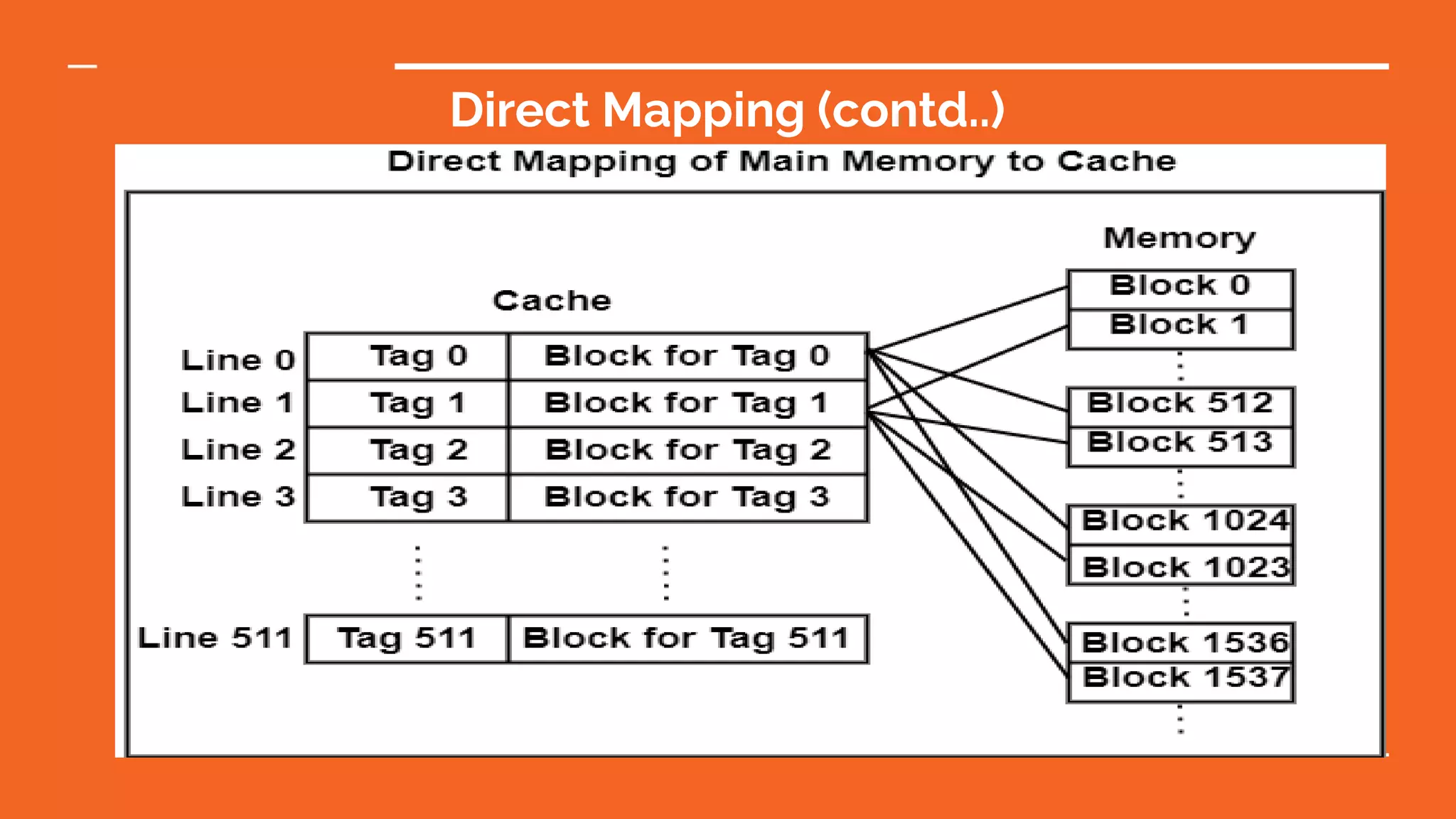
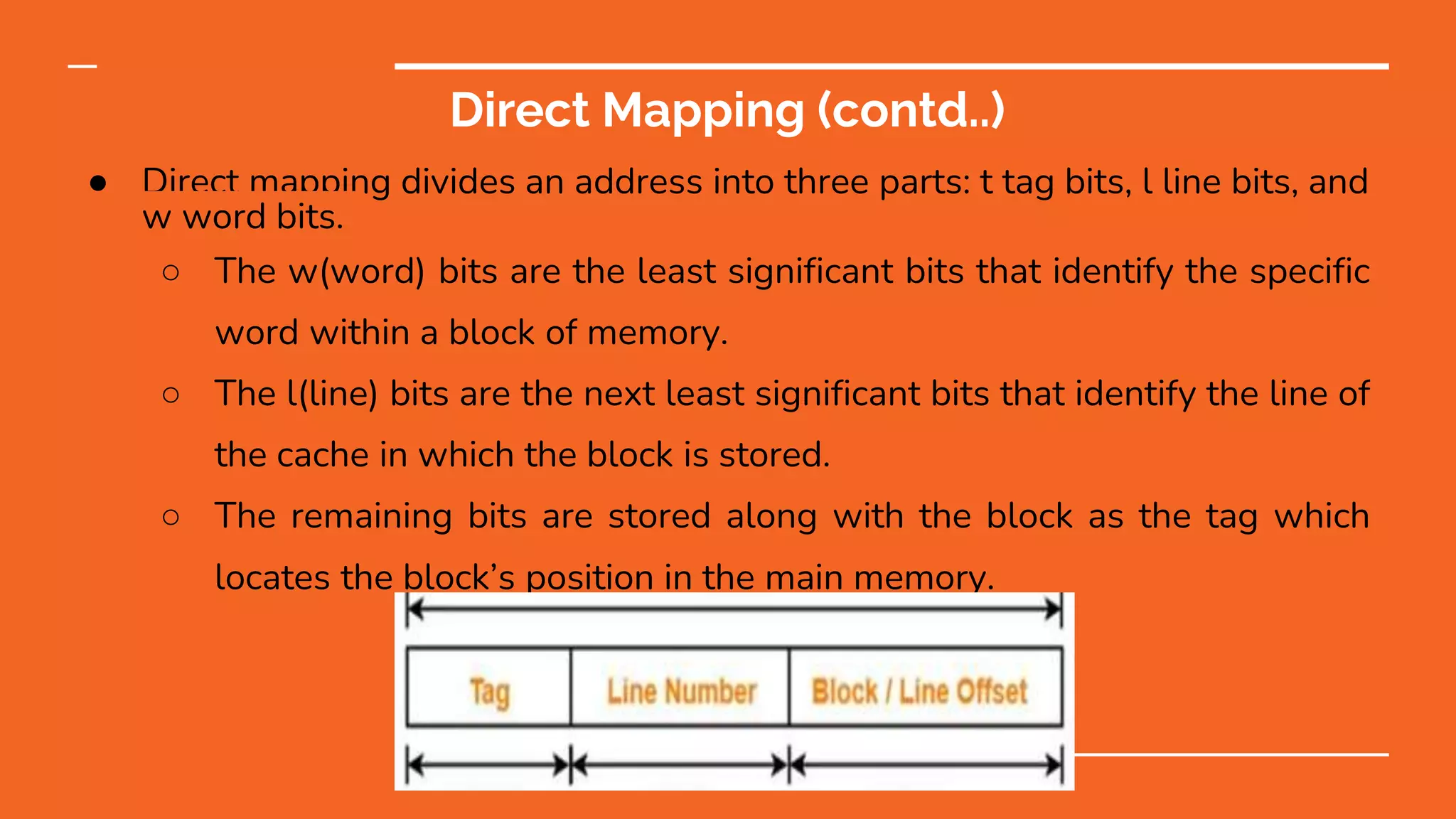
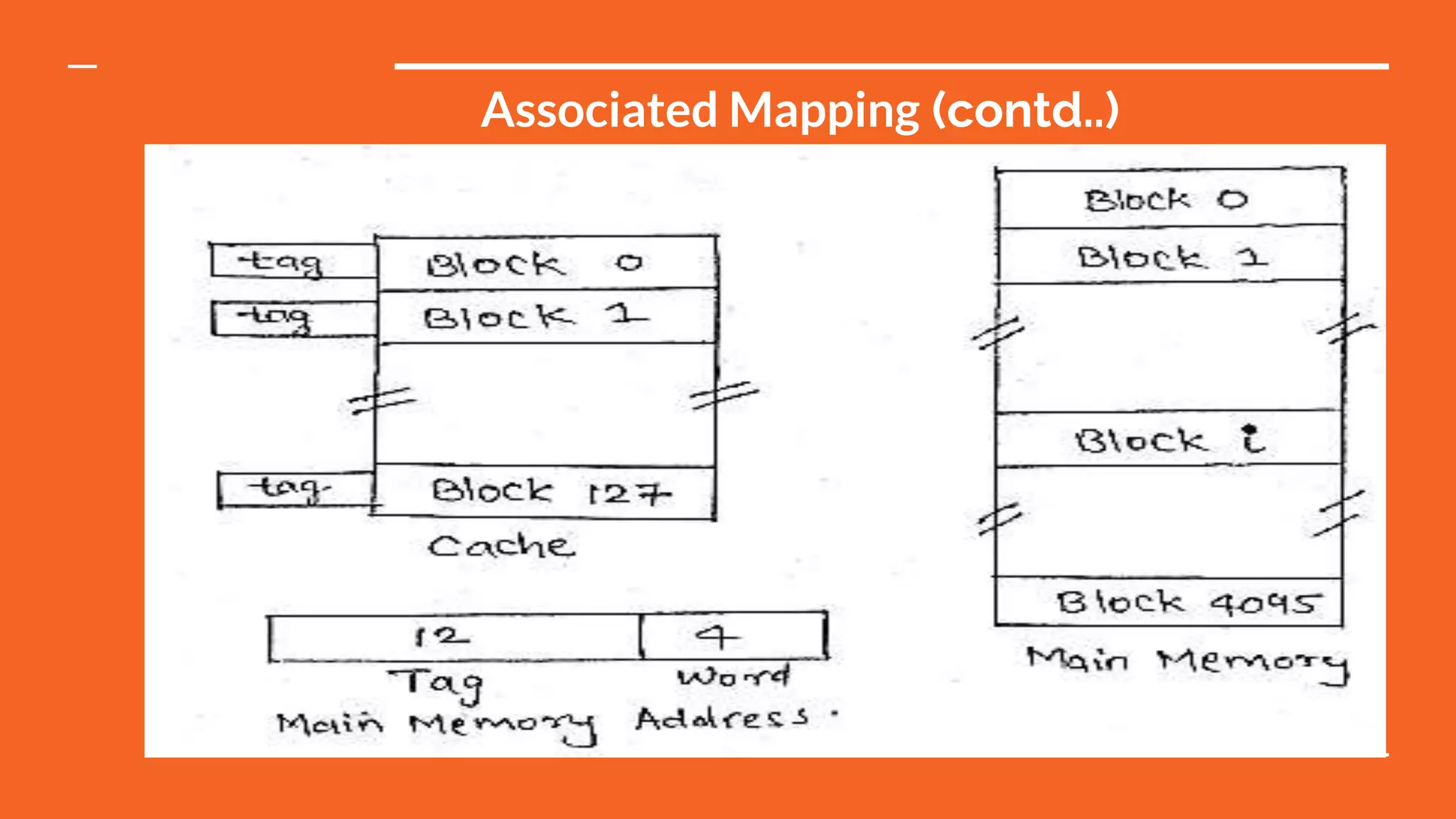
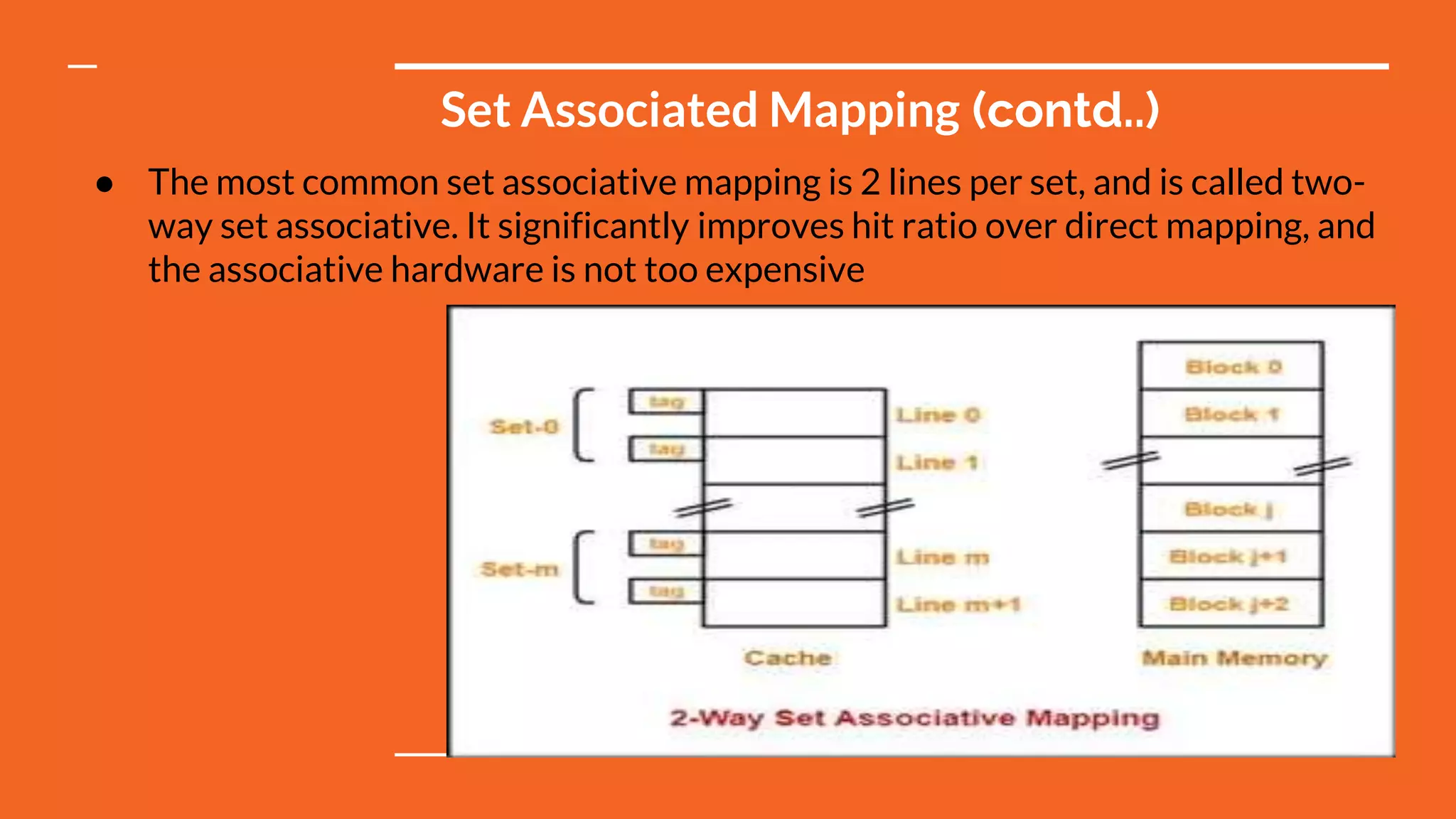
This document discusses different types of memory mapping techniques used in computer systems. Memory mapping is a mechanism that maps portions of files or entire files stored on disk to addresses in an application's memory space. There are three main types of memory mapping: direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping. Direct mapping assigns each memory block to a single cache line. Associative mapping allows memory blocks to be placed in any cache line but requires complex circuitry. Set associative mapping divides the cache into sets, each with multiple lines, providing a compromise between direct and full associative mappings.