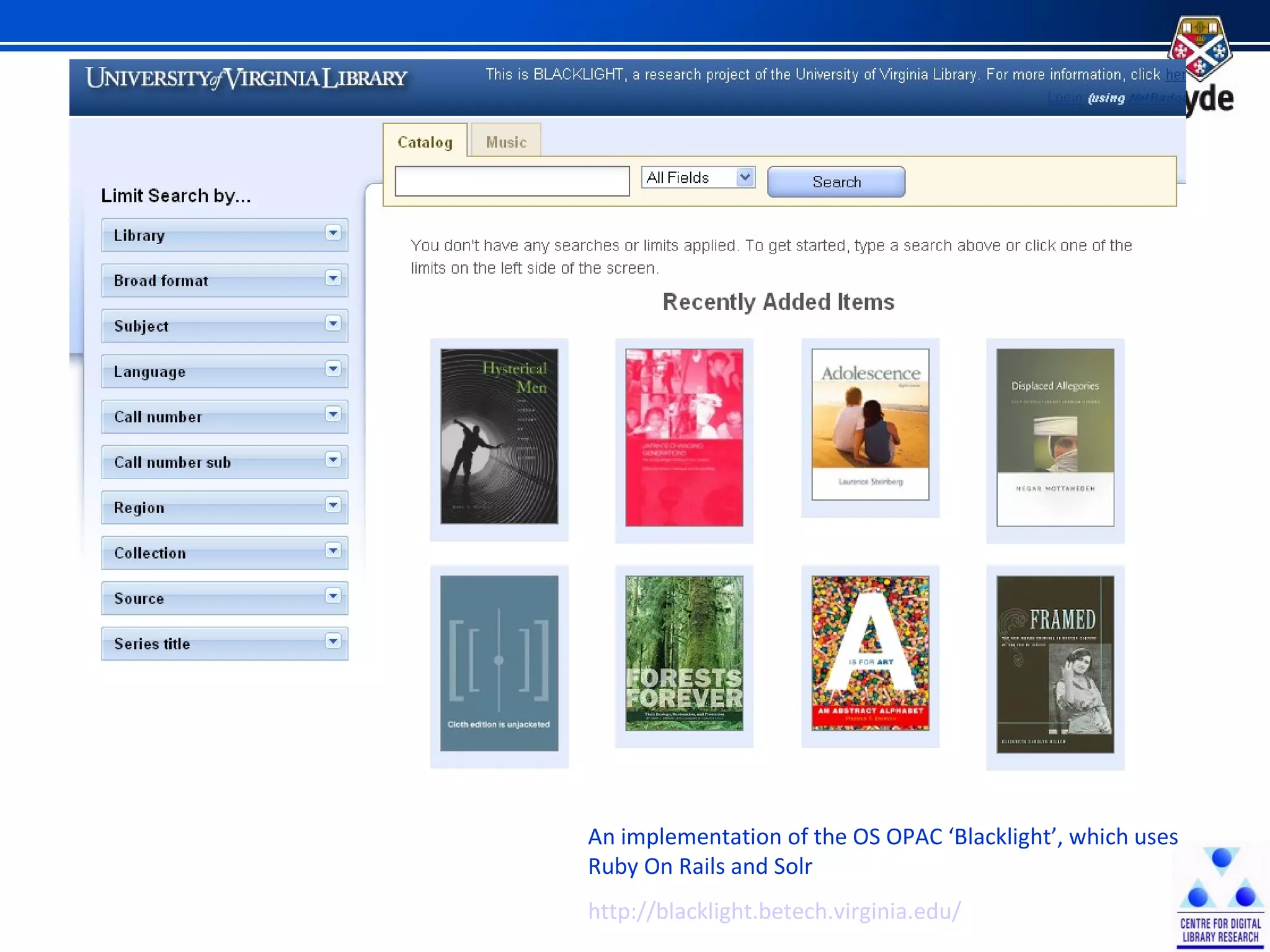
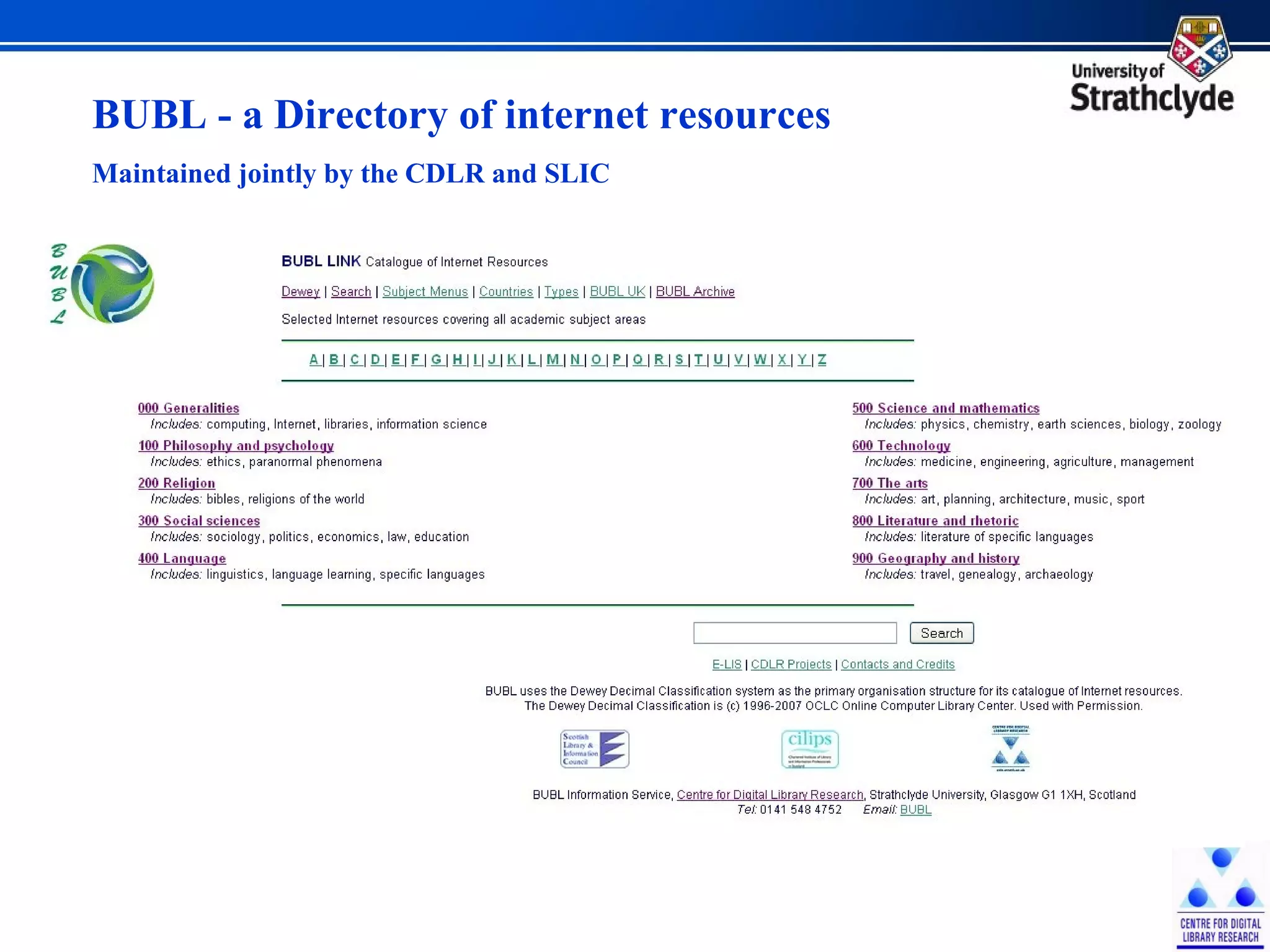
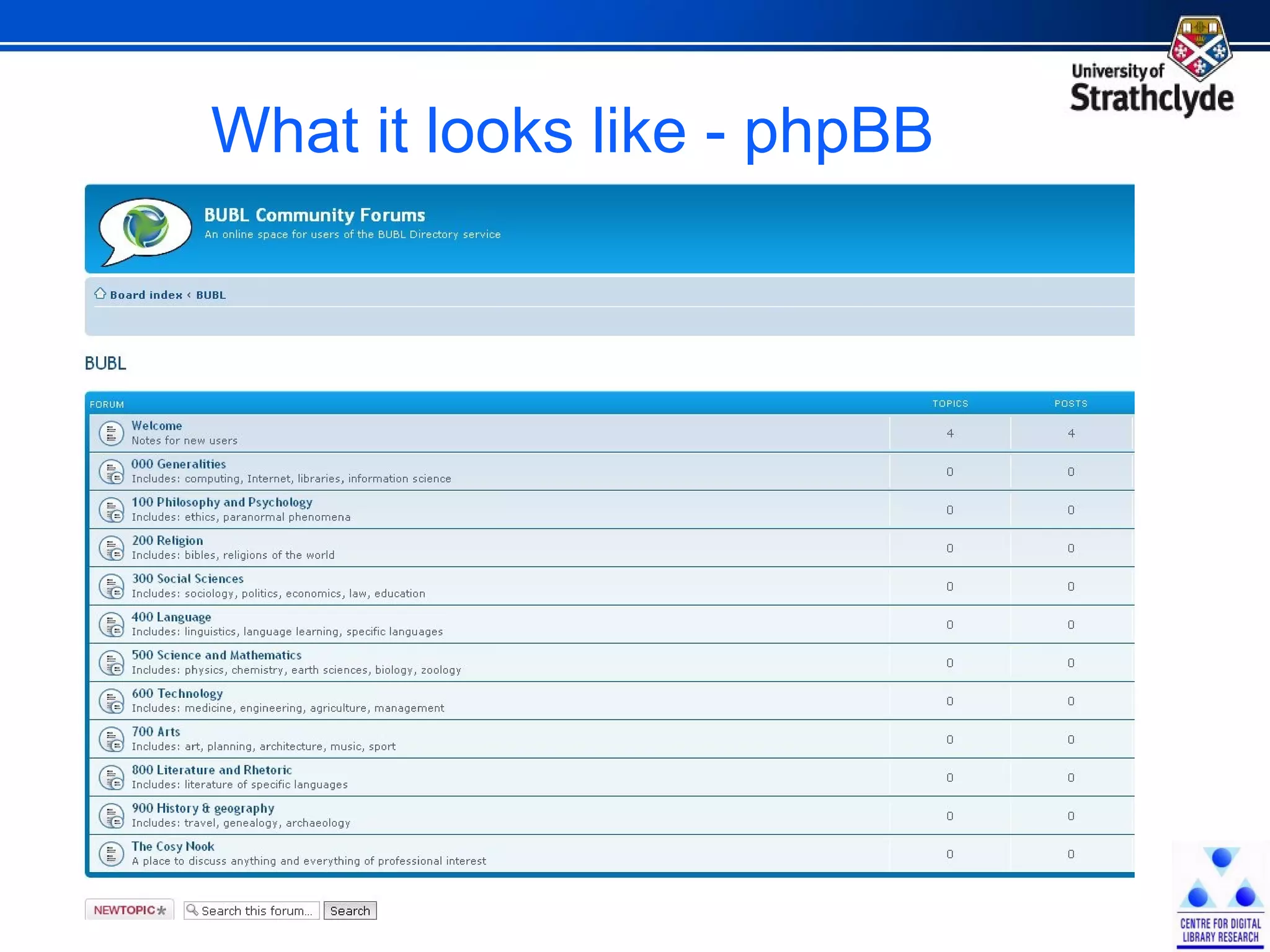
