- Medical devices range greatly in size and cost, from small and inexpensive devices worn on the body to large and expensive equipment like patient monitors.
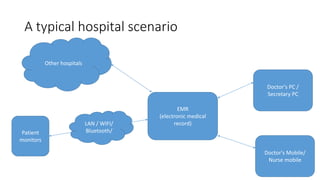
- Hospitals face challenges in securing these increasingly networked and mobile medical devices from cyber attacks due to lack of funding, outdated infrastructure, and lack of skilled security personnel.
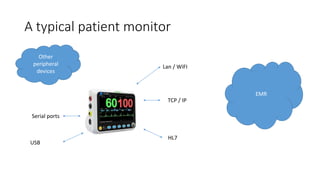
- The HL7 protocol is commonly used in medical devices to transmit patient data, but was designed in the 1980s and has security vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to access and manipulate sensitive health information if devices are connected to networks without proper protections.