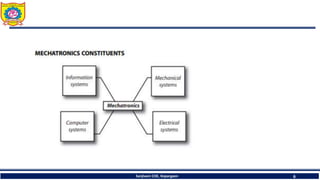
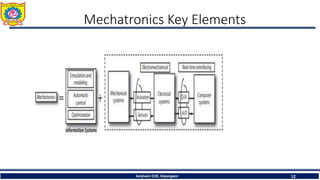
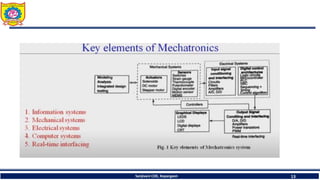
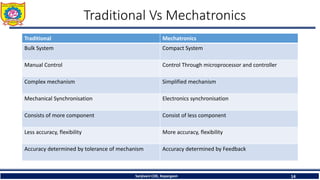
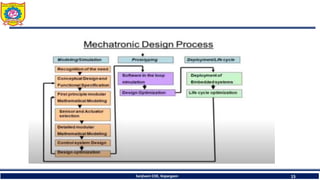
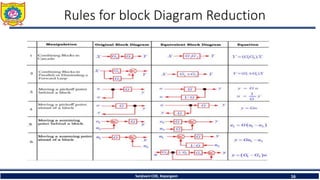
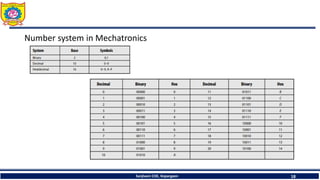
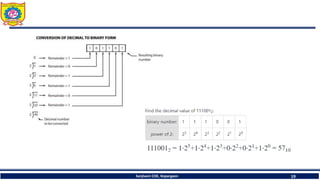
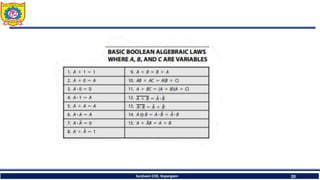
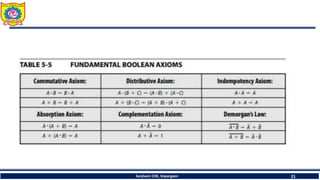
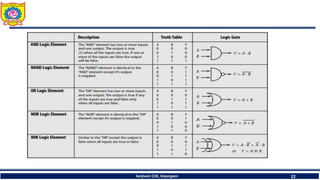
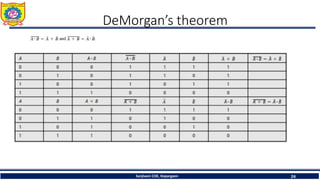
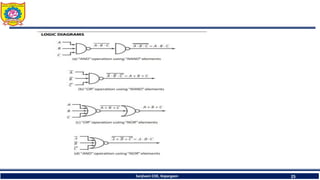
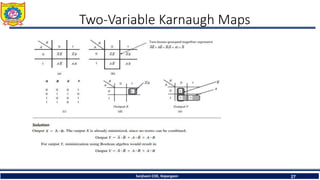
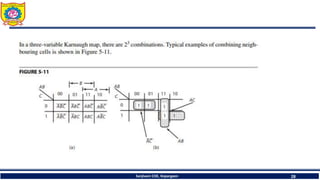
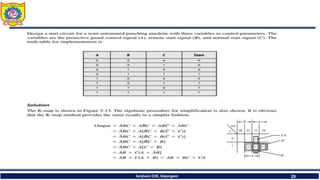
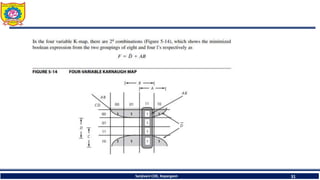
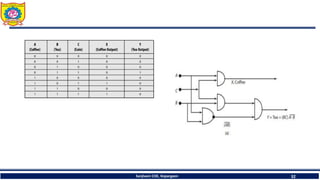
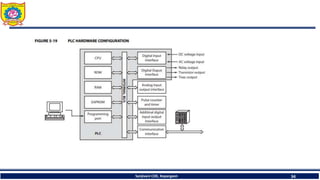
The document discusses mechatronics system design. It explains that mechatronics is an interdisciplinary approach that integrates mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, computer science, and control engineering in the design of products and processes. It describes the key benefits of mechatronics such as increased quality, productivity, and flexibility compared to traditional automated systems. The document outlines the differences between multidisciplinary and mechatronic concurrent design approaches. It also discusses some common hardware components in mechatronics systems like digital and analog electronics and programmable logic controllers.