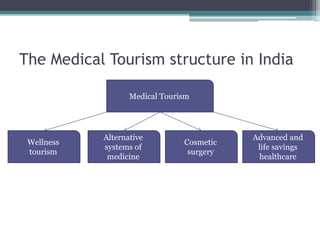
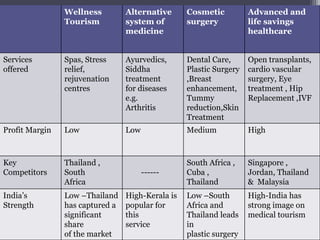
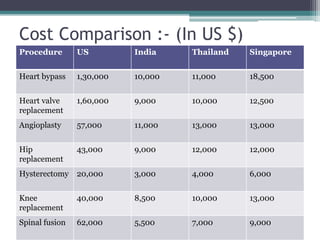
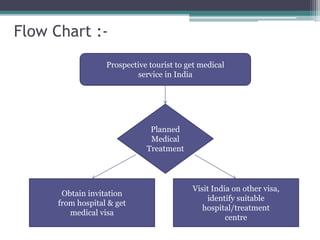
The document discusses medical tourism, defining it as the practice of traveling internationally for healthcare, particularly from industrialized nations to countries like India due to lower costs and advanced medical procedures. India is showcased as a competitive destination for medical tourism because of its low prices, high-quality healthcare, and a rich variety of tourist attractions, though challenges like lack of government support and inconsistent hospital standards persist. The document highlights various medical services offered, compares treatment costs internationally, and emphasizes the need for government initiative and infrastructure development to foster growth in this sector.






















![• Turkey :- Average medical cost is 50 % - 75% lower than
USA with international accredited heath care services.
• Ukraine :- Modern Dental clinics with high quality
equipments.
• Israel :- For surgeries & In Vitro Fertilization [IVF].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medicaltourism-rishith-161212085903/85/Medical-Tourism-24-320.jpg)