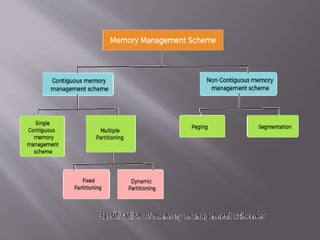
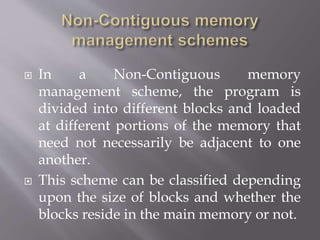
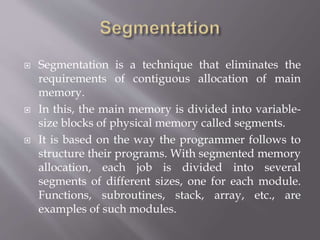
The document discusses process stack management in real-time operating systems (RTOS), emphasizing its role in efficiently allocating and maintaining memory stacks for tasks to ensure predictable execution and adherence to deadlines. It outlines the advantages of strong task isolation and efficient memory usage, as well as the disadvantages including complexity in managing multiple stacks and potential stack overflows. Additionally, it explains memory management techniques such as contiguous and non-contiguous schemes, along with paging and segmentation as methods to optimize memory allocation.