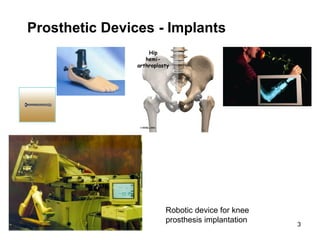
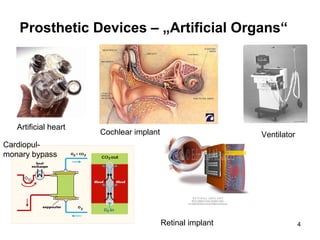
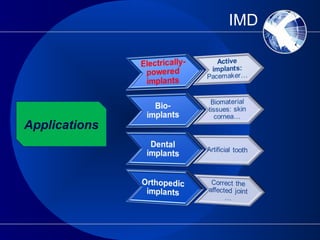
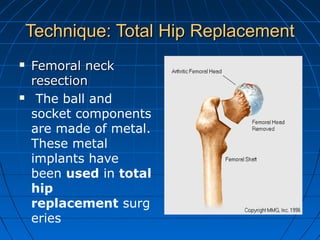
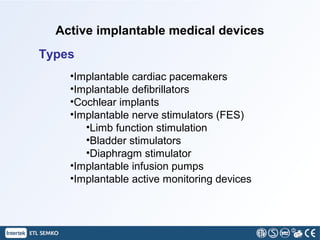
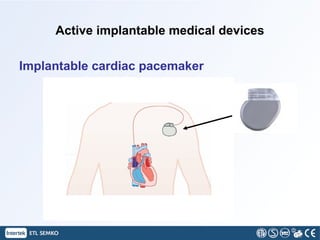
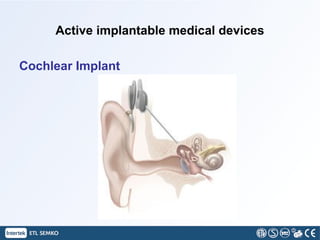
This document discusses implantable medical devices (IMDs). It provides examples of different types of IMDs including implantable cardiac pacemakers, defibrillators, cochlear implants, nerve stimulators, and infusion pumps. The document outlines the definition of a medical device and discusses applications of IMDs like heart failure, obesity, and diabetes treatment. It also describes recent advancements in prosthetic legs that use Bluetooth to regulate stride and pressure and robotic microprocessor knees that provide greater walking control.







![References
[1] Roland Gubisch, Intertek ETL SEMKO,
EMC for active implantable medical devices
[2]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Implant_(medici
ne)
[3] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medical_device
[4] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VeriChip](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imd1-140421082039-phpapp01/85/Implantable-medical-devices-17-320.jpg)