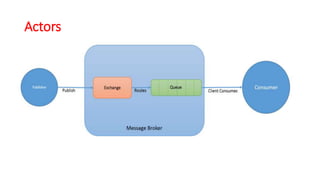
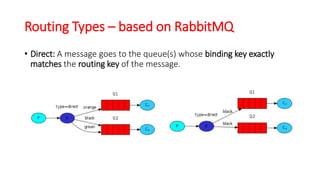
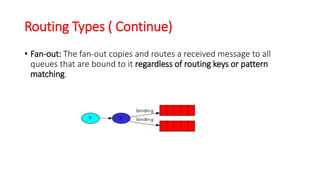
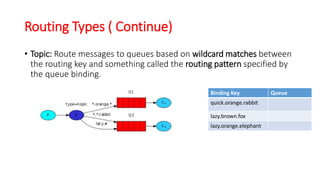
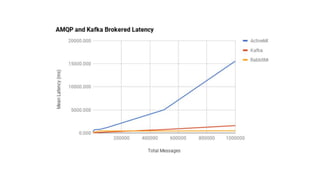
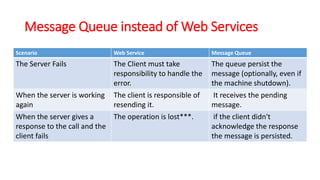
This document discusses message queue architecture. It defines message queues as providing asynchronous communication where the sender and receiver do not need to interact at the same time. Messages are stored in the queue until retrieved. It describes how message queues work with producers publishing messages to an exchange which routes them to queues until handled by consumers. A message broker is described as mediating communication between applications by routing and transforming messages. Examples of message queue systems like ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ and SQS are provided. The document contrasts using message queues versus web services, noting how message queues allow for decoupling and ensure message delivery in failure scenarios.