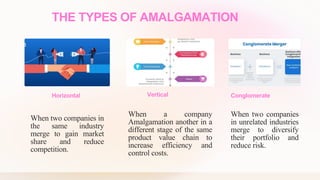
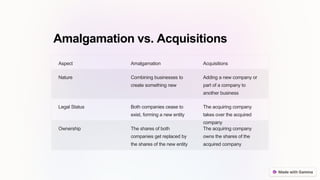
The document explains the concepts of amalgamation, acquisition, and external reconstruction, detailing their definitions, differences, and types. Amalgamation combines multiple companies into a new entity, while acquisitions involve one company taking over another, and external reconstruction pertains to the transfer of business with liquidation and formation of a new company. The document further discusses the advantages of amalgamation in business strategy, including market expansion, cost savings, and cross-selling opportunities.