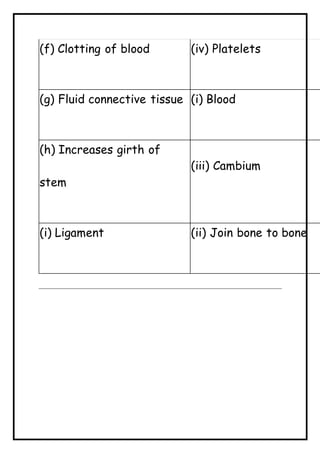
This document contains 33 multiple choice questions about tissues in class 9 science. It tests knowledge about the different types of tissues like epithelial tissue, connective tissue, and muscular tissue. It includes questions about the structure and function of tissues in plants and animals, like which tissue increases the girth of the stem, where adipose tissue is stored in the body, and what type of epithelial cells absorb digested food in the intestine. The document also contains fill-in-the-blank questions to test understanding of tissue terms and concepts.