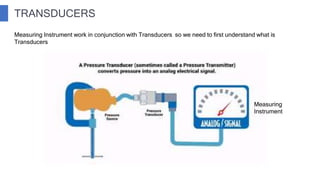
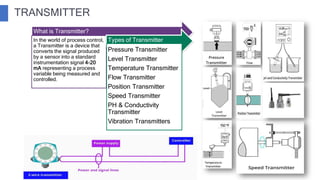
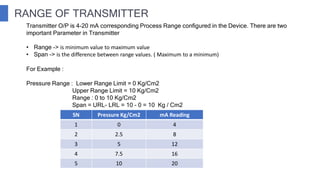
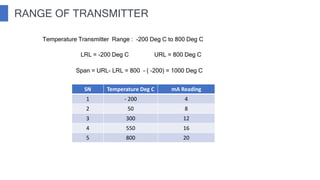
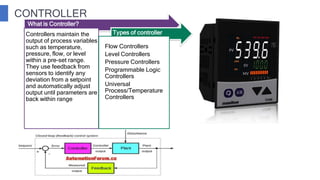
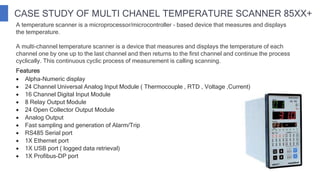
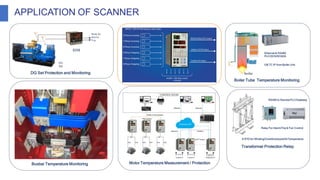
The document discusses industrial measuring instruments and their importance in process control, highlighting both analogue and digital types. It explains transducers, their classifications, and the role of transmitters and controllers in converting physical signals for measurement. Additionally, it covers various applications and configurations in industrial settings, emphasizing the growing popularity of digital instruments for accuracy and ease of use.