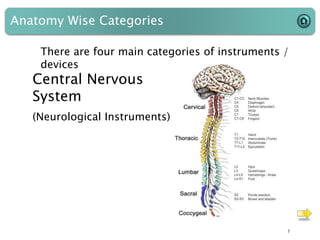
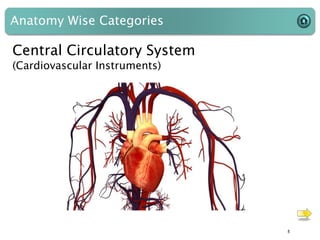
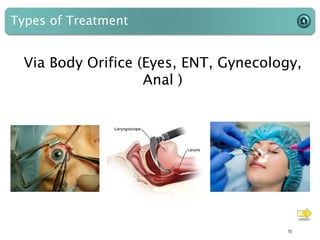
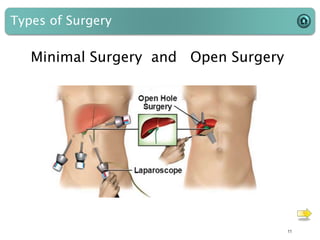
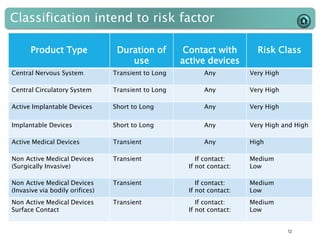
This document provides an introduction to medical devices. It begins with definitions of medical devices as any instrument intended for medical use to diagnose, treat or alleviate disease or injury. Major groups of instruments are identified as surgical, dental/orthopedic, ophthalmology, implants and diagnostic devices. Classification of devices is described based on risk levels related to device type, duration of use, contact and anatomy. Variants and required materials information are outlined. Process validations are introduced as critical to ensuring consistent product quality and performance from batch to batch.