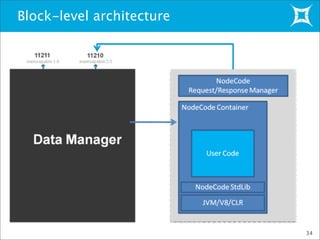
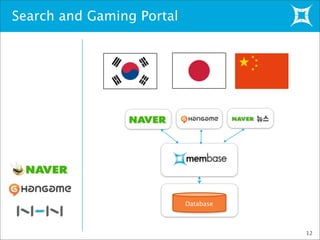
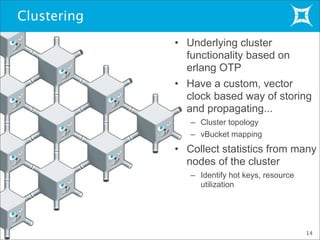
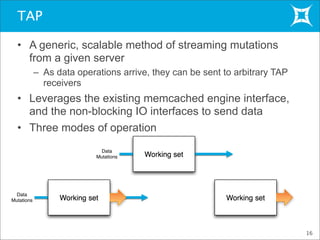
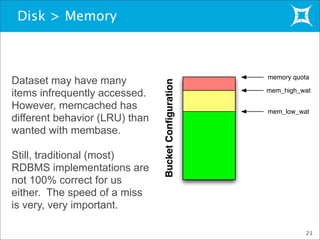
This document provides an overview and demonstration of Membase, a distributed database. It discusses how Membase can be deployed in five minutes or less on a single node or cluster. It is simple to develop applications using Membase's key-value interface without requiring a schema. The document also summarizes several use cases for Membase in domains like social games, advertising, and search/gaming portals. It provides a high-level overview of Membase's architecture, including its clustering functionality and TAP interface. Finally, it briefly previews Membase's NodeCode feature for extending the database with custom modules.












![Membase Datatypes
• byte[]
– Does your data have
1s and 0s?
26
“Any customer can have
a car painted any colour
that he wants so long as
it is black.”
• Items do have flags
– Many clients use flags
–Data type options
• Google protobuf
• Thrift
• Avro](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/membaseroadshow-101110151548-phpapp02/85/Membase-East-Coast-Meetups-26-320.jpg)