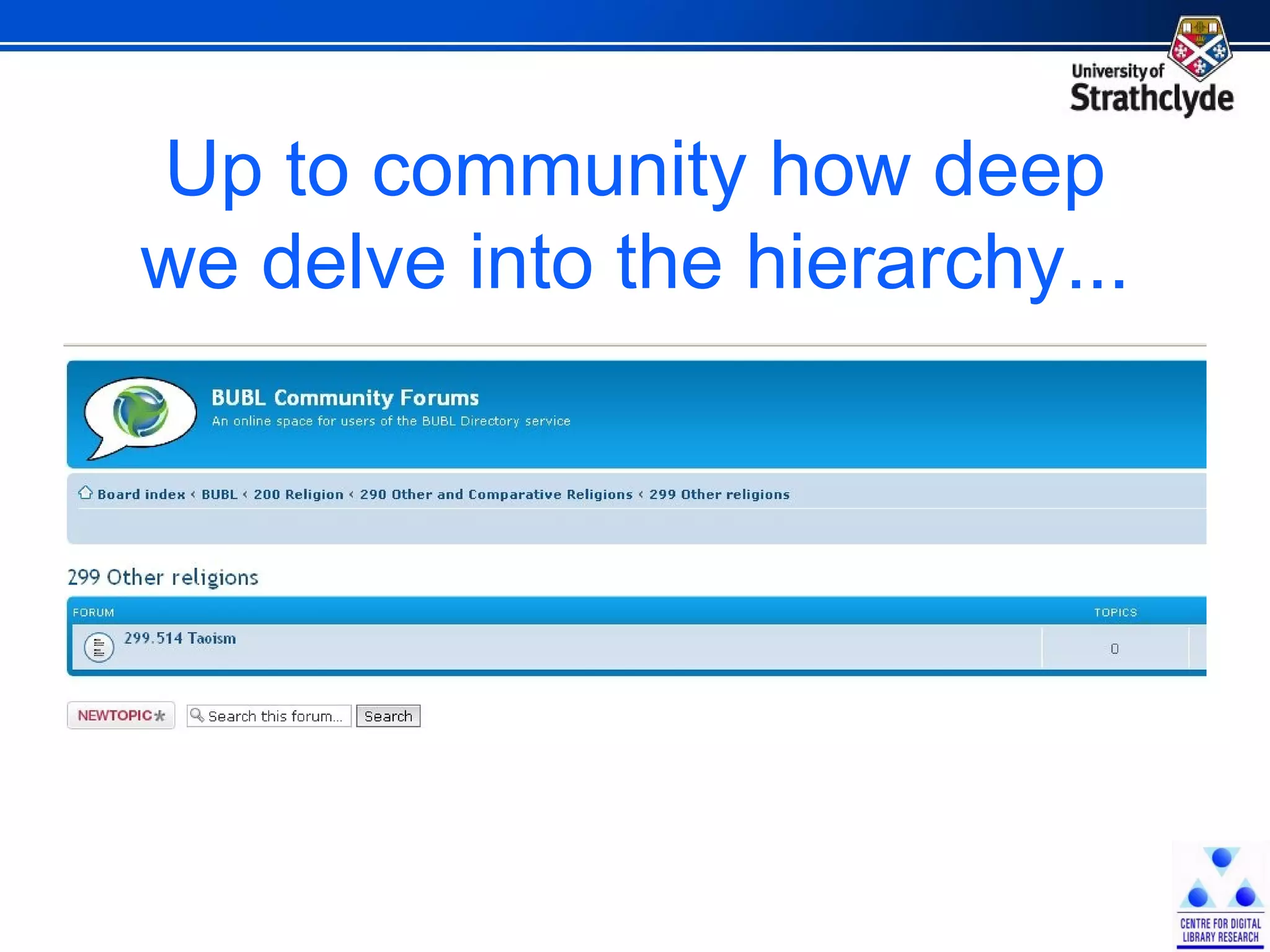
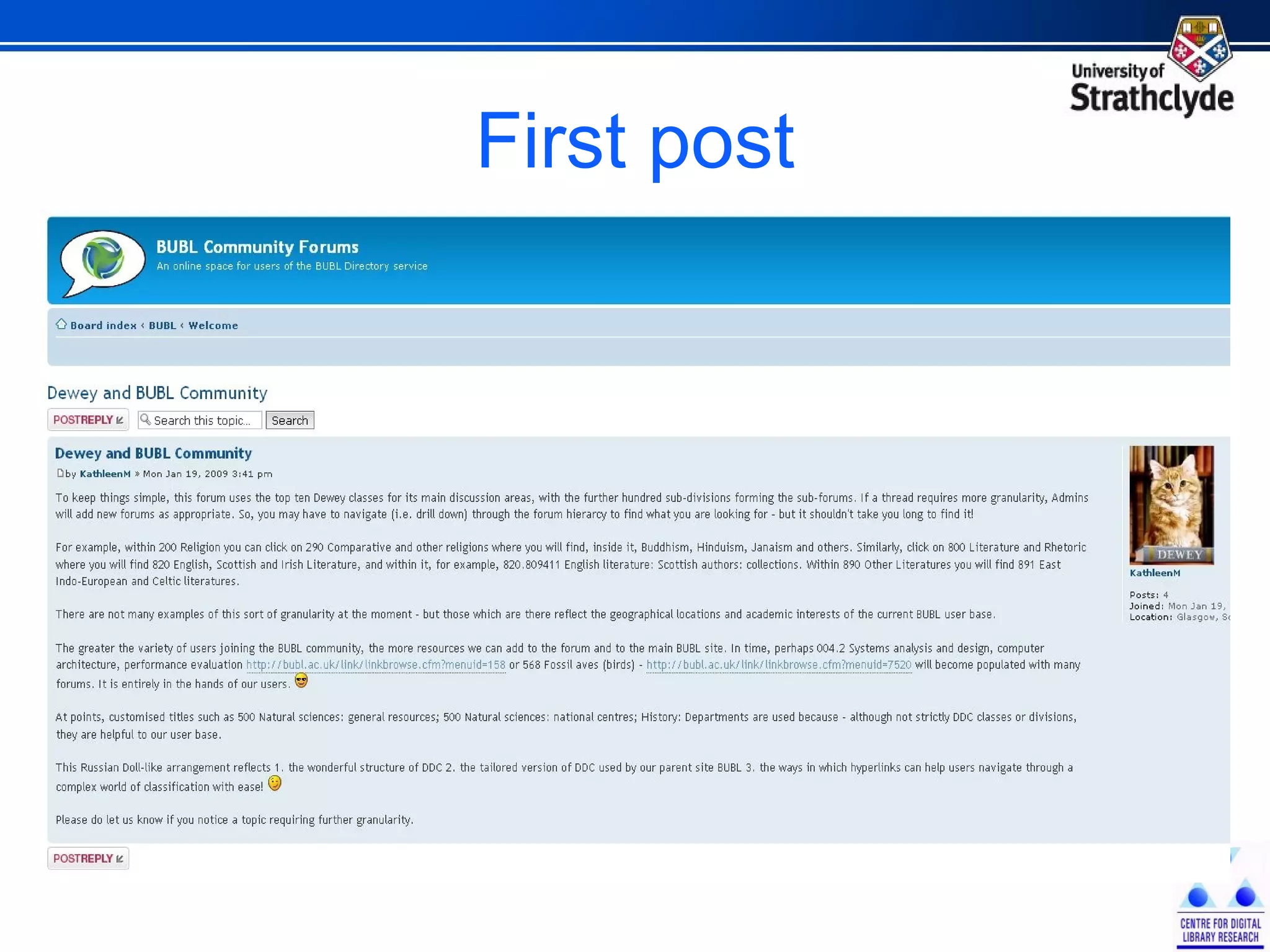
The document discusses the development of Scotland's Information Landscape (SIL) and the integration of Web 2.0 technologies to enhance library and information services. It emphasizes the role of user contributions, collaboration, and the use of metadata and folksonomies to improve accessibility and relevance of information resources. Examples include the BUBL directory project and the HILT service, which aim to foster community engagement and streamline information retrieval in libraries.