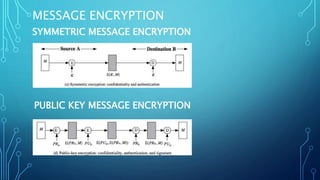
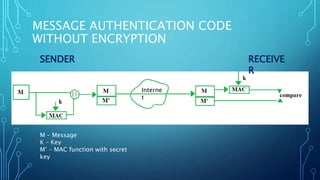
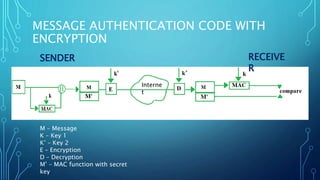
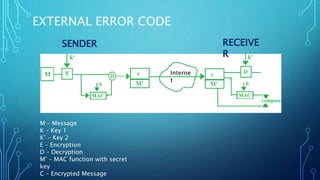
The document discusses message authentication codes (MACs) which protect message integrity, validate the originator's identity, and ensure non-repudiation. It details the use of a secret key to generate a MAC, which is appended to a message, and how the receiver verifies it. Additionally, it briefly mentions Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) as a variant of MAC that utilizes a cryptographic hash function with a shared secret key